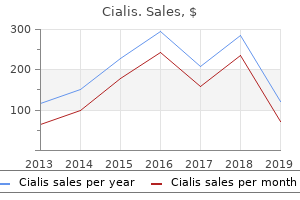
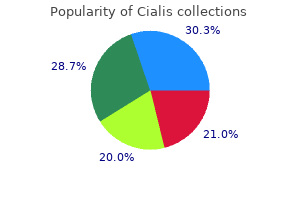
Cialis
"2.5mg cialis free shipping, impotence with beta blockers".
By: S. Ketil, M.B.A., M.D.
Assistant Professor, University of South Alabama College of Medicine
The potential market size can be estimated from current research data erectile dysfunction injection test buy cialis master card, showing the number of patients in the countries of interest and the total value of treatment erectile dysfunction 38 cfr discount cialis 20mg amex. Trends in disease prevalence should be noted, whether the number of patients is increasing or decreasing. However, it should also be noted that market research can sometimes be Early Drug Development 183 misleading and could result in missed opportunities. A good example to illustrate this point is the introduction of a new therapeutic class of drugs where there was no existing market. Before the introduction of the H2-receptor antagonist cimetidine, there was little evidence that many people suffered from gastric ulcers. It was only after an effective treatment was available that people came forward, and an enormous market was established. One way of assessing the commercial viability for a new product is to subtract the total development costs from the potential market share value. The potential market share value is estimated by multiplying the percentage of the potential number of patients by the potential commercial price for the new product. The CoG is an estimate of the sum of the cost of the drug substance, excipients, packaging materials, manufacture, labor, and overheads, among other things, that contribute to making the product. It has been estimated that 85% of the future cost of a new product can be determined at the product design phase (Matthews, 1997). The industry average for the CoG has gradually increased over the last decade from about 10% to 20% of the commercial price. A CoG target of 5% to 10% is about the industry average, with a maximum of no more than 40%. Higher than this would be difficult to justify developing, as the margins would be too small. The choice of the commercial dosage form and manufacturing process can have a significant impact on the CoG. For example, if a product is freeze-dried, the processing costs will be extremely high because of the limited batch sizes and lengthy process involved. The relative costs in terms of development time, raw materials used, production equipment, facilities, and validation for the manufacture were considered. There is a general belief that tablets are easier and cheaper to produce than dry-fill capsules, but surprisingly, Cole found that a capsule-manufacturing facility is cheaper to build, validate, and operate than a tablet-manufacturing facility. Only when the costs of excipients are considered in isolation does the tablet process have an advantage, mainly because gelatin capsules are relatively expensive. Technical Issues and Risk Assessment There may be a variety of issues that should be documented in the product design report to highlight the perceived risks involved in developing the product. Some of these risks will be related to pharmaceutical development and others to clinical, safety/toxicology, or other areas. For pharmaceutical development, risk may be associated with the technical challenges anticipated in developing a novel or complex drug delivery system or manufacturing process. Information from early preformulation and biopharmaceuticals studies should indicate the potential problems for drug delivery, formulation development, and manufacture. There may be a lack of in-house expertise, resulting in the need to contract out the work or the need to develop an in-house capability. Alternatively, there may be a lack of in-house facilities or equipment to handle the candidate drug. These issues need to be resolved quickly or else time penalties could be incurred. Some excipients or packaging components may only be available from one supplier, with the risk that the supplier could go out of business. The importance of identifying these issues in a product design report is to make the company aware of the risks it is taking and to make effective plans to overcome problems and manage the risks. In the United States, specific requirements for "new" excipients are detailed in the U. There may be incompatibility problems with the candidate drug and existing excipients or there may be a need to use new excipients in a new drug delivery system.
The present chapter gives an overview on various targeted nanomedicines for effective treatment of psoriasis erectile dysfunction differential diagnosis order cialis 2.5mg. Pathophysiology involved in psoriasis erectile dysfunction prescription drugs buy 2.5 mg cialis otc, available therapies, and their challenges are also covered. This process is responsible for hyperkeratosis and neovascularization in psoriasis [1,2]. Moreover, there are several predisposing factors in the pathogenesis of psoriasis which include eicosanoid metabolism, lymphokine secretion, and free radical generation [4,7]. Topical therapies gained wider popularity in psoriasis treatment, but they suffer from limited absorption of drugs through skin, limiting their therapeutic effectiveness [3]. Systemic administration of drug such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, hydroxycarbamide, fumaric acid esters, etc. Other than these therapies, biological agents have been employed in psoriasis treatment. Biological agents are proteins which are obtained from microorganisms and exhibit fewer side effects. However, they are not common in clinical practice due to their immunosuppressive effects, high cost, and availability in only injection form which leads to poor patient compliance [1,2]. Lipid-based nano-vehicles include vesicular carriers, particulate carriers, and emulsion-based carriers, while polymeric carriers subclassify as particulate and capsular carriers [10]. Lipid Based Vesicular Nanocarriers Lipid based vesicular nanocarriers are mainly composed of physiological lipids; they may further be classified as liposomes, ethosomes, niosomes, and transfersomes. Liposome is a vesicular nanocarrier, which may compose of phospholipids and cholesterol. Its size varies from nanometer to several 100 micrometers, depending on whether it is a unilamellar or multilamellar vesicle [11]. They can encapsulate hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs in the central core and in bilayer, respectively. Moreover, they exhibit higher encapsulation efficiency, enhanced biocompatibility, and controlled drug release [11]. However, it does not penetrate well through the skin, cause irritation and staining of the skin [2]. An ex vivo study compared niosomes and liposomes containing resveratrol in terms percutaneous absorption, and concluded that niosomes showed better behavior than liposomes [15]. Cyclosporine A (CsA) is an immunosuppressant drug and widely used in management of psoriasis by blocking the activity of T cells via binding of cytosolic immunophilin. Their application is hindered due the systemic toxicity and restricted permeation [2,4,16]. To overcome these limitations, researchers have developed CsA-loaded lecithin vesicular carriers and delivered them through a transdermal route. Higher skin permeation was observed, which may be attributed to the flexibility of vesicles [17]. In another study iontophoresis was applied on lecithin vesicular carrier with monoolein which acts as a permeation enhancer; they received appreciable drug transport across the human cadaver skin [18]. Another group of researchers developed multicompartmental liposomes and a microemulsified system and found enhanced skin permeation of CsA through psoriatic skin [20]. It is metabolized by the liver to its active metabolite 4-hydroxytamoxifen which has a higher affinity to estrogen receptor than tamoxifen itself. Applications of tamoxifen are limited due to inappropriate solubility, limited absorption, and systemic side effects [23]. Emulsomes, a different type of vesicular nanocarrier, are proven to be highly efficacious in treatment of topical diseases including psoriasis by reducing the problems such as incompatibility with skin. As previously discussed, dithranol, although a highly effective drug for psoriasis, has limitations and unwanted effects for patients. To overcome these limitations, dithranol was encapsulated into emulsomes, which was reported to enhance antipsoriatic activity in an in vivo model.
When this solvate was exposed erectile dysfunction pump hcpc buy discount cialis 2.5mg line, elevated relative humidities deliquescence took place erectile dysfunction statistics uk cialis 10mg lowest price, which did not change the underlying solvate structure. Associated with the desolvated solvate there may be residual solvent, which must be controlled. Perhaps a more direct and complete method of desolvation is to suspend the solvate in water. When the solvent is removed from the crystal lattice, which retains its three-dimensional order, a so-called isomorphic desolvate is created (Stephenson et al. The desolvated structure is highly energetic and reduces this situation by simply taking up moisture from the atmosphere or undergoing a certain degree of structural collapse to reduce the unit cell volume. The dihydrate 56 Steele and Austin and the tetrahydrofuran solvate lost their solvent anisotropically, which was followed by a cooperative structural rearrangement to an anhydrous polymorph. In contrast the dimethylformamide and dimethylsulfoxide solvates desolvated via a partial dissolution of the internal part of the crystals. Hydrates the most common case of solvation is the incorporation of water molecules, and they are almost always involved in hydrogen bonding. Indeed, it is the hydrogen-bonding network that contributes to the coherence of the crystal, such that they usually show, for example, slower dissolution rates compared with the corresponding anhydrates. As shown by Salameh and Taylor (2006), excipients can also have an effect on the stability of hydrates. A full understanding of the hydration state of compounds is not only important from a scientific perspective, it can also be important from an intellectual property point of view. This was exemplified by the case where a generic company, Apotex, which was successful in demonstrating noninfringement of the patent on paroxetine hydrochloride. This observation was attributed in part to the increase in free energy of the structure if solvents were included (as a result of loss of entropy by including solvent molecules), particularly if scope for favorable intermolecular interactions exists in the parent structure. The formation and occurrence of hydrates, as with all other processes, results from a fine thermodynamic balance, that is, compensation between enthalpy and entropy of the system. Generally, the formation of hydrates is governed by a net increase in favorable intermolecular interactions and the requirement of water is to satisfy specific roles to stabilize the crystal structure. Furthermore, the presence of water may serve to increase packing efficiency within the three-dimensional framework, thus maintaining a stable low-energy structure in accordance with the edict on the stability of the structure being related to density (Kitaigorodskii, 1961). By using the data from 3315 structures, they found that the two most common ways that water interacted was through the formation of three or four H-bonds with neighboring molecules. Statistically, they found the donor/ acceptor ratio and the molecular weight of the compounds, proposed earlier as factors, to be predictors of hydrate formation. Rather they found that the total polar surface increased the propensity for hydrate formation. For example, Hulme and Price (2007) were successful in predicting the structures within 5 kJ/mol of 5-azauracil monohydrate. Inclusion of water of crystallization can alter the free energy of a crystal structure and consequently, as with polymorphism, can have a profound impact on physicochemical properties such as solubility, dissolution (and hence bioavailability in the case of pharmaceuticals), and stability. An understanding of the properties and stability of hydrates relative to any parent anhydrate is important to rationalize material selection. Knowledge of the structural disposition to form hydrates would also impact on crystal-engineering developments. In instances for which water plays a crucial role in maintaining the crystal structure via the formation of a hydrogen-bonding network, dehydration can often lead to complete structural collapse, giving rise to an amorphous anhydrate, as observed with eprosartan mesylate dihydrate (Sheng et al. In this particular case, the water of crystallization forms a hydrogen-bonding framework directly to the parent drug and the salt counterion. Dehydration results in an amorphous material, which becomes annealed upon heating, giving rise to a crystalline hydrate. Such hydrates are considered to be very stable and represent developable materials. Hydrates in which water acts as a "space filler" occupying voids or crystallographic channels can dehydrate to give isomorphous anhydrates or undergo a change of structure to give a more densely packed arrangement. Generally, these types of hydrates are nonstoichiometric and the number of equivalent water molecules in the structure is directly related to the water activity (aw) in the surrounding environment. The geometry and size of the solvent channels in these structures can vary significantly from long, wide rigid structures that are maintained by a robust hydrogen-bonded framework to small interweaving arrangements for which the water may interact with the "host" structure.
Performance of likelihood ratio tests of evolutionary hypotheses under inadequate substitution models erectile dysfunction treatment options injections cheap cialis 20 mg free shipping. Although phylogenies have been used for almost 150 years erectile dysfunction in young males buy generic cialis online, statistical, computational, and algorithmic work on phylogenies-often referred to as computational phylogenetics-is only 50 years old. The analysis of phylogenetic trees does not only serve human curiosity but also has practical applications in different fields of science. Phylogenies help to address biological problems such as drug design [5], multiple sequence alignment [8], protein structure [27], gene function prediction [9], or studying the evolution of infectious diseases [13]. In the past decade, the molecular revolution [24] has led to an unprecedented accumulation of molecular data for inferring phylogenies. Public databases such Pattern Recognition in Computational Molecular Biology: Techniques and Approaches, First Edition. In practice, however, our ability to infer such comprehensive trees resurrects old problems and gives rise to novel challenges in computational phylogenetics. First, reconstructing the phylogeny that best fits the data is a combinatorial optimization problem. The number of phylogenetic trees increases super-exponentially with the number of taxa [10]. However, for even larger phylogenies with up to tens of thousands of species, we are not sure whether we are obtaining a plausible, let alone correct answer, given the literally astronomical size of the tree search space. Reconstructing large phylogenies is particularly difficult when the alignment length remains constant. In other words, accuracy decreases as we add taxa while keeping the number of sites in the alignment fixed [16, 23]. Although genomic data are becoming available at an increasing rate, many species are undersampled because it is difficult to obtain or collect the sequencing samples. For example, prokaryotic organisms that have small genomes, or model organisms and model genes are sampled more frequently than other species. For that reason, increasing the number of taxa in a data set typically also increases the amount of missing data [26], which leads to potentially biasing the results and, therefore, to decreased phylogenetic accuracy [30]. So given a large phylogeny, how can we assess the biological plausibility of such a large tree Visual inspection to assess the plausibility of trees with more than 50,000 taxa is not an option because (i) it is impossible to do so for humans and (ii) there are only but a few tools available for visualizing such large phylogenies. One can follow two avenues to address the plausibility assessment problem: either devise novel visual tools for phylogenetic data exploration or design algorithms for automated plausibility analysis. While we use a reference database containing a billion of small reference trees, one could also use reference trees from the literature or from the treebase database [21]. The rest of this chapter is organized as follows: initially, we discuss the preliminaries and present the formal problem description. We say a node has height h if the length of the longest path from to some leaf is h. We denote a node of a tree T as central if there is no other node u such that the length of its longest undirected path to a leaf is shorter than that of. Trivially, a tree can have at most two central nodes, otherwise there would exist a cycle. We further only consider rooted binary trees and unrooted trees that only consist of inner nodes of degree 3 and leaves (degree 1), that is, strictly bifurcating trees. If is not a leaf: call Step with the left child as parameter, then call Step with the right child as parameter and finally list/print. The length of the Euler tour for a rooted binary tree of n nodes is exactly 2(n - 1). We list each leaf only once, each inner node 2 with the exception of the root node three times, and the root node exactly twice. Step: Call Step with left child as parameter, list and call Step with right child as parameter.