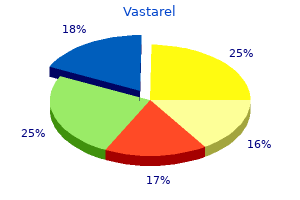
Vastarel
"Buy 20mg vastarel, medications zithromax".
By: E. Faesul, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Clinical Director, Medical University of South Carolina College of Medicine
The process of an intracellular electrical potential being transmitted through extracellular fluid and tissue is known as volume conduction medications by mail purchase 20 mg vastarel with mastercard. Although the theory of volume conduction is complex and beyond the scope of this text symptoms west nile virus buy vastarel from india, volume-conducted potentials can be modeled as either near-field or far-field potentials. Nearfield potentials can be recorded only close to their source, and the characteristics of the potential depend on the distance between the recording electrodes and the electrical source. With near-field potentials, a response generally is not seen until the source is close to the recording electrodes. The closer the recording electrodes are to the current source, the higher the amplitude. The electrical correlate of an action potential traveling toward, under, and then away from the recording electrode is an initial positive phase, followed by a negative phase, and then a trailing positive phase, respectively. The first positive peak represents the time that the action potential is first beneath the active electrode; this is the point at which the onset latency should be measured for nerve action potentials. The initial positive peak may be very small or absent with some sensory responses. In that case, the initial negative deflection best marks the true onset of the potential. Top, An advancing action potential recorded by volume conduction will result in a triphasic potential that initially is positive, then is negative, and finally is positive again. Bottom, If the depolarization occurs directly beneath the recording electrode, the initial positive phase will be absent, and a biphasic, initially negative potential will be seen. Note that, by convention, negative is up and positive is down in all nerve conduction and electromyographic traces. With the active recording electrode (G1) over the motor point, depolarization first occurs at that site, with the depolarization subsequently spreading away. The corresponding waveform has an initial negative deflection without any initial positivity (top trace). If the active recording electrode is off the motor point, depolarization begins distally and then travels under and past the active electrode, resulting in an initial positive deflection (middle trace). If the depolarization occurs at a distance and never travels under the recording electrode, only a small positive potential will be seen (bottom trace). There is no advancing action potential, as muscle fiber depolarization begins at the endplate; hence, the waveform has no initial positive deflection. For example, this pattern is seen when stimulating the median nerve and recording a hypothenar muscle, as might be done during routine motor studies looking for an anomalous innervation. The muscle action potential of the median-innervated thenar muscles occurs at a distance but never travels under the recording electrodes located over the hypothenar muscles. Far-field potentials are electrical potentials that are distributed widely and instantly. Two recording electrodes, one closer and the other farther from the source, essentially see the source at the same time. Median motor study, recording the abductor pollicis brevis muscle, stimulating at the wrist (top trace) and antecubital fossa (bottom trace). At each site, a compound muscle action potential is present, representing a nearfield recording of the underlying muscle fiber action potentials. The compound muscle action potential latencies occur at different times, reflecting their different arrival times at the recording electrode. The stimulus artifact is an example of a far-field potential being transmitted instantaneously and seen at the same time, despite the difference in distances between the two stimulation sites. The shock artifact is instantly transmitted and is seen at the same time at distal and proximal recording sites. Those potentials whose latencies do not vary with distance from the stimulation site usually are all far-field potentials. Peripheral nerves usually can be easily stimulated and brought to action potential with a brief electrical pulse applied to the overlying skin. In the upper extremity, the median, ulnar, and radial nerves are the most easily studied; in the lower extremity, the peroneal, tibial, and sural nerves are the most easily studied (see Chapters 10 and 11). Motor, sensory, or mixed nerve studies can be performed by stimulating the nerve and placing the recording electrodes over a distal muscle, a cutaneous sensory nerve, or the entire mixed nerve, respectively.
Pyogenic granulomas are neither pyogenic nor granulomatous; they are neovascularizations medicine rheumatoid arthritis vastarel 20 mg on-line. The three common causes of acquired circumscribed hair loss are alopecia areata treatment xdr tb order vastarel 20 mg free shipping, tinea capitis, and hair pulling. Tuberous sclerosis and neurofibromatosis are two important genetic disorders in which skin findings are often the presenting feature. Alopecia areata is thought to be an autoimmune disorder, whereas tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp hairs. Hair pulling is secondary to acute stress, trichotillomania, or other psychiatric disorder. Scalp appearance is normal in alopecia areata and scaly in tinea capitis; hair pulling is associated with petechiae. The scalp is the most common location, but areas of aplasia cutis congenita may be seen anywhere on the body. When either of these lesions is present on the scalp, no hair grows in the affected area. Such a child is likely to have either a hair shaft defect or a type of ectodermal dysplasia. Hair shaft defects are structural abnormalities that cause hair to be fragile and easily breakable. The ectodermal dysplasias may affect not only hair but also nails, teeth, and sweat glands. Two congenital lesions may be seen: hypopigmented macules and connective tissue nevi (shagreen patch). The acquired lesions are facial angiofibromas, fibrous forehead plaque, and periungual fibromas. Large blue-gray Mongolian spot of the sacral area and dark brown congenital nevus. Small/medium congenital pigmented nevi are quite common (1 in 100), whereas large congenital pigmented nevi are rare (1 in 20,000). Lifetime risk for the development of melanoma in large congenital pigmented nevi is 1% to 2% in lesions greater than 40 cm adult predicted size. This problem frequently presents as hypopigmented perianal and perivaginal plaques. Survey studies have demonstrated that skin diseases are more common in the geriatric population than in the general population. One study revealed that 40% of Americans between the ages of 65 and 74 years had a cutaneous disease significant enough to warrant treatment by a physician. Patients older than 74 years are even more likely to develop significant skin diseases. Aging of the skin may be divided into that due to intrinsic aging and that secondary to extrinsic aging (Table 58-1). Intrinsic aging includes those changes that are due to normal maturity and senescence and thus occurs in all individuals. Classically, intrinsic aging has not been considered to be preventable, but there is renewed interest in the role of antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, in preventing intrinsic aging. Research in this area is still in its infancy and well-designed, controlled long-term studies are still lacking. Extrinsic aging of the skin consists of those changes produced by external agents. The cutaneous changes produced by sunlight are collectively referred to as dermatoheliosis. Less important extrinsic agents that accelerate aging of the skin include smoking and possibly environmental pollutants. The dermis demonstrates atrophy with fewer fibroblasts, mast cells, and blood vessels associated with depigmentation of hair, loss of hair follicles, and fewer sweat glands. The answer is complicated, because some authorities recognize as many as five different subtypes of wrinkles.
California medicine 7253 pill buy discount vastarel on-line, Texas symptoms of mono cheap vastarel on line, New York, and Florida account for over 50% of the national case total. Crowded urban environments, immigration, poverty, homelessness, intravenous drug abuse, loss of tuberculosis control programs, increased use of immunosuppressive medications. The caseation granuloma (also known as tubercle) is the histopathologic hallmark of tuberculosis. This consists of giant and epithelioid cells with varying amounts of caseation necrosis. The patient was a microbiologist in a hospital laboratory, and this was an accidental inoculation. The organism cannot penetrate intact skin and requires a break in the skin, such as a minor cut or abrasion. Reports have also implicated tattooing, ear piercing, circumcision, mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, mesotherapy, blepharoplasty, acupuncture, and needle-sticks. Primary tuberculosis may occur in any age group, but is most common in children up to 4 years of age and young adults. The face, mucous membranes (conjunctiva and oral mucosa), and lower extremity are the usual sites of infection. Lupus pernio is a cutaneous manifestation of sarcoidosis that presents as a violaceous patch on the face. Lupus vulgaris is a chronic progressive form of cutaneous tuberculosis that originates from another site and involves the skin or mucous membranes via contiguous, lymphatic, or hematogenous spread. In 40% of patients, there is underlying lymphadenitis, and 10% to 20% have underlying pulmonary involvement. Lupus vulgaris lesions have a characteristic "apple jelly" color with this technique. Scrofuloderma is a form of cutaneous tuberculosis that originates in tuberculous lymph nodes, bones, joints, or epididymis and spreads directly to the overlying skin. The most common locations include the lateral neck and the parotid, submandibular, and supraclavicular areas. As the lesion matures, there is extensive necrosis leading to a soft, doughy consistency, ulceration with bluish margins, and formation of a sinus tract. It has not been widely used in the United States, with the exception of a very small number of at-risk infants who cannot receive chemoprophylaxis. This vaccination is contraindicated in immunosuppressed individuals who are at risk of disseminated M. First-line essential chemotherapeutic agents include isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. Second-line drugs include cycloserine, ethionamide, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, gatifloxacin, p-aminosalicylic acid, rifabutin, streptomycin, amikacin/kanamycin, and capreomycin. Isoniazid is the cornerstone of therapy, and rifampin is the second major antituberculous drug. The 6-month regimens include an intensive 2-month therapy with three to four agents followed by a 4-month therapy with isoniazid plus rifampin or rifapentine. In the United States, miniepidemics of drug resistance are centered in New York City, Miami, and Michigan. Treatment of cutaneous tuberculosis is the same as for systemic tuberculosis and consists of effective chemotherapeutic agents. Small lesions of lupus vulgaris or tuberculosis verrucosa cutis may be excised, but the treatment must also include standard antituberculous therapy. Surgical drainage of scrofuloderma may shorten the treatment course, and surgical intervention is necessary in any draining lesion. Cutaneous tuberculosis has a broad clinical spectrum, depending on the route of infection, virulence of the organism, and immune status of the host. Lupus vulgaris and scrofuloderma, although rare, are the two most common forms of cutaneous tuberculosis.
A variety of plastic surgical procedures has been used to improve or correct lipoatrophy medicine hunter generic vastarel 20mg without a prescription. Lipohypertrophy treatment menopause vastarel 20mg online, which manifests as induration of involved skin, occurs in some individuals due to repeated injections of insulin. This effect is apparently independent of the source of insulin, and can even occur with human recombinant insulin. In lipohypertrophy, lipocytes are enlarged and appear to encroach upon the midportion of the dermis. Rotation of insulin injection sites is a key to management of lipohypertrophy, both to prevent or minimize the hypertrophic changes and to assure adequate insulin absorption. Alopecia (hair loss) can be divided into (1) disorders of the hair shaft and (2) all other forms of hair loss. Abnormalities of the hair shaft can produce alopecia because the shafts are fragile and "break off. Both cicatricial and noncicatricial alopecia can be divided into diffuse and patterned hair loss. In diffuse hair loss, hair thins evenly from all parts of the scalp, and discrete "bald spots" do not occur. In the setting of alopecia, cicatricial means that there has been permanent destruction of hair follicles, and they have been replaced by fibrous tissue. The texture of the scalp may remain soft and supple, although sometimes induration or firmness is palpable. People who become bald have hair follicles that are genetically programmed to miniaturize under the influence of postpubertal androgens. Probably, several genes (inherited from both mother and father) influence the severity of balding. Until very late in the balding process, the number of hairs does not decrease, but the hairs become progressively smaller until they are no longer visible to the naked eye. Except in very marked and long-standing balding, very fine, short hairs can be seen exiting from follicular orifices if a magnifying lens is used. About one third of balding patients who use topical minoxidil solution experience significant (cosmetically obvious) hair regrowth. Oral finasteride, a 5-reductase inhibitor, is somewhat more effective, and can be used in combination with topical minoxidil. In the absence of elevated circulating androgens, nonspecific therapy directed at suppressing ovarian androgen production or blocking the peripheral effect of androgens is sometimes tried. Oral contraceptive agents (to suppress ovarian androgen production) and spironolactone are most often utilized for this purpose. Topical minoxidil solution is also useful, but oral finasteride is seldom used in women. Men, and occasionally women, can achieve permanent cosmetic improvement by undergoing a hair transplantation procedure. Hair follicles from the occipital area (donor site) are moved to the balding area (recipient site). The procedure is tedious and expensive, but the cosmetic results can be quite good. Central, centrifugal, cicatricial alopecia, a common form of hair loss in the African-American population. In this patient, the smooth skin, devoid of most follicular openings, reflects light like a mirror. A large bald patch studded with small inflammatory papules surrounded by smaller, similar lesions. B, A patch of alopecia areata showing shorter, thinner, and less deeply pigmented hairs growing within the bald zone. Although many forms of alopecia can result in a circular bald patch, the most common causes are tinea capitis and alopecia areata.
Bexarotene (Targretin) is a synthetic retinoid that selectively activates retinoid X receptors treatment zone tonbridge 20mg vastarel otc. Partial response rate (50% improvement) was 67% and complete response occurred in 7% of patients 7 medications that can cause incontinence order vastarel with a mastercard. Like other retinoid drugs, bexarotene is teratogenic and should not be given to pregnant women. In a study of 58 patients with patch- and plaque-stage disease, side effects included hyperlipidemia in 83%, neutropenia in 47%, central hypothyroidism in 74%, and hypercholesterolemia in 47% of patients. Presented at the American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting, New Orleans, 1999. Other statins include simvastatin (Zocor), pravastatin (Pravachol), fluvastatin (Lescol), lovastatin (Mevacor), and rosuvastatin (Crestor). It is recommended that one start the preferred statin 1 week before starting bexarotene. Of the interferon group of drugs, recombinant interferon- has been the most promising. Low-dose treatment protocols are as effective as high-dose protocols and have fewer side effects. The recommended dose is 3 million units, given subcutaneously, three times weekly. Both partial and complete remissions can be achieved with both single-drug and multidrug chemotherapy protocols. However, the remissions are short-lived, and no one drug or combination of drugs appears to be superior. After a median follow-up of 75 months, there was no difference in response rates or survival in the two groups. The mechanism of action is thought to be activation of cellular apoptosis and possible immunomodulatory effects. The treatment is expensive, requires the availability of specialized equipment, and is administered on an outpatient basis in a hospital setting. Management of mycosis fungoides is best accomplished by the involvement of several specialists, such as those in dermatology, dermatopathology/pathology, hematology/oncology, and radiation oncology. The origin of the cell is debated, with marker studies having shown both T- and B-cell immunoenzymatic staining. It is characterized by a particular type of Reed-Sternberg cell, called the lacunar cell, which is a large cell with a hyperlobulated nucleus and multiple nucleoli surrounded by a clear space (lacunae). There is a diffuse fibrotic and a reticular variant of the lymphocyte-depleted subtype. This type tends to occur in older patients, with disseminated involvement and a poor prognosis. Nonspecific skin lesions are common and include pruritus, pigmentation, prurigo, ichthyosis, alopecia, and herpes zoster. It is very helpful in identifying subpopulations of T- and B-cell lymphocytes (Table 45-3). Type B has moderately large atypical cells with cerebriform nuclei similar to the cell type found in mycosis fungoides. Type C is composed of sheets of cells that resemble the cells of anaplastic T-cell lymphoma.