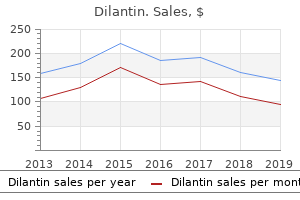
Dilantin
"Purchase 100 mg dilantin with amex, medications for factor 8".
By: Z. Cole, M.A., M.D.
Co-Director, University of New Mexico School of Medicine
Increased susceptibility to cortical spreading depression in an animal model of medication-overuse headache treatment ulcerative colitis cheap dilantin 100mg. Orexin 1 receptor activation attenuates neurogenic dural vasodilation in an animal model of trigeminovascular nociception medications look up purchase dilantin 100 mg online. Conditioned pain modulation in populations with chronic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tracing transformation: chronic migraine classification, progression, and epidemiology. The acute treatment of migraine in adults: the american headache society evidence assessment of migraine pharmacotherapies. New insights into headache: an update on functional and structural imaging findings. Pathophysiology of medication overuse headache: insights and hypotheses from preclinical studies. Waning of "conditioned pain modulation": a novel expression of subtle pronociception in migraine. Sensitisation of spinal cord pain processing in medication overuse headache involves supraspinal pain control. Individual differences in acute pain-induced endogenous analgesia predict time to resolution of postoperative pain in the rat. Descending serotonergic facilitation and the antinociceptive effects of pregabalin in a rat model of osteoarthritic pain. Orexins and Orexin Receptors: A Family of Hypothalamic Neuropeptides and G Protein-Coupled Receptors that Regulate Feeding Behavior. Abnormal modulatory influence of diffuse noxious inhibitory controls in migraine and chronic tension-type headache patients. Sarchielli P, Rainero I, Coppola F, Rossi C, Mancini M, Pinessi L, Calabresi P (2008). Involvement of corticotrophin-releasing factor and orexin-A in chronic migraine and medication-overuse headache: findings from cerebrospinal fluid. Brainstem facilitations and descending serotonergic controls contribute to visceral nociception but not pregabalin analgesia in rats. The activation of bulbo-spinal controls by peripheral nociceptive inputs: diffuse noxious inhibitory controls. Molecular depletion of descending serotonin unmasks its novel facilitatory role in the development of persistent pain. Analgesic effect of intrathecally administered orexin-A in the rat formalin test and in the rat hot plate test. Individual migraineurs try many different classes of compounds in order to find the drug that best ameliorates their migraine headaches. Over-the-counter analgesics provide benefit for some patients, but many still experience more severe or frequent migraine attacks that are ineffectively treated, leading them to prescription medicines for the acute treatment and prevention of migraines [2]. Reviews of clinical experience have, however, found that cardiovascular events, while present, are relatively rare [4], and there is inadequate evidence data to determine the real risk of serotonin syndrome [5]. It is estimated that 40% of migraine sufferers could benefit from prophylactic therapy, but only 13% are taking existing therapies. This is perhaps because currently approved preventative treatments have modest efficacy, and are often associated with safety or tolerability issues. Thus, there remains a large unmet medical need for migraineurs, and a need to have new classes of acute treatment and preventative anti-migraine drugs. Similarly, sumatriptan was also shown to reduce meningeal extravasation, mediated by substance P acting at neurokinin 1 receptors, evoked by electrical trigeminal ganglion stimulation [21]. This effect, on a proven biomarker of sensory nerve activation, has given further support to the peripheral trigeminal inhibitory effects of the serotonin agonist class. Williamson, in the Merck Research Laboratories, developed an intra-vital microscopy model [22] to monitor meningeal blood vessel diameter in response to electrical stimulation of the dura mater [23]. At the time, it was suggested that these data supported the hypothesis that vasodilation in the meninges is capable of sensitizing the trigeminal system.
The dual but sparse innervation of organs medicine 751 m discount dilantin 100mg otc, coupled with significant central arborization in the spinal cord treatment viral conjunctivitis order dilantin mastercard, contribute to several key features of visceral pain that distinguish it from most other types of pain, namely localization and referral. The divisions of the trigeminal nerve innervate all tissues in the head except the brain, but including the dura and dural vasculature. The cell bodies of their afferent terminals are located in trigeminal ganglia positioned bilaterally at the level of the pons. Furthermore, in contrast to visceral organs that receive bilateral innervation, the dura and dural vasculature, like the majority of other craniofacial structures on either size of midline, only receive innervation arising from the ipsilateral trigeminal ganglion. Several other features of the trigeminal system make innervation of the dura/dural vasculature distinct from that of the viscera. First, the trigeminal ganglia are somatotopically organized, such that the somata of neurons innervating a particular area of the head are located within the ganglia in relatively close proximity to neurons innervating adjacent areas. This is in contrast to the spinal and nodose ganglia, which appear to have no somatotopic organization. Given evidence of intra-ganglionic communication via the release of transmitters within the ganglia following the activation of afferent terminals (Matsuka et al. Second, while the axons of proprioceptive afferents are contained in branches of the trigeminal nerve, the somata giving rise to these axons are actually located in the brainstem, in the mesencephalic nucleus of the fifth cranial nerve. This is in contrast to spinal dorsal root ganglia, where the somata giving rise to proprioceptive afferents are co-localized with other types of sensory neurons. The functional implications of the spatial isolation of these two types of neurons in the trigeminal system, at least in the context of nociceptive processing, has yet to be elucidated. However, this organization does appear to facilitate the integration of sensory information arising from bi-lateral structures, such as the eyes and the muscles of mastication. Third, the central terminals of trigeminal afferents are organized in a rostro-caudal orientation, with proprioceptive and non-nociceptive afferents terminating rostrally in the mesencephalic nucleus and primary or main sensory nucleus, respectively, and deep touch, pain and temperature-sensitive afferents, terminating in the spinal trigeminal nucleus. This latter structure is further subdivided, and spread rostral-caudally into nucleus oralis, interpolaris and caudalis; the majority of nociceptive afferents terminate in nucleus caudalis. This is in contrast to the dorsal-ventral termination pattern of sensory input to the spinal cord. The result is a significantly greater distance between the non-nociceptive and nociceptive terminals in the trigeminal system, which will necessarily change the timing of interactions between these afferent types thought to be necessary for phenomena such as mechanical allodynia and referred pain, as described below (see also Chapter 1). Finally, somewhere between a difference and a similarity is the embryological origin of the sensory innervation of the head and viscera. That is, spinal ganglia are derived from neural crest cells, while the cells in the nodose ganglia are derived from ectodermal placode cells. The result is that the two nerves innervating most viscera are embryologically distinct. Similarly, the trigeminal ganglia are a mix of both neural crest and placode-derived cells. Unfortunately, it is not yet possible to identify these two cell 5 Visceral pain 95 types in the adult and, consequently, it is not possible to determine whether the two cell types give rise to distinct or overlapping patterns of innervation. As a result, the functional consequences of the mixed embryological origin of trigeminal ganglia have yet to be determined. However, differences between spinal and nodose ganglia, with respect to the dependence of afferent phenotype on specific trophic factors. While pain is a sensory phenomenon, there is compelling evidence to suggest that autonomic efferent fibers contribute to the pain of injury. Because of their role in mediating components of both neuropathic (Perl, 1999) and inflammatory (Raja, 1995) pain, sympathetic efferents have received considerably more attention than parasympathetic efferents. This is not necessarily so in the context of migraine, where there is evidence that disruption of parasympathetic outflow can abort a migraine attack (Khan et al. And while the vascular hypothesis of migraine has largely fallen under the weight of negative evidence (Goadsby, 2009; but see Karatas et al. Importantly, mast cell degranulation has been implicated in migraine (Levy, 2009), and can be driven by cholinergic receptor activation (Messlinger et al. Nevertheless, in contrast to the relatively dense sympathetic innervation (at least in the rodent) of the dura, the parasympathetic innervation of this structure appears to be relatively sparse (Artico et al. More recently, it has been shown that the serotonin 1D receptor, a target for the anti-migraine triptan drugs, is present on cranial sympathetic efferents (Harriott and Gold, 2008). Furthermore, there is also evidence that norepinephrine, a primary sympathetic mediator, can sensitize dural afferents (Wei et al.
C Retrograde sinus and retrograde cortical venous drainage There are two major classification systems for dural arteriovenous fistulae medications not to be crushed dilantin 100mg otc, the Borden classification and the Cognard classification medicine xarelto buy genuine dilantin. C Heart failure Vein of Galen malformations present in neonates with evidence of high output heart failure. D Carotid-cavernous fistula Traumatic carotid-cavernous fistulae can occur after motor vehicle accidents or other intracranial trauma. They present with orbital pain, chemosis, proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, and visual loss. Patients should undergo vascular imaging and may require interventional or surgical treatment of the fistula. B False Radiation therapy damages cells by firing particles into an atom and releasing free electrons causing damage downstream. In fully oxygenated cells, oxygen combines with unpaired free electrons to form peroxides, which are more stable and lethal than free radicals, and therefore an oxygenated cell is more sensitive to damage by radiation therapy. B > 3 years Children less than 3 years of age are particularly sensitive to cranial radiation and can have severe developmental side effects. Children should be greater than 3 years of age to be eligible for cranial radiation. B 3 cm or less Gamma knife radiosurgery can be useful for cranial masses, but should be reserved for patients with brain tumors that are 3 cm or less in maximum diameter. This size cutoff decreases the risk of harmful radiation side effects to surrounding brain structures. B 10 Gy Safe doses of radiation to the optic apparatus are generally thought to be 8 to 10 Gy. C 10 Gy or less the lens of the eye can tolerate 10 Gy or less radiation with minimal side effects. D 40 to 50% At 10 years posttreatment, approximately 40 to 50% of patients who receive sellar radiation will experience hypopituitarism as a side effect from radiation. B 4 to 6 Gy Based on current literature, the mean safe radiation dose to the cochlea is considered to be approximately 4. There is some controversy on this topic currently, but based on data available, doses from 4 to 6 Gy should be considered optimal. C Whole brain radiation Current literature supports the use of whole brain radiation in patients who have undergone resection of a cerebral metastasis. Doses up to 50 Gy have been shown to control > 90% of micrometasases, but at this dose there is a very high chance of early radiation side effects. B 10 or less Based on current studies, up to 10 concurrent cerebral metastases can be treated with stereotactic radiosurgery with good outcome and low risk of side effects. There are surgeons who feel that even this number can be safely extended, research is pending. Radiation works by causing damage to the endothelium and ultimately causing fibrosis. This process can take 2 to 3 years to develop, so risk of hemorrhage needs to be discussed with the patient over that treatment timeframe. Higher radiation doses have been associated with an increased risk of complications and no significant improvement in obliteration rates. D Dementia Dementia is the main complication from whole brain radiation after use for intracranial metastases. Incidence has been shown to be higher when patients receiving doses of 25 to 39 Gy receive those doses in fractionations that are > 300c Gy Further Reading: Greenberg. A 8 Gy Emergency radiation can be delivered to radiosensitive spine tumors when there is evidence of compression. In many circumstances, an initial dose of 8 Gy will be given to shrink the tumor, followed by further fractionated radiation after the acute situation has resolved. C 30 Gy in 10 fractions Radiation to the spine for metastatic disease in the setting of radiosensitive tumors is often administered at a dose of 30 Gy delivered over 10 fractions. A Anesthesia dolorosa Anesthesia dolorosa is a feared complication of intentional damage to the trigeminal nerve. It occurs after damage to the V1 segment of the nerve, and can lead to anesthesia of the cornea, causing patients to get recurrent corneal abrasions.
You are performing deep brain stimulation electrode implantation in a patient with essential tremor medicine quizlet buy dilantin 100 mg mastercard. During test stimulation medications harmful to kidneys discount 100 mg dilantin visa, the patient notices ipsilateral paresthesias that are persistent and do not improve with time. Eosinophilic granuloma Skull epidermoid Calcified cephalohematoma Osteochondroma Growing skull fracture 333. If the underlying tumor depicted in this pathological specimen is of the primary variety rather than secondary, what mutation status would you expect What particle is released during annihilation of the positron that allows for this imaging modality What type of pathological structure is seen in anterior horn cells of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Which of the following patients would be best suited for a vagal nerve stimulator He initially had symptoms of an upper respiratory tract infection 2 weeks ago and has been noticing weakness in his legs that has worsened over time. You successfully resect a posterior fossa mass in a 16-year-old adolescent girl that was cystic with a mural nodule. You are taking a neonate to the operating room to repair a myelomeningocele 48 hours after birth. During the procedure, you are meticulously dissecting the placode away from the associated skin. You take care during this portion of the procedure since failure to fully separate the skin from the placode in the correct plane may result in what development Higher risk of infection Worsened hydrocephalus Higher risk of spinal cord tethering More difficult watertight closure Inclusion dermoid 366 18 Stand-Alone 375-Question Examination 340. You are performing a Chiari decompression in the sitting position, and while you are performing your craniectomy, the anesthesiologist reports that the precordial Doppler is suggesting the presence of air embolism. You irrigate the wound with saline and use bone wax on the edges of the craniectomy, but the air persists. Left Trendelenburg positioning Right Trendelenburg positioning Open the dura Quickly finish the case Close the wound and abort the procedure 342. Which of the following ventilator settings demonstrate a patient most suitable to be weaned from the ventilator You are caring for a patient with severe brain trauma who has been intubated and sedated. What technique would be useful during microsurgical clipping of an ophthalmic artery aneurysm Intradural posterior clinoidectomy Frontal sinus cranialization Anterior clinoidectomy Cisterna magna decompression Frontotemporal orbitozygomatic approach 345. Based on large studies, what is the approximate chance of a patient experiencing a shunt failure requiring revision within 1 year of receiving a ventriculoperitoneal shunt You have been asked to see a patient who suffered a gunshot wound to the forearm (pictured) and has evidence of a complete transection of the radial and ulnar nerves on examination. Which of the following is not required for transfer of a patient under the emergency medical treatment and labor act Transferring hospital has provided maximum care Insurance covers receiving hospital Benefits of transfer outweigh risks Accepting hospital agrees to accept patient Transfer occurs with qualified personnel and equipment 348. You are seeing a 4-year-old boy with a skull mass that is demonstrated in the X-ray. You have been asked to partake in formulating a consensus statement on cervical spine fusion techniques by the national organization. Help formulate the statement Disclose your financial agreement and participate Recuse yourself from the discussion Send another researcher without a financial agreement 368 18 Stand-Alone 375-Question Examination 353. What structure is labeled "6" in the corresponding image of the third ventricular floor Decrease "on" time Decrease "off" time Increase "off" time No change in medication dosing Elimination of symptoms A. Mammillary bodies Lamina terminalis Anterior commissure Optic chiasm Tuber cinereum 356. Which of the following helps differentiate between amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and cervical spondylotic myelopathy Imaging demonstrates that the graft is open and he has recovered from surgery well.