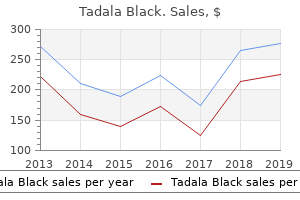
Tadala Black
"80mg tadala black mastercard, erectile dysfunction diabetes pathophysiology".
By: T. Tom, M.A.S., M.D.
Deputy Director, Columbia University Roy and Diana Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons
In cases where the disease does progress webmd erectile dysfunction treatment proven tadala black 80 mg, the major complications erectile dysfunction after prostatectomy discount tadala black 80mg otc, which can take years to appear, involve the heart and the intestinal tract. Dilation of the intestinal tract is due to similar processes in nerve cells, and the organs become incapable of proper peristalsis; megaoesophagus and megacolon are the two commonest manifestations. Leishmaniasis Leishmania parasites are transmitted by sandflies and cause New World and Old World leishmaniasis Several species of Leishmania parasites cause disease in both the New World and the Old World (Table 28. In the latter areas especially, dogs can act as an important reservoir of infection. Antiparasitic therapy of Chagas disease is with oral benznidazole or oral nifurtimox. In recent years, there has been a re-evaluation of the role of drug therapy in chronically infected adults such that most practitioners now consider them for antiparasitic drug therapy. Leishmaniasis is diagnosed by demonstrating the organism microscopically and is treated with antimonials Demonstration of the organism by microscopy of splenic aspirate or biopsies of bone marrow or skin lesions (depending upon the clinical picture) is definitive proof of leishmaniasis. Detection of antileishmanial antibody by the Leishmania direct agglutination test and rK39 rapid test is valuable in the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. The precise choice of agent depends on the infecting species but, in principle, cutaneous leishmaniasis is treated by local injection of the edge of the ulcer with sodium stibogluconate (an antimonial). Intravenous sodium stibogluconate is used to treat multiple or potentially disfiguring lesions. The agent of choice for the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis is intravenous liposomal amphotericin B. Intravenous sodium stibogluconate is an alternative, though there is now significant antimony-resistant visceral leishmaniasis in parts of India. Impregnated bed nets are effective against the sandfly vector and a Leishmania infantum vaccine is available for use in dogs. A variety of vaccines against the cutaneous disease are under development for human use, including those composed of sandfly salivary proteins with or without Leishmania antigens. They contain Leishmania amastigotes and constitute a reservoir of infection that can infect biting sandflies. Cutaneous leishmaniasis is characterized by plaques, nodules or ulcers Classic cutaneous leishmaniasis progresses insidiously, from a small papule at the site of infection to a large ulcer. More cases are therefore likely to be seen, as such biologics are increasingly being used to treat a variety of medical conditions. However, schistosomes are the only group in which larvae penetrate directly into the final host after release from the snail. Infected freshwater snails, which are always aquatic, release fork-tailed larvae into the surrounding water. The life cycle is completed when eggs laid by the female worms move across the walls of the bladder or bowel and leave the body. Clinical features of schistosomiasis result from allergic responses to the different life cycle stages the stages of skin penetration, migration and egg production are each associated with pathological changes, collectively affecting many body systems. Penetration can cause a dermatitis, which becomes more severe on repeated re-infection. As a consequence, there is hepatosplenomegaly, collateral connections form between the hepatic vessels and fragile oesophageal varices develop. The collateral circulation can lead to eggs being washed into the capillary bed of the lungs. Serum antibody detection is helpful in non-endemic areas, especially in travellers. Treatment of individuals with praziquantel removes the worms, but does not kill the eggs, which die naturally in about 2 months. Control of infection at a population level is achieved by breaking the transmission cycle, through avoidance of infected water and improvement in sanitation.
Stability in the environment Microorganisms that resist drying spread more rapidly in the environment than those that are sensitive to drying (Table 14 erectile dysfunction shake ingredients discount 80 mg tadala black overnight delivery. Microorganisms also remain infectious for longer periods in the external environment when they are resistant to thermal inactivation erectile dysfunction causes weight buy tadala black 80mg with amex. Drying directly from the frozen state (freeze drying) can make them very resistant to environmental temperatures. The fact that spores and cysts are dehydrated accounts for much of their stability. Microorganisms that are sensitive to drying depend for their spread on close contact, vectors, or contamination of food and water for spread. Number of microorganisms required to infect a fresh host the efficiency of the infection varies greatly between microorganisms, and helps explain many aspects of transmission. For instance, volunteers ingesting 10 Shigella dysenteriae bacteria (from other humans) will become infected, whereas as many as 106 Salmonella spp. A single tissue culture infectious dose of a human rhinovirus instilled into the nasal cavity causes a common cold and, although this dose contains many virus particles, about 200 such doses are needed when applied to the pharynx. As few as 10 gonococci can establish an infection in the urethra, but many thousand times this number are needed to infect the mucosa of the oropharynx or rectum. Activities of the infected host may increase the efficiency of shedding and transmission. Coughing and sneezing are reflex activities that benefit the host by clearing foreign material from the upper and lower respiratory tract, but they also benefit the microorganism. Strains of microorganism that are more able to increase fluid secretions or irritate respiratory epithelium will induce more coughing and sneezing than those less able and will be transmitted more effectively. Similar arguments can be applied to the equivalent intestinal activity: diarrhoea. A separate set of infections is acquired from animals, either directly from vertebrates (the zoonoses) or indirectly from biting arthropods. Infections acquired from other species are either not transmitted or transmit very poorly from human to human. Transmission from the respiratory tract Respiratory infections spread rapidly when people are crowded together indoors An increase in nasal secretions with sneezing and coughing promotes effective shedding from the nasal cavity. Some strains of a given microorganism are therefore more readily transmitted than others, although the exact mechanism is often unclear. Arthropod-borne infections and zoonoses can be controlled by controlling vectors or by controlling animal infection; there is virtually no person-to-person transmission of these infections (except for pneumonic plague and Ebola virus infection, see Ch. A smaller number of microorganisms (hundreds) are expelled from the mouth, throat, larynx and lungs during coughing (whooping cough, tuberculosis). It is surely no accident that many of the most abusive words in the English language begin with these letters, so that a spray of droplets (possibly infectious) is delivered with the abuse! The largest droplets fall to the ground after travelling approximately 4 m, and the rest settle according to size. The air in ill-ventilated rooms is also more humid, favouring survival of suspended microorganisms such as streptococci and enveloped viruses. Air conditioning is another factor, as the dry air leads to impaired mucociliary activity. This is in striking contrast to the material expelled from the gastrointestinal tract, and helps explain why respiratory infections spread so rapidly when people are indoors. Handkerchiefs, hands and other objects can carry respiratory infection such as common cold viruses from one individual to another, although coughs and sneezes provide a more dramatic route. For instance, it can be assumed that rhinoviruses arrive in the lower respiratory tract on a large scale, but fail to grow there because, like leprosy bacilli, they prefer the cooler temperature of the nasal mucosa.
Fracture at the pterion should be considered a medical emergency because the anterior branches of the middle meningeal artery travel adjacent to the site in the potential epidural space erectile dysfunction age young buy tadala black 80mg cheap. Rupture of the middle meningeal artery will lead to an epidural hematoma and sudden erectile dysfunction causes purchase discount tadala black online, if left untreated, can lead to acute death. Of particular importance are the paired occipital condyles, superior sites for articulation with C1 (atlas) to form the atlanto-occipital joint. The mastoid and styloid processes (petrous temporal) are located laterally to the occipital condyles. Posteriorly, the occipital bone is characterized by a midline palpable elevation of bone called the external occipital protuberance. The superior nuchal line extends laterally from the protuberance, serving as the superiormost attachment site for neck structures. Viscerocranium: Located anteriorly, the viscerocranium represents the bony scaffold of the face and is made up of bones that surround and form three main facial regions-orbit, nose, and mouth. Cranium [1] Frontal bone: this bone forms the majority of the forehead of the face and contributes to the superior rim (supraorbital margin) of the orbit. A smooth, midline depression, the glabella, sits between the paired supraciliary arches and is easily palpated between the eyebrows, superior to the nasal bridge-formed by paired nasal bones. Each zygomatic bone has a zygomaticotemporal foramen anterior to the temporal process of the zygomatic bone. This process articulates with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone to form the zygomatic arch. The external acoustic meatus (petrous temporal) lies just posterior to the zygomatic arch. Bilateral infraorbital foramina are located just inferior to the infraorbital margin on the superior aspect of the maxilla. The intermaxillary suture represents the fusion site for the paired maxillae, forming the upper jaw and characterized by alveolar processes that support the upper (maxillary) teeth. A midline mental protuberance is found inferiorly and is framed by bilateral mental foramina. Superior to the ramus, the coronoid process and head of the mandible are situated anteriorly and posteriorly, respectively. The head of the mandible articulates with the mandibular fossa (petrous temporal) to form the temporomandibular joint. Scalp the scalp is a multilayer structure that covers the neurocranium, spanning between the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the superior nuchal lines posteriorly and extending laterally to the zygomatic arches. Head and Cranial Nerves Scalp: Skin Connective tissue Aponeurosis,- Loose connective ! Scalp proper: the first three layers of the scalp are called the scalp proper and comprise skin, connective tissue, and aponeurosis. The skin of the scalp has a rich blood supply and contains multiple sweat and sebaceous glands and hair follicles. The thick subcutaneous connective tissue layer also has a substantial neuromuscular supply. Loose connective tissue layer: Deep to the aponeurosis, the loose connective tissue layer allows for movement of the scalp proper on the skull and contains emissary veins. Pericranium: Finally, the innermost layer, the pericranium, is a dense connective tissue layer that is firmly attached to the calvaria, forming the periosteum. Posterolateral scalp: this area is innervated by the lesser occipital nerve (anterior rami C2, C3). Posterior and superior scalp: this area is innervated by the greater occipital nerve (posterior rami C2). Vasculature: the scalp receives blood supply primarily from branches of the external carotid artery, including posterior auricular, occipital, and superficial temporal arteries. The anterior scalp is supplied by vessels that indirectly arise from the internal carotid artery, including the supratrochlear and supraorbital arteries. There are no lymph nodes in the superficial scalp, so all lymph is drained into the superficial ring of lymph nodes located at the intersection of the head and neck. Protective and physiologic membranous coverings, called meninges, surround structures of the brain. Brain development: Neurulation begins when the primitive node/ notochord induces the overlying ectoderm to form the neural plate, which is a thick plate of pseudostratified, columnar neuroepithelial cells called neuroectoderm. Even before neurulation begins, the primordia of the three primary brain vesicles.
The caudal portion of the paramesonephric (Mullerian) ducts in the female fuse in the mid line to form the uterovaginal primordium erectile dysfunction drugs dosage 80 mg tadala black overnight delivery. The caudal portion of the paramesonephric (Mullerian) ducts in the female projects into the dorsal wall of the cloaca and induces the formation of the sinovaginal bulbs erectile dysfunction daily pill buy generic tadala black 80mg on-line. These fuse to form the solid vaginal plate, which later canalizes and develops into the inferior third of the vagina. Vestigial remnants of the mesonephric duct (called the appendix vesiculosa and Garner duct) may be found in the female. Vestigial remnants of mesonephric tubules (called the epoophoron and paroophoron) may be found in the female. Vestigial remnants of the paramesonephric duct (called the hydatid of Morgagni) may be found in the adult female. These structures are adjacent or continuous with one another and are generally positioned between the bladder and rectum. Uterine tubes: the uterine tube is divided into four regions: infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus, and the intramural segment. The fimbriae are delicate, finger-like projections that extend from the infundibulum toward the ovary. Neonatal 11 Hysterosalpingography is a fluoroscopy imaging study that assesses the patency of the uterus and uterine tubes. At term, the fundus may extend as high as the xiphoid process (vertebral level T9). The isthmus is part of the body and is the dividing line between the body of the uterus and the cervix. The cervix is divided into two portions: the supravaginal portion lies above the vaginal vault, and the vaginal portion protrudes into the vagina. The vast majority (96%) of ectopic pregnancies occur in the uterine tube, although they can also occur in the cervix, intramural segment, abdomen, or ovary. Vaginal bleeding, often accompanied by abdominal/pelvic pain, is the most common manifestations of an ectopic pregnancy. In addition to a pregnancy test to measure human chorionic gonadotropin, transvaginal ultrasound is used to assess the location of an ectopic pregnancy. As the vaginal portion of the cervix extends into the superior vagina, a circumferential recess is created. Continuous zones of the recess are called the anterior fornix, posterior fornix, and lateral fornix. Symptoms include pelvic pain, pressure, reproductive dysfunction, and uterine bleeding. Fibroids can be located in the uterine wall (intramural myomas), just deep to endometrium (submucosal myomas), at the serosal surface of uterus (subserosal myomas) or in the cervix (cervical myomas). Pelvic ultrasound is used to assess uterine fibroids location and characteristics. Squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma are two major histologic types of cervical cancer. Cervical cancer can begin in the cervix and invade adjacent structures, such as the uterus, vagina, and rectum, by direct extension. Metastasis through the lymphatic system can occur through pelvic or para-aortic lymph nodes first, before spreading. Cervical smear showing small-cell carcinoma cells demonstrating classic cytomorphology with salt-pepper chromatin. Of importance is the proximity of the ureter to the uterine artery, which must be ligated to remove the uterus. The ureter needs to be identified prior to ligation to minimize the risk of injury. Removal of the uterus can be partial (subtotal, leaves cervix), total (removes cervix and uterus) or radical (includes removal of superior vagina). The procedure is indicated for endometriosis, uterine fibroids, abnormal bleeding, carcinoma, and chronic pelvic pain. Abdominal hysterectomy Vaginal hysterectomy [1] Broad ligament: Uterus position is maintained by the broad ligament, which has three parts: mesometrium (attached along uterine body), mesovarium (attached to ovary), and mesosalpinx (attached to uterine tube). Although not a true ligament, this double layer of peritoneum drapes over the uterus, extends along the sides of the uterine body, and attaches to the pelvic walls.
Inferiorly erectile dysfunction medications otc proven 80 mg tadala black, the sac communicates with the nasolacrimal duct erectile dysfunction differential diagnosis tadala black 80 mg free shipping, which serves as a conduit to transport lacrimal fluid from the sac to the nasal cavity and, eventually, the nasopharynx. Eye Nasolacrimalduct this duct communicates with the nasal cavity through the inferior meatus. In the developing eye, an optic cup of neuroectoderm is surrounded by an embryonic connective tissue called mesenchyme. The answer is that the mesenchyme directly around the optic cup forms a vascular tunic called the choroid, and the outermost V. Orbit 353 As the neural plate folds (arrows), the neuroectoderm indents to form the optic sulci. Middle tunic Choroid Mesenchyme Outermost tunic Sciera Mesenchyme mesenchyme forms a fibrous tunic called the sclera. Consequently, the general feature of the adult eye is that it consists of three concentric tunics: the innermost tunic (optic cup; neuroectoderm), middle tunic choroid; mesenchyme), and the outermost tunic (sclera; mesenchyme). Embryology: At day 22, the eye begins to develop when the neural plate in the forebrain region. The optic vesicle grows toward the surface ectoderm and induces the formation of the lens placode. Optic cup development: At day 28, the optic vesicle invaginates to form a double-layered optic cup of neuroectoderm. The double-layered optic cup consists of an outer pigment layer and an inner neural layer. The optic cup gives rise to the retina, the epithelium of the ciliary body, and the epithelium of the iris. The inner neural layer of the optic cup gives rise to the inner neural layer of the retina. Head and Cranial Nerves Choroid Outer pigment layer Inner nuclear layer (a) Strama: the stroma of the ciliary body is derived from mesenchyme that is continuous with the choroid. The ciliary processes give rise to the suspensory fibers of the lens, which are attached to and suspend the lens. Two layers of columnar cells Keep in mind the three concentric tunics: the ciliary body and iris are formed from the middle tunic. The intraretinal space separates the outer pigment layer from the inner neural layer. Although the intraretinal space is obliterated in the adult, it remains a weakened area prone to retinal detachment. Ciliary muscle Suspensory fibers (a) Strama: the stroma of the iris is derived from mesenchyme that is continuous with the choroid. The hyaloid artery supplies the developing retina and the developing lens vesicle. The fully mature lens ceases to need a blood supply, so the portion of the hyaloid artery that crosses the vitreous body degenerates and leaves a remnant called the hyaloid canal. At week 7, the optic fissure seals and entraps the hyaloid artery and vein, which later become the central artery and vein of the retina. As the inner neural layer continues to proliferate, the increasing number of axons from the ganglion cell layer of the retina obliterate the intraretinal space. When a physician examines the eye with an ophthalmoscope, the blood vessels that are seen are small branches of the central artery of the retina. Orbit 355 Optic cup fil",/ Sciera is continuous with the dura mater around the optic nerve. These cross sections show how the hyaloid artery and vein become trapped in the center of the optic nerve as the optic fissure seals. Cornea development: the cornea develops from both surface ectoderm and mesenchyme that lies anterior to the anterior chamber and that is continuous with the sclera. The surface ectoderm forms upper and lower infoldings that eventually develop into the upper and lower eyelids (Recall that the space between the two layers of ectoderm is the conjunctiva! A portion of the surface ectoderm reflects over the mesenchyme that is continuous with the sclera.