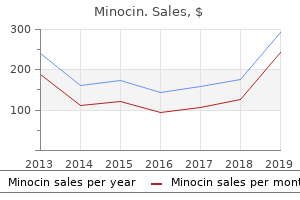
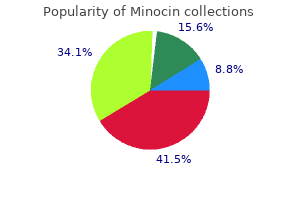
Minocin
"Order 50 mg minocin visa, bacterial spores".
By: P. Anog, M.A., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, Idaho College of Osteopathic Medicine
Concomitant psoriasis infection staph order 50 mg minocin with mastercard, seborrheic dermatitis antimicrobial laminate discount 50mg minocin visa, and disseminated cutaneous histoplasmosis in a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Cutaneous manifestations of histoplasmosis in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Cutaneous lesions of disseminated histoplasmosis in human immunodeficiency virusinfected patients. Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Erythema nodosum and erythema multiforme as clinical manifestations of histoplasmosis in a community outbreak. Rapid diagnosis of Histoplasma capsulatum endocarditis using the AccuProbe on an excised valve. Zaragoza 0, Nielsen K Titan cells in Cryptococcus neoformans: cells with a giant impact. Titan cells formation in Cryptococcus neoforrnans is finely tuned by environmental conditions and modulated by positive and negative genetic regulators. Blastomycosis acquired occupationally during prairie dog relocation-Colorado, 1998. Clinicopathologic spectrum of specific cutaneous lesions of disseminated coccidiomycosis. Coccidioi-domycosis: a study of 95 cases of the disseminated type with special reference to the pathogenesis of the disease. Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis associated with pulmonary coccidioidomycosis. African histoplasmosis masquerading as carcinoma ofthe colon: report of a case and review ofliterature. Colombier M-A, Alanio A, Denis B, et al Dual invasive infection with Phiieoacremonium piiriisiticum and Piiriiconiothyrium cyclothyrioides in a renal transplant recipient: case report and comprehensive review of the literature of Phaeoacremonium Phaeohyphomycosis. Skin infection due to Alterniiriii species in kidney allograft recipients: report of a new case and review of the literature. Cutaneous infection by Phomopsis longicolla in a renal transplant recipient from Guinea: first report of human infection by this fungus. Ten-year experience of cutaneous and/or subcutaneous infections due to coelomycetes in France. Nocardiosis: a case series and a mini review of clinical and microbiological features. Actinomycosis: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations and a review of 32 cases. Garcia-Hermosa D, Dromer F, Alanio A, et al Agents of systemic and subcutaneous mucormycosis and entomophthoromycosis. Early clinical and laboratory diagnosis of invasive pulmonary, e:xtrapulmonary, and disseminated mucormycosis (zygomycosis). Cutaneous mycormycosis with subsequent visceral dissemination in a child with neutropenia: a case report and review of the pediatric literature. Systemicmucormycosis diagnosed by fine needle aspiration and confirmed with enzyme immunoassay. Primary cutaneous infection by Aspergillus ustus in a 62-year-old liver transplant recipient. Metastatische aspergilluspannikulitis bei blastischer transformation eines myelodysplastischen syndromes und agranulozytose. Prospective multicenter international surveillance of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Azole resistance of Aspergillus fumigatus in immunocompromised patients with invasive aspergillosis. Hickman catheter-associated primary cutaneous aspergillosis in a patient with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
The shoulder joint through a separate branch which enters the humerus along with its nutrient artery antibiotic 93 2264 order minocin now. Communicating branches: the musculocutaneous nerve through lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm communicates with the neighbouring nerves antibiotic meaning discount minocin 50 mg free shipping, namely the superficial branch of the radial nerve, the posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm, and the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve. In the upper part, it is lateral to the artery; in the middle of the arm, it crosses the artery from lateral to the medial side; and remains on the medial side of the artery right up to the elbow. In the arm, the median nerve gives off a branch to the pronator teres just above the elbow and vascular branches to the brachial artery. In the fascial septum between the two muscles lies the musculocutaneous nerve (a branch of the lateral cord of brachial plexus). Trace the tendinous long head of biceps arising from the supraglenoid tubercle and the short head arising from the tip of the coracoid process of scapula. Tap the tendon of biceps with forearm pronated and partially extended at the elbow. It ends at the level of the neck of radius in the cubital fossa by dividing into its two terminal branches, the radial and ulnar arteries. It extends from the lower border of the teres major muscle to a point in front of the elbow, at the level of the neck of the radius, just medial to the tendon of the biceps brachii. Beginning, Course and Termination Brachial artery begins at the lower border of teres major muscle as continuation of axillary artery. It runs 1 It runs downwards and laterally, from the medial side of the arm to the front of the elbow. Anastomoses around the elbow joint link the brachial artery with the upper ends of the radial and ulnar arteries. Behind the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, the posterior descending branch of the profunda brachii artery (middle collateral) anastomoses with the interosseous recurrent branch of the posterior interosseous artery. In front of the medial epicondyle of the humerus, the inferior ulnar collateral branch of the brachial artery anastomoses with the anterior ulnar recurrent branch of the ulnar artery. Behind the medial epicondyle of the humerus, the superior ulnar collateral branch of the brachial artery anastomoses with the posterior ulnar recurrent branch of the ulnar artery. Look for the radial nerve on the posterior aspect of artery before it enters the radial groove. Clean the branches of brachial artery and identify other arteries which take part in the arterial anastomoses around the elbow joint. Changes at the Level of Insertion of Coracobrachialis 1 Bone: the circular shaft becomes triangular below this level. The brachial artery passes from the medial side of the arm to its anterior aspect. The superior ulnar collateral artery originates from the brachial artery, and pierces the medial intermuscular septum along with the ulnar nerve. Section Cubital (Latin cubitus, elbow) fossa is a triangular hollow situated on the front of the elbow. Superficial fascia containing the median cubital vein joining the cephalic and basilic veins. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm lies along with cephalic vein and the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm along with basilic vein. Supinator surrounding the upper part of radius Contents the fossa is actually very narrow. In the fossa, it gives off the posterior interosseous nerve or deep branch of the radial nerve which gives branches to extensor capri radialis brevis and supinator. The common interosseous branch divides into the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries, and latter gives off the interosseous recurrent branch. It is used for introducing cardiac catheters to get sample of blood from various chambers of heart. Insertion medial head is inserted partly into the superficial tendon, and partly into the olecranon process. Although the medial head is separated from the capsule of the elbow joint by a small bursa, a few of its fibres are inserted into this part of the capsule: this prevents nipping of the capsule during extension of the arm.
The apical group lies behind and above the pectoralis minor antibiotics for sinus infection and sore throat cheap minocin 50 mg on-line, medial to the axillary vein infection quality control staff in a sterilization unit of a hospital 50mg minocin with mastercard. Infection of the hair follicles and sebaceous glands gives rise to boils which are common in this area. Medial Axillary vein: the first part of the axillary artery is enclosed (together with the brachial plexus) in the axillary sheath, derived from the prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia. One branch arises from the first part, two branches from the second part, and three branches from the third part. Superior Thoracic Artery Thoracoacromial artery is a branch from the second part of the axillary artery. It emerges at the upper border of the pectoralis minor, pierces the clavipectoral fascia, and soon divides into the following four terminal branches. The pectoral branch passes between the pectoral muscles, and supplies these muscles as well as the breast. The deltoid branch runs in the deltopectoral groove, along with the cephalic vein. The acromial branch crosses the coracoid process and ends by joining the anastomoses over the acromion process. The clavicular branch runs superomedially deep to the pectoralis major, and supplies the acromioclavicular joint and subclavius. Lateral Thoracic Artery Superior thoracic artery is a very small branch which arises from the first part of the axillary artery (near the subclavius). It emerges at, and runs along, the lower border of the pectoralis minor in close relation with the anterior group of axillary lymph nodes. In females, the artery is large and gives off the lateral mammary branches to the breast. It runs along the lower border of the subscapularis to terminate near the inferior angle of the scapula. It gives off a large branch, the circumflex scapular artery, which is larger than the continuation of the main artery. In order to check bleeding from the distal part of the limb (in injuries, operations and amputations), the artery can be effectively compressed against the humerus in the lower part of the lateral wall of the axilla. It passes laterally in front of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus, and anastomoses with the posterior circumflex humeral artery, to form an arterial circle round the surgical neck of the humerus. Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery the axillary vein is the continuation of the basilic vein. The axillary vein is joined by the venae comitantes of the brachial artery, a little above the lower border of the teres major. It receives 5 out of 6 tributaries corresponding to the branches of axillary artery and the cephalic vein. Veins accompanying branches of thoracoacromial artery drain directly into the cephalic vein. Lateral thoracic vein of upper limb is joined to superficial epigastric vein of lower limb by thoracoepigastric vein enabling blood to return to heart in blockage of inferior vena cava (see Flowcharts 14. It arises from the third part of the axillary artery at the lower border of the subscapularis. It supplies the shoulder joint, the deltoid, and the muscles bounding the quadrangular space. It gives off a descending branch which anastomoses with the ascending branch of the profunda brachii artery. They receive lymph from the posterior wall of the upper half of the trunk, and from the axillary tail of the breast. Dorsal root is sensory and is characterised by the presence of spinal or dorsal root ganglion and enters the dorsal horn and posterior funiculus of spinal cord. The motor and sensory fibres get united in the spinal nerve which divides into short dorsal ramus and long ventral ramus. In addition, these also manage to obtain sympathetic fibres via grey ramus communicans. The origin of the plexus may shift by one segment either upward or downward, resulting in a prefixed or postfixed plexus, respectively.
Section 1 Upper Limb the superficial palmar arch lies deep to the palmaris brevis and the palmar aponeurosis antibiotic xi proven minocin 50 mg. It crosses the palm over the flexor digiti minimi antibiotics for sinus infection bactrim order minocin from india, the flexor tendons of the fingers, the lumbricals, and the digital branches of the median nerve. Thus it passes through the anatomical snuffbox to reach the proximal end of the first interosseous space. The artery is superficial to the lateral ligament of the wrist joint, the scaphoid and the trapezium. At first it lies deep to the oblique head of the adductor pollicis, and then passes between the two heads of this muscle to form deep palmar arch. From there, it passes forwards to reach first interosseous space and then into the palm. Dorsum of hand: On the dorsum of the hand, the radial artery gives off: 1 A branch to the lateral side of the dorsum of the thumb. It at once divides into two branches for the adjacent sides of the thumb and the index finger. Deep Palmar Arch the deep branch of the ulnar nerve lies within the concavity of the arch. Branches Formation the arch lies on the proximal parts of the shafts of the metacarpals, and on the interossei; under the cover of the oblique head of the adductor pollicis, the flexor tendons of the fingers, and the lumbricals. This is adductor Upper Limb Deep palmar arch provides a second channel connecting the radial and ulnar arteries in the palm (the first one being the superficial palmar arch already considered). The digital perforating arteries connect the palmar digital branches of the superficial palmar arch with the dorsal metacarpal arteries. It passes backwards between the abductor and flexor digiti minimi, and then between the opponens digiti minimi and the fifth metacarpal bone, lying on the hook of the hamate. Branches From Superficial Terminal Branch Ulnar nerve is the main nerve of the hand (like the lateral plantar nerve in the foot). It divides into two proper palmar digital nerves for the adjoining sides of the ring and little fingers. As the nerve crosses the palm, it supplies the medial two lumbricals and eight interossei. The deep branch terminates by supplying the adductor pollicis, and occasionally the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis. The patient is unable to spread out the fingers due to paralysis of the dorsal interossei. The power of adduction of the thumb, and flexion of the ring and little fingers are lost. Ulnar nerve injury at the elbow: Flexor carpi ulnaris and the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus are paralysed. The intermetacarpal spaces are hollowed out due to wasting of the interosseous muscles. Claw hand deformity is more obvious in wrist lesions as the profundus muscle is spared: this causes marked flexion of the terminal phalanges (action of paradox) (see p 197). Five muscles, namely the abductor pollicis brevis, the flexor pollicis brevis, the opponens pollicis and the first and second lumbrical muscles. The muscular branch curls upwards around the distal border of the retinaculum and supplies the thenar muscles. Out of the three digital branches, two supply the thumb and one the lateral side of the index finger. The flexor pollicis longus and lateral half of flexor digitorum profundus are paralysed. The hand is adducted due to paralysis of the flexor carpi radialis, and flexion at the wrist is weak. Flexion at the interphalangeal joints of the index and middle fingers is lost so that the index and the middle (to a lesser extent) fingers tend to remain straight while making a fist. This syndrome consists of motor, sensory, vasomotor and trophic symptoms in the hand caused by compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel. However, the skin over the thenar eminence is not affected as the branch of median nerve supplying it arises in the forearm.