Zyvox
"Cheap zyvox 600mg amex, antibiotic resistant uti in dogs".
By: E. Tom, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, A. T. Still University Kirksville College of Osteopathic Medicine
They are all based on the same concept of fabricating a structure with a drug imbedded or enclosed [16] antibiotics in food buy zyvox without a prescription. The fabrication of microdevices depends on the microfabrication techniques available antimicrobial jobs discount zyvox online, and 3D printing is also becoming part of the techniques that can be used to produce such devices [5, 16, 21]. Micropatches can, therefore, have a long contact time with the intestinal membrane, where the drug has the possibility to be released over a longer period of time than normal drug formulations in the continuous flow of the intestine. The differences between the wells and the containers are that the wells are sticking into the surface layer, whereas the microcontainers are built on top of this layer [16]. For all three designs, it is possible to protect the drug in the device until it reaches the intestine, where the devices have shown to be mucoadhesive and to improve the retention time. Due to their design, the devices provide unidirectional release, and thereby avoiding luminal loss of the drug [5, 13, 16]. When designing devices for oral drug delivery, there are size constraints to take into account. Hence, this is not an issue for individualized microdevices or when added to the commercially available gelatin capsules. Materials for the fabrication of microdevices Once the microdevice is designed, the second step is to choose the material for its fabrication. This choice plays a fundamental role and, depending on the material, the microdevice can obtain specific mechanical, physical and biological properties. Biocompatible and biodegradable materials are always preferred to prevent, for example, toxicity and inflammation in the body. In fact, Si was successfully used to fabricate not only porous particles, but also the first planar bioadhesive microdevices [34, 35]. In some studies, Si has been associated with inflammation and, in particular, Si nano- and microparticles have been widely tested in vitro to evaluate their cytotoxicity [36, 37]. In other studies, it has been shown that the exposure of SiO2 to Caco-2 cells damaged the brush border membrane, decreasing the number of intestinal microvilli, and this resulted in a decreased surface area available for absorption [38]. Additionally, the use of SiO2 nanoparticles at physiologically relevant oral doses has ultimately caused adverse outcomes in an in vitro model [38]. These studies demonstrated that Si can be used as an initial prototyping material for the fabrication of microdevices for oral drug delivery, but not for devices that should be tested in animals or in humans. However, it has been used for the fabrication of planar microdevices for oral drug delivery that were tested in vitro and in vivo [45]. These abovementioned materials are suitable for the fabrication of proof-of-concept microdevices but, for being non-biodegradable, there is the risk of accumulation of toxic material in the body. However, biodegradable materials are more suitable for the production of oral drug delivery systems [27]. Moreover, most of the biodegradable materials are polymers in which it is possible to adjust the mechanical properties and their degradation rate [46]. The fabrication of the microdevices using biodegradable materials required longer time in development compared to the devices made from non-biodegradable materials. This is due to the fact that microfabrication techniques had to shift to polymeric materials that are more suitable for disposable devices [47, 48]. Microwells were also tested for a pH-triggered release, showing that it is also possible to use them for oral drug delivery [26]. In this study, the material of stainless steel allowed to determine the localization and orientation of the device using X-rays in vivo [6]. This also means that, for proof-of-concept studies, the material chosen may not be determinant as long as it suits the fabrication method or serves to provide essential information toward the device and its application as an oral drug delivery system. Methods for microfabrication of oral drug delivery devices Most drug formulations are produced by bottom-up methods, where weak and noncovalent bonds between molecules make them to self-assemble into particulate systems such as liposomes and vesicles. These systems have had a high success rate in all aspects of drug delivery, and also for oral administration [52]. Even though there is a good success rate, they also have their limitations and, therefore, top-down methods can add benefits to the area of drug delivery.
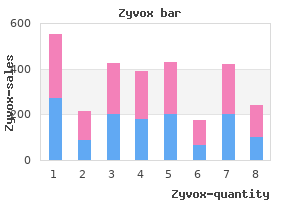
If Pseudomonas or Stenotrephomonas is the causative organism infection prevention week trusted 600 mg zyvox, patients should be treated with two effective agents for three to four weeks antibiotics for sinus infection buy zyvox australia. In addition, catheter removal is also indicated in patients with recurrent or relapsing peritonitis and those with polymicrobial infections, which indicate a bowel perforation. Other indications for catheter removal include fungal and tubercular peritonitis [4, 27]. The early inflammatory phase is associated with vague abdominal discomfort and a change to a rapid membrane transport status. The inflammatory phase can then progress to a sclerosing phase, where a fibrotic cocoon slowly encapsulates the small bowel. The patient will generally lose weight, experience nausea and vomiting, and suffer recurrent bowel obstructions [7]. These will include coverage for both Grampositive organisms, such as a firstgeneration cephalosporin or vancomycin, and Gramnegative organisms, such as an aminoglycoside [27]. Unless patients have systemic Peritoneal Dialysis 287 Abdominal imaging is helpful for diagnosis in the sclerosing phase, which demonstrates cocooning of the bowel, in conjunction with generalized thickening, tethering, enhancement, and calcification of the peritoneal membrane. In the inflammatory stage, corticosteroids are the treatment of choice, while in the fibrotic stage, tamoxifen may be beneficial. In practice, distinguishing between these stages may be difficult and both are often used. In patients with established abdominal cocoon and recurrent bowel obstructions, surgery may be necessary. Beyond its contribution to small solute removal, residual renal function is also associated with a reduction in blood pressure and left ventricular hypertrophy, increased sodium removal, larger molecular weight solute clearances and maintenance of metabolic and endocrine function [32]. Cognitive barriers include history of nonadherence, psychiatric illness or dementia; and psychosocial barriers include unsuitable place of residence (poor hygiene). Contraindications are factors that absolutely disqualify 288 Peritoneal Dialysis associated with poorer outcomes. However, literature does seem to highlight certain differences within select subgroups of patients. Acute peritoneal dialysis in neonates: comparison of two types of peritoneal access. Peritoneal dialysis in children with acute kidney injury: a developing country experience. Peritoneal dialysis for acute renal failure in infants: a comparison of three types of peritoneal access. A systematic review and metaanalysis of the influence of peritoneal dialysis catheter type on complication rate and catheter survival. Guideline on targets for solute and fluid removal in adult patients on chronic peritoneal dialysis. Mupirocin for preventing exitsite infection and peritonitis in Peritoneal Dialysis 289 23. A prospective study of the efficacy of local application of gentamicin versus mupirocin in the prevention of peritoneal dialysis catheterrelated infections. Randomized, controlled trial of topical exitsite application of honey (Medihoney) versus mupirocin for the prevention of catheter associated infections in hemodialysis patients. Catheterrelated interventions to prevent peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis: a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials. Predictors of the rate of decline of residual renal function in incident dialysis patients. The relative importance of residual renal function compared with peritoneal clear- 35. Healthcare costs in chronic kidney disease and renal replacement therapy: a populationbased cohort study in Sweden. Impact of contraindications, barriers to selfcare and support on incident peritoneal dialysis utilization. Mortality studies comparing peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: what do they tell us Similar outcomes with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in patients with endstage renal disease.
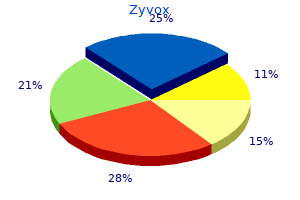
Batch and microfluidic reactors in the synthesis of enteric drug carriers 325 Immunoglobulins (IgG) can cross the polarized epithelial barriers due to the use of the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) bacterial 16s rrna universal primers buy discount zyvox 600mg on-line, which mediates the transfer of IgGs from mother to child virus 43 states order zyvox in india. Following the transcytosis pathway mediated by the FcRn, those immunonanoparticles showed an 11. Mucolytic enzymes have also been grafted to the surface of dye-loaded polymeric nanoparticles to promote drug permeation in the gastrointestinal tract. The in vivo biodistribution of the mucolytic enzyme-modified nanoparticles revealed an increased number of dye-loaded nanoparticles in the mucus layer of the proximal segments compared to the unmodified nanoparticles. The high surface area per volume ratio of nanoparticles represents a clear advantage to release their cargo in the large absorptive surface area of the gastrointestinal tract. Also, their morphology, surface area, and surface functionalization can be easily optimized to increase their permeability [44]. The authors reported how the adsorption of the hydrophobic drug on the mesopores enhanced its dissolution profile compared to the solubility of the free drug, fact that was attributed to a transformation from the crystalline structure of the drug to a more amorphous one and to the hydrophilic character provided by the silica. The in vivo bioavailability of the drug adsorbed on rod-shaped nanoparticles was approximately 4. This phenomenon was attributed to the prolonged circulation times and different recognition behavior by the mononuclear phagocytic system. Therefore, by controlling the nanoparticles morphology tunable drug release profiles and desirable pharmacokinetics are possible to obtain. They showed that the mucoadhesive nanoparticles were clumped together in the lumen of the jejunum and ileum, incapable to penetrate between the villi. Interestingly they show that depending on the feeding volume, the biodistribution may vary, finding similar biodistribution profiles for both adhesive and non-adhesive nanoparticles when large administration volumes were used. However, mucus-penetrating liposomes synthesized by liposome surface functionalization with Pluronic F127 showed better oral absorption in vivo of an encapsulated model drug (cyclosporine A). Chitosan is a commonly used natural polymer with mucoadhesive character thanks to its electrostatic interaction with the negatively charged sialic and sulfonic acids present in the mucus layer [49]. Other authors show that mucoadhesive nanoparticles produce a better biodistribution profile than the administration of the free drug. A prolonged reduction of the blood calcemia in rats was found when using the mucoadhesive formulation; although in this case it is not clear if the use of the permeation enhancer played a pivotal role. The authors demonstrated that the thiolated nanoparticles were able to prolong the drug plasma levels for 24 h. Thiolation is commonly used to promote mucoadhesion, since it enables the formation of disulfide bonds between sulfhydryl groups of the nanoparticulated carrier and cysteine-rich subdomains of the mucus [51]. A trade-off between a rapid clearance from the intestinal mucosa and a prolonged bioavailability should be reached when using mucoadhesive carriers to prolong drug delivery rates. Thiolated polymers, commonly named thiomers, have been extensively used in oral drug delivery to promote mucoadhesion. They modified anionic polyacrylic acid and cationic chitosan nanoparticles with cysteine and 2-iminothiolane, respectively, to obtain thiolated versions of those polymers. This adhesive effect was attributed to the presence of disulfide bonds between the thiomers and the mucus glycoproteins. A chemical modification to introduce thiol groups on commercial enteric pH-dependent polymers. In this work, the thiolated copolymers derived from esters of acrylic and methacrylic acid were modified with cysteine, and insulin was loaded inside the resulting nanoparticles, which were obtained by nanoprecipitation. They evaluated the peptide effect on the blood calcium levels, demonstrating that the liposomes coated with thiomers protected against oxidation produced a 35% reduction of the blood calcium levels, whereas the unprotected nanoparticles produced a more moderate reduction (approx. Biodistribution studies using a gamma camera imaging revealed that 6 h after administration only the thiolated Eudragit microspheres remained adhered to the intestine wall. Mucoadhesive pre-activated thiomers constitute another important group in oral drug delivery when the prevention of oxidation of the thiol-groups present in thiomers is sought. Ex vivo tests on mucosal adhesion of the resulting nanoparticles revealed that, compared to unmodified nanoparticles, the mucosal residence time of the thiolated ones was 1.
Syndromes
- BUN
- Larger-than-normal veins in the neck
- Problems with the heart valves
- The type of vulvar cancer
- Surgery for impingement syndrome: Damaged or inflamed tissue is cleaned out in the area above the shoulder joint itself. Your surgeon may also cut a specific ligament, called the coracoacromial ligament, and shave off the under part of a bone. This under part of the bone is called the acromion. The spur can be a cause of inflammation and pain in your shoulder.
- Paranoid personality disorder
- Swollen lymph nodes (glands)
- Disability (differs from person to person)
Coronary perfusion pressure and the return of spontaneous circulation in human cardiopulmonary resuscitation antibiotics for kidney bladder infection purchase zyvox pills in toronto. Death by hyperventilation: a common and life-threatening problem during cardiopulmonary resuscitation virus 1 purchase cheap zyvox line. Chest compression and ventilation rates during cardiopulmonary resuscitation: the effects of audible tone guidance. Interruptions of chest compressions during emergency medical systems resuscitation. Effects of compression depth and pre-shock pauses predict defibrillation failure during cardiac arrest. Clinical and hemodynamic comparison of 15:2 and 30:2 compression-to-ventilation ratios for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Difference in acid-base state between venous and arterial blood during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Adverse hemodynamic effects of interrupting chest compressions for rescue breathing during cardiopulmonary resuscitation for ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest. Effect of epinephrine on cerebral and myocardial perfusion in an infant animal preparation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Determinants of blood flow to vital organs during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in dogs. Mechanisms by which epinephrine augments cerebral and myocardial perfusion during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in dogs. Improving the efficiency of cardiopulmonary resuscitation with an inspiratory impedance threshold valve. Improving active compression-decompression cardiopulmonary resuscitation with an inspiratory impedance valve. Evaluation of an impedance threshold device in patients receiving active compression-decompression cardiopulmonary resuscitation for out of hospital cardiac arrest. Clinical and hemodynamic comparison of 15:2 and 30:2 compression-to-ventilation ratios for cardiopulmonary resuscitation*. Clinical evaluation of an inspiratory impedance threshold device during standard cardiopulmonary resuscitation in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Comparison of standard cardiopulmonary resuscitation versus the combination of active compression-decompression cardiopulmonary resuscitation and an inspiratory impedance threshold device for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Effect of ventilation on acid-base balance and oxygenation in low blood- flow states. Effect of one-rescuer compression/ventilation ratios on cardiopulmonary resuscitation in infant, pediatric, and adult manikins. An analysis of the efficacy of bag-valve-mask ventilation and chest compression during different compressionventilation ratios in manikin-simulated paediatric resuscitation. Theoretically optimal duty cycles for chest and abdominal compression during external cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Age-related effects of compression rate and duration in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. A preliminary study of cardiopulmonary resuscitation by circumferential compression of the chest with use of a pneumatic vest. Effects of vasopressin and epinephrine on splanchnic blood flow and renal function during and after cardiopulmonary resuscitation in pigs. Assisted ventilation does not improve outcome in a porcine model of single-rescuer bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation. A technique revisited: hemodynamic comparison of closed- and open-chest cardiac massage during human cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Open- versus closed-chest cardiac compressions in a canine model of pediatric cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Outcome and cost of open- and closed-chest cardiopulmonary resuscitation in pediatric cardiac arrests. Epinephrine dosage effects on cerebral and myocardial blood flow in an infant swine model of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Influence of epinephrine on systemic, myocardial, and cerebral acid-base status during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Effects of epinephrine and vasopressin on cerebral microcirculatory flows during and after cardiopulmonary resuscitation.