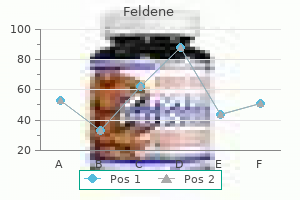
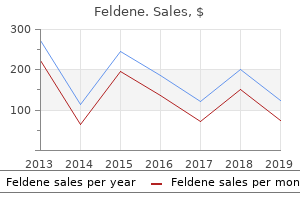
Feldene
"Order feldene 20mg on-line, arthritis treatment legs".
By: Q. Bradley, M.A.S., M.D.
Clinical Director, Albany Medical College
Note that this conjugal transfer is under the control of the genes of the R plasmid and not of the F (fertility) plasmid arthritis in fingers food generic feldene 20mg free shipping, which governs the transfer of the bacterial chromosome (see Chapter 4) arthritis in lower back vertebrae buy feldene. R factors exist in two broad size categories: large plasmids, with molecular weights of about 60 million, and small ones, with molecular weights of about 10 million. In addition to conveying antibiotic resistance, R factors impart two other traits: (1) resistance to metal ions. In addition to producing drug resistance, R factors have two very important properties: (1) they can replicate. For example staphylococcal penicillinase is inducible by penicillin and is secreted into the medium. In contrast, some -lactamases produced by several gram-negative rods are constitutively produced, are located in the periplasmic space near the peptidoglycan, and are not secreted into the medium. The -lactamases produced by various gram-negative rods have different specificities: some are more active against cephalosporins, others against penicillins. Clavulanic acid, tazobactam, sulbactam, and avibactam are penicillin analogues that bind strongly to -lactamases and inactivate them. However, these bacteria remain sensitive to combinations such as piperacillin/tazobactam. This plasmid confers high-level resistance to many antibiotics and has spread from Klebsiella to other member of the Enterobacteriaceae. These changes account for both the low-level and high-level resistance exhibited by S. The relative resistance of Enterococcus faecalis to penicillins may be due to altered penicillin-binding proteins. High-level resistance is due to the presence of a plasmid coding for penicillinase. This is attributed to a failure of activation of the autolytic enzymes, murein hydrolases, which degrade the peptidoglycan. Carbapenems-Resistance to carbapenems, such as imipenem, is caused by carbapenemases that degrade the -lactam ring. This enzyme endows the organism with resistance to penicillins and cephalosporins as well. Carbapenemases are produced by many enteric gram-negative rods, especially Klebsiella, Escherichia, and Pseudomonas. Carbapenem-resistant strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae are an important cause of hospital-acquired infections and are resistant to almost all known antibiotics. Vancomycin-Resistance to vancomycin is caused by a change in the peptide component of peptidoglycan from d-alanyl-d-alanine, which is the normal binding site for vancomycin, to d-alanine- d-lactate, to which the drug does not bind. Of the four gene loci mediating vancomycin resistance, VanA is the most important. It is carried by a transposon on a plasmid and provides high-level resistance to both vancomycin and teicoplanin. Aminoglycosides-Resistance to aminoglycosides occurs by three mechanisms: (1) modification of the drugs by plasmid encoded phosphorylating, adenylylating, and acetylating enzymes (the most important mechanism); (2) chromosomal mutation. Tetracyclines-Resistance to tetracyclines is the result of failure of the drug to reach an inhibitory concentration inside the bacteria. This is due to plasmid-encoded processes that either reduce the uptake of the drug or enhance its transport out of the cell. Chloramphenicol-Resistance to chloramphenicol is due to a plasmid-encoded acetyltransferase that acetylates the drug, thus inactivating it. An efflux pump that reduces the concentration of erythromycin within the bacterium causes low-level resistance to the drug. An esterase produced primarily by enteric gramnegative rods cleaves the macrolide ring, which inactivates the drug. Sulfonamides-Resistance to sulfonamides is mediated primarily by two mechanisms: (1) a plasmid-encoded transport system that actively exports the drug out of the cell, and (2) a chromosomal mutation in the gene coding for the target enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, which reduces the binding affinity of the drug. Trimethoprim-Resistance to trimethoprim is due primarily to mutations in the chromosomal gene that encodes dihydrofolate reductase, the enzyme that reduces dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate.
Different doses of palonosetron for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in children undergoing strabismus surgery early onset arthritis in dogs purchase feldene online pills. Early vs late intraoperative administration of tropisetron for the prevention of nausea and vomiting in children undergoing tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy arthritis in fingers cure buy feldene 20mg visa. Dexamethasone for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a quantitative systematic review. A comparison between dexamethasone and methylprednisolone for vomiting prophylaxis after tonsillectomy in inpatient children: a randomized trial. Dexamethasone and risk of nausea and vomiting and postoperative bleeding after tonsillectomy in children: a randomized trial. The effects of droperidol and ondansetron on dispersion of myocardial repolarization in children. Information for Healthcare Professionals: Intravenous promethazine and severe tissue injury, including gangrene. Metaanalysis of acustimulation effects on postoperative nausea and vomiting in children. Effect of systemic steroids on post-tonsillectomy bleeding and reinterventions: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. A solid understanding of the etiology, biochemical pathways, risk factors and the available treatment modalities is essential in order to provide excellent anesthesia care to both the ambulatory and inpatient surgical population. A multimodal approach to the problem, utilizing a validated risk assessment model, combined with risk-reducing anesthetic techniques and prophylaxis/treatment with medications of different pharmacologic classes, provides the clinician with the proper tools to manage the at-risk patient. Modifiable anesthetic risk factors include exposure to volatile anesthetics and nitrous oxide, as well as postoperative opioid use[7]. A volatile-free technique, utilizing propofol for anesthetic maintenance, has been demonstrated to reduce baseline risk by 19%[8]. Omitting nitrous oxide in favor of nitrogen as a carrier gas yields a risk reduction of 12%[8]. The data are based on all 5,161 randomly assigned patients who completed the study, with the exceptions of the data for carrier gas (4,277 patients) and for remifentanil versus fentanyl (4,789 patients). Other factors to consider are surgical/medical implications of vomiting, including increases in intracranial pressure, and increases in intra-abdominal pressure after hernia repair and esophageal surgery[2]. Even at high doses administered during cardiac surgery, 1 mg/kg dexamethasone has not been shown to impair wound healing[34]. The hyperglycemic effects of dexamethasone 8 mg given during major noncardiac surgery was shown to be limited, and less in diabetics than nondiabetics[35]. Anticholinergics Scopolamine is a belladonna alkaloid, which possesses centrally acting anticholinergic effects, producing sedation and antiemetic effects[36]. Haloperidol Haloperidol is a butyrophenone with a high affinity for the dopamine D2 receptor[44]. As is the case with droperidol, its antinausea effects are more pronounced than its antivomiting effects[44]. Of the almost 1,400 patients receiving haloperidol in one meta-analysis, there were no reported cases of arrhythmias, torsades or sudden cardiac death[44]. Promethazine can cause sedation, lethargy, dry mouth, urinary retention and extrapyramidal effects. Promethazine appears to also have opioid-sparing effects, which might contribute to its antiemetic effects[50]. The timing of administration, either pre- or postoperatively, did not significantly alter its efficacy. Patients taking ondansetron were twice as likely to experience vomiting during the first 24 h when compared with those taking aprepitant[55]. The most common side effects of aprepitant are pyrexia, constipation, headache and bradycardia[55]. Metoclopramide Metoclopramide is a dopamine D2 antagonist that possesses both central and peripheral serotonergic antagonism. When compared with droperidol and placebo, patients who received ephedrine had lower sedation scores, with a trend towards shorter time to discharge[59].
Influence of peripheral nerve stimulation on human motor cortical excitability in patients with ventrolateral thalamic lesion arthritis research and therapy proven feldene 20 mg. Dissociated effects of diazepam and lorazepam on short-latency afferent inhibition arthritis pain ulcerative colitis order feldene online pills. Muscarinic receptor blockade has differential effects on the excitability of intracortical circuits in the human motor cortex. Short latency inhibition of human hand motor cortex by somatosensory input from the hand. Silent period to transcranial magnetic stimulation: construction and properties of stimulus-response curves in healthy volunteers. Spinal motor neuron excitability during the silent period after cortical stimulation. Spinal and supraspinal mechanisms contribute to the silent period in the contracting soleus muscle after transcranial magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Effects of diazepam, baclofen and thiopental on the silent period evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation in humans. Interactions between long latency afferent inhibition and interhemispheric inhibitions in the human motor cortex. Impaired crossed facilitation of the corticospinal pathway after cervical spinal cord injury. Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on recov ery of function after spinal cord injury. Determinants of the induction of cortical plasticity by noninvasive brain stimulation in healthy subjects. Modulation of cortical excitability induced by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: influence of timing and geometrical parameters and underlying mechanisms. Magnetic brain stimulation can improve clinical outcome in incomplete spinal cord injured patients. Action of 5Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on sensory, motor and autonomic function in human spinal cord injury. Motor and gait improvement in patients with incomplete spinal cord injury induced by high-frequen cy repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Chronic enhance ment of serotonin facilitates excitatory transcranial direct current stimulation-in duced neuroplasticity. Intensity dependent effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on corticospinal excitability in chronic spinal cord injury. Paired associative stimulation increases motor cortex excitability more effectively than theta-burst stimulation. Paired associative stimulation induces change in presynaptic inhibition of Ia terminals in wrist flexors in humans. Motor recovery after spinal cord injury enhanced by strength ening corticospinal synaptic transmission. The effects of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation and patterned electrical stimulation on spinal inhibitory interneurons and motor function in patients with spinal cord injury. H reflex modulation by transcranial magnetic stimulation in spinal cord injury subjects after gait training with electromechanical systems. Short-term cortical plasticity associated with feedback-error learning after locomotor training in a patient with incomplete spinal cord injury. Increases in corticospinal tract function by treadmill training after incomplete spinal cord injury. Improvements in hand function in adults with chronic tetraplegia following a multiday 10-Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation intervention combined with repetitive task practice. Exercise builds brain health: key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Capitalizing on cortical plasticity: influence of physical activity on cognition and brain function. Long-term motor training induced changes in regional cerebral blood flow in both task and resting states. Prolonged exercise induces angiogenesis and increases cerebral blood volume in primary motor cortex of the rat. Impact of exercise on neuroplasticity-related proteins in spinal cord injured humans.
Syndromes
- Breathing - rapid
- Nerve damage due to pelvic surgery
- Are severe
- Periods that occur every 21 days or sooner
- Clean coffee or tea
- Fever
- Echocardiography
- Breathing difficulty
Management of pneumonia in neonates follows the same principles as neonatal sepsis because the syndrome is difficult to distinguish clinically from sepsis arthritis relief gloves reviews generic feldene 20mg overnight delivery. Trials are underway in Nigeria arthritis vinegar discount feldene online master card, Kenya, Democratic Republic of Congo, and Pakistan evaluating the efficacy of therapy in young infants who present with fast breathing as their sole clinical sign of illness. The investigators enrolled 4029 infants over a period of 3 years and compared them with 4878 matched control subjects. Four pathogens were significantly associated with moderate-to-severe diarrhea: rotavirus, Cryptosporidium, Shigella, and enterotoxigenic E. Rotavirus was the most common agent, with an incidence of 7 episodes per 100 child-years during infancy. Black and colleagues82 performed community studies of diarrheal epidemiology and etiology in a periurban community in Peru. Mahmud and colleagues83 prospectively followed a cohort of 1476 Pakistani newborns from four different communities. Eighteen percent of infants evaluated in the first month of life (180/1028) had diarrhea. Aye and associates84 studied diarrheal morbidity in neonates born at the largest maternity hospital in Rangoon, Myanmar. Diarrhea was a significant problem, with rates of 7 cases per 1000 live births for infants born vaginally and 50 per 1000 for infants delivered by cesarean section. These differences were attributed to the following: infants born by cesarean section remained hospitalized longer, were handled more by staff and less by their own mothers, and were less likely to be exclusively breastfed. Rotavirus is one of the most important causes of diarrhea among infants and children worldwide, occurring most commonly in infants aged 3 months to 2 years. Cicirello and associates89 screened 169 newborns at six hospitals in Delhi, India and found a rotavirus prevalence of 26%. More recently, Ramani and associates91 found the prevalence of rotavirus among neonates with gastrointestinal symptoms to be as high as 55% in a tertiary hospital in southern India. Gladstone and colleagues92 studied a cohort of 373 children in India and found 56% were infected with rotavirus by 6 months of age. The high prevalence of neonatal infections in India (and perhaps in other low-resource country settings) could lead to priming of the immune system and have implications for vaccine efficacy. Several of the communitybased studies reviewed earlier present data on diarrhea as a cause of neonatal death. In 9 of the 10 studies, 70 of 2673 neonatal deaths (3%) were attributed to diarrhea. Furthermore, prompt diagnosis and antimicrobial therapy have decreased morbidity and mortality if omphalitis develops. The umbilical stump is rapidly colonized by bacteria from the maternal genital tract and from the environment. This colonized necrotic tissue, in close proximity to umbilical vessels, provides microbial pathogens with direct access to the bloodstream. Thus invasion of pathogens via the umbilicus may occur with or without the presence of signs of omphalitis, such as redness, pus discharge, swelling, or foul odor. Infants who present with abdominal wall cellulitis or necrotizing fasciitis have a high incidence of associated bacteremia (often polymicrobial) and a high mortality rate. A key risk factor for development of omphalitis in the community included topical applications of potentially unclean substances. Hand washing by the birth attendant with soap provided in the clean delivery kit, consistent hand washing by the mother, and the practice of skin-to-skin care reduced the risk of omphalitis. Gram-positive organisms were isolated from 68% of umbilical cultures; gram-negative organisms were isolated from 60%, and multiple organisms were cultured in 28% of patients. Aerobic bacteria were isolated from 70%, and anaerobic bacteria were isolated from 30%. Sixty percent of the aerobic isolates were gram-positive organisms, and polymicrobial isolates were common.