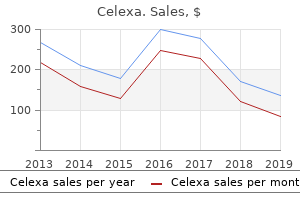
Celexa
"Discount 20mg celexa, ok05 0005 medications and flying".
By: T. Masil, MD
Co-Director, Midwestern University Arizona College of Osteopathic Medicine
If the patient has hypocalcemic seizures treatment yeast infection home generic 10 mg celexa mastercard, he or she should also be treated with 10 to 20 mL 10% calcium gluconate (0 medications restless leg syndrome order celexa 10mg without a prescription. Ethanol therapy should be initiated immediately if fomepizole (Antizol) is unavailable (see next paragraph). Ethanol should be administered intravenously (the oral route is less reliable) to produce a blood ethanol concentration of 100 to 150 mg/dL. The loading dose is 10 mL/kg of 10% ethanol intravenously, administered concomitantly with a maintenance dose of 10% ethanol of 1. The blood ethanol concentration should be measured hourly and the infusion rate should be adjusted to maintain a blood ethanol concentration of 100 to 150 mg/dL. Hemodialysis reduces the ethylene glycol half-life from 17 hours on ethanol therapy to 3 hours. Therapy (fomepizole and hemodialysis) should be continued until the serum ethylene glycol concentration is less than 10 mg/dL, the glycolate level is nondetectable (not readily available), the acidosis has cleared, there are no mental disturbances, the creatinine level is normal, and the urinary output is adequate. Disposition All patients who have ingested significant amounts of ethylene glycol (calculated level above 20 mg/dL), have a history of a toxic dose, or are symptomatic should be referred to the emergency department and admitted. If the serum ethylene glycol concentration cannot be obtained, the patient should be followed for 12 hours, with monitoring of the osmolal gap, acid-base parameters, and electrolytes to exclude development of metabolic acidosis with an anion gap. Hydrocarbons the lower the viscosity and surface tension of hydrocarbons or the greater the volatility, the greater the risk of aspiration. Toxicologic Classification and Toxic Mechanism All systemically absorbed hydrocarbons can lower the threshold of the myocardium to dysrhythmias produced by endogenous and exogenous catecholamines. A few aspirated drops are poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and produce no systemic toxicity by this route. Mineral seal oil (signal oil), found in furniture polishes, is a low-viscosity and low-volatility oil with minimum absorption that never warrants gastric decontamination. Aromatic hydrocarbons are six carbon ring structures that are absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract. Halogenated hydrocarbons are aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbons with one or more halogen substitutions (Cl, Br, Fl, or I). Ingestion of these substances may warrant gastric emptying with a small-bore nasogastric tube. Heavy hydrocarbons have high viscosity, low volatility, and minimal gastrointestinal absorption, so gastric decontamination is not necessary. Examples are asphalt (tar), machine oil, motor oil (lubricating oil, engine oil), home heating oil, and petroleum jelly (mineral oil). Liver and renal function should be monitored in cases of inhalation of aromatic hydrocarbons. Management Asymptomatic patients who ingested small amounts of aliphatic petroleum distillates can be followed at home by telephone for development of signs of aspiration (cough, wheezing, tachypnea, and dyspnea) for 4 to 6 hours. The victim must be removed from the environment, have oxygen administered, and receive respiratory support. Gastrointestinal decontamination is not advised in cases of hydrocarbon ingestion that usually do not cause systemic toxicity (aliphatic petroleum distillates, heavy hydrocarbons). In cases of ingestion of hydrocarbons that cause systemic toxicity in small amounts (aromatic hydrocarbons, halogenated hydrocarbons), the clinician should pass a small-bore nasogastric tube and aspirate if the ingestion was within 2 hours and if spontaneous vomiting has not occurred. Some toxicologists advocate ipecac-induced emesis under medical supervision instead of small-bore nasogastric gastric lavage; we do not. Patients with altered mental status should have their airway protected because of concern about aspiration. The use of activated charcoal has been suggested, but there are no scientific data as to effectiveness and it may produce vomiting. The symptomatic patient who is coughing, gagging, choking, or wheezing on arrival has probably aspirated.
Typically symptoms ms women buy discount celexa 40mg online, stage 3 to 4 pressure injuries start as a deep tissue injury that may then progress to the surface treatment skin cancer cheap 40 mg celexa visa. There is little evidence to suggest that a stage 4 pressure injury develops as a gradual progression from stage 1 to stage 4. Pathophysiology Differential Diagnosis Therapy Besides pressure injuries, other chronic skin ulcers are arterial ulcers, venous stasis ulcers, and diabetic ulcers: arterial ulcers occur in distal digits or over bony prominences, venous stasis ulcers occur on the lateral aspect of the lower leg in the setting of chronic edema, and diabetic ulcers occur in regions of callous formations. Traumatic injuries such as abrasions, skin tears, or burns are not pressure injuries; nor are surgical incision sites. Only pressure injuries are staged; never stage a wound that arises from a different etiology. Diagnosis Staging is done according to the National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel Pressure Injury Staging System: Stage 1: Nonblanchable erythema of intact skin. Color changes do not include purple or maroon discoloration; this indicates deep tissue injury. The wound bed is viable, pink or red, and moist, and may also present as an intact or ruptured serum-filled blister. Adipose (fat) is visible in the ulcer and granulation tissue and rolled skin edges are often present. Position the patient frequently at fixed intervals to relieve pressure over compromised areas. There is no evidence to suggest an optimal interval at which to reposition patients, although every 2 hours is recommended based on expert opinion. Advanced static support surfaces (mattress overlays and foam, gel, or air mattresses) rather than standardized hospital mattresses should be used to prevent pressure injuries in high-risk patients. Pressure injuries occur in sicker individuals in whom overall intake may be reduced by coexisting illness. Protein supplementation may improve outcomes in the treatment of pressure ulcers, as per current guidelines. However, a 2014 Cochrane review concluded that there is no clear evidence that nutritional interventions. There is no evidence to support the use of vitamin C or zinc to treat pressure injuries in patients who are not deficient in these nutrients. There is no difference in healing rates associated with supratherapeutic doses of vitamin C or zinc. If slough or eschar obscures the extent of tissue loss, then it is an unstageable pressure injury. Exposed or directly palpable fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage, or bone is in the ulcer. The extent of tissue damage within the ulcer cannot be determined because it is obscured by slough or eschar. Stable eschar (dry, adherent, intact, without erythema or fluctuance) on the heel or ischemic limb should not be softened or removed. Deep tissue injury: Persistent, nonblanchable, deep red, maroon, or purple discoloration. The wound may evolve rapidly to reveal the actual extent of injury or may resolve without tissue loss. If necrotic tissue, subcutaneous tissue, granulation tissue, fascia, muscle, or other underlying structure is visible, then it is a full-thickness pressure injury (unstageable or stage 3 or 4). Do not use deep tissue injury to describe vascular, traumatic, neuropathic, diabetic, or dermatologic conditions. The resultant pressure injury generally conforms to the pattern or shape of the device. Mucosal membrane pressure injury: Found on mucous membranes in patients with a history of a medical device in use at the location of the injury. The choice of a particular e dressing depends on the wound characteristics, such as amount of exudate, dead space, or wound infection. A hydrocolloid, foam, or other nonadherent dressing that promotes a moist wound environment should be used (Table 2). Document the presence of exudate, necrotic tissue, eschar, slough, undermining, and tunneling.
Clinically the lesions are located in reachable areas of the skin and can mimic any skin disease medications related to the lymphatic system order generic celexa online. After a diagnosis is made symptoms syphilis order celexa master card, the physician needs to discuss it with the patient in a nonjudgmental, empathetic way. Supportive dermatologic care should be provided for wounds, and the patient should be referred for psychological evaluation. Antidepressant and antianxiety medications can help to treat underlying depression and anxiety. Neurotic Excoriation and Acne Excoriee Patients with acne excorie create excoriations by repetitive e scratching or skin picking. However, patients may inflict excoriations without the trigger of any skin pathology because the condition is a psychological process with dermatologic manifestations. Patients usually have ritualistic picking habits and report building of tension before picking and release of tension after picking. In this case a pruritus workup to rule out causes such as iron deficiency and gluten sensitivity is important. For any self-injurious behavior, patients must be screened for underlying psychopathologies such as personality disorders. However, in many patients, the behavior results from an impulse control problem or is a compulsive act in response to stressors or simply part of excessive grooming. In addition to treatment of the underlying psychopathology, a combination of behavioral therapy and medications that help with impulsive behavior is used. Motivational interviewing could help patients explore and resolve their ambivalence and participate fully in treatment. Patients need to replace picking with other relaxing behaviors that are not harmful to skin, such as breathing relaxation or use of stress balls, Chinese exercise balls, Greek worry beads, stuffed animals, or Silly Putty. Another therapy model for skin pickers is to consider chronic picking as an addiction and apply addiction therapy models to picking. If this is insufficient, the physician can add antianxiety medications, such as buspirone (BuSpar), and some of the newer anticonvulsant medications, such as lamotrigine (Lamictal). In the case of severe picking, such as in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome, multiple infections and scarring can occur. Naltrexone (ReVia), as well as the occasional use of neuroleptics such as aripiprazole (Abilify) and quetiapine (Seroquel), can help to break the cycle of scratching and give time for behavioral treatments to take effect. Once the patient has improved, medications can be tapered and discontinued, but he or she may need to stay on a maintenance dose of medications. The new lesions are usually red and inflamed, whereas the old lesions are pigmented. Lesions are mostly located on the extensor surface of limbs, but they can also be located on the face, scalp, and trunk. Histopathology evaluation shows lichenification, a dense infiltrate in dermis and neural hyperplasia, and proliferation of Schwann cells. A good history and physical examination should include a medication history because pruritus is a side effect of many classes of medications. In chronic cases laboratory testing needs to be repeated at regular intervals since in some diseases itch may be the first sign and other symptoms may take some time to appear. Potent topical steroids such as betamethasone dipropionate (Diprosone) ointment under occlusion or intralesional injection of steroids such as triamcinolone acetonide (Kenalog-10) may be successful, but they have the risk of skin atrophy. In some cases topical vitamin D3 derivative (calcipotriene [Calcitrene]1) may help. Thalidomide (Thalomid)1 200 to 400 mg in different studies has been an effective treatment for prurigo nodularis. Thalidomide is difficult to obtain because of its teratogenicity, and it does have serious side effects such as irreversible peripheral neuropathies. A similar compound, lenalidomide (Revlimid)1 5 mg/day, with less potential for peripheral neuropathy, was effective in one case of a patient resistant to all the other treatments. Other synthetic retinoids such as acitretin (Soriatane)1 may be considered in severe resistant cases. Patients need to have periodic cardiovascular evaluations if they use tricyclic medications long term.
A number of prenatal and intrapartum factors are associated with a higher chance that the infant will have a delay in transition and require resuscitation (Table 1) medications vs medicine discount celexa 40 mg. However treatment 100 blocked carotid artery best purchase for celexa, some infants with no risk factors need resuscitation; therefore, preparations for neonatal resuscitation should be made during all deliveries. The changes that occur in the transition from fetus to newborn are unmatched in any other time of life. Most newborns manage to make this transition on their own, but about 10% require some assistance. Risk Factors for Newborn Resuscitation Reaction to Hypoxia and Asphyxia the environment of the fetus differs greatly from that of the infant after birth. The fetus depends on receiving oxygen and nutrients from the mother through the placental circulation. The fetus experiences relative hypoxia and almost constant body temperature in the amniotic fluid. The fetal lungs are filled with fluid and do not participate in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood from the mother enters the fetus by means of the placenta through the umbilical vein. Most of this oxygenated blood bypasses the liver through the ductus venosus and enters the inferior vena cava. On entering the right atrium, this oxygenated blood is directed toward the patent foramen ovale into the left atrium, bypassing the fetal lungs. Fetal blood also passes through the right atrium into the right ventricle and then into the pulmonary artery. The vascular resistance and blood pressure of the pulmonary vessels in the fetal lung are higher than in the aorta and systemic circulation; most of the blood is therefore shunted away from the lungs through the ductus arteriosus into the ascending aorta. Only a small amount of fetal blood passes through the lungs to the left atrium and then to the left ventricle. The umbilical arteries branch off from the internal iliac arteries and return fetal blood to the placenta. The functional organ for gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the fetus is the placenta. At birth, the newborn is no longer connected to the placenta, and the lungs become the only source of oxygen. The first breaths of the infant cause the fluid in the lung alveoli to be replaced with air. This increases the vascular resistance and blood pressure of the systemic circulation. As the oxygen level in the alveoli increases, the blood vessels in the lung start to relax, decreasing pulmonary vascular resistance. Blood in the pulmonary artery travels toward the lung and away from the ductus arteriosus because the blood pressure in the systemic circulation is higher than that in the pulmonary circulation. Although the initial steps in this transition occur within a few minutes of birth, the entire process may not be completed for several hours to days. The ductus venosus, foramen ovale, and ductus arteriosus remain potentially patent and do not completely involute for days or weeks. The infant may not breathe adequately, in which case the lung fluid is not forced out of the alveoli. The process of leaving the warm, dark, and liquid environment in utero is replaced by cold air, dryness, and bright lights. Drying the infant with towels and wiping the mouth and nose are all the assistance that most newborns require. The end result of any mechanism that delays transition is a period of hypoxia for the fetus or newborn infant. Laboratory studies have shown that the first sign of oxygen deprivation in the newborn is a change in the breathing pattern. After an initial period of rapid breathing attempts, cessation of breathing occurs.