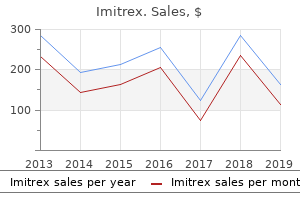
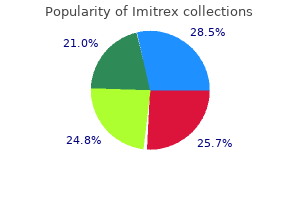
Imitrex
"Buy imitrex 50mg low cost, esophageal spasms xanax".
By: U. Zapotek, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, University of Texas Medical Branch School of Medicine
Enrichment of the lung microbiome with gut bacteria in sepsis and the acute respiratory distress syndrome spasms of the larynx generic imitrex 100mg on-line. Pathogen recognition and toll-like receptor targeted therapeutics in innate immune cells muscle relaxant drugs z purchase line imitrex. Sepsis occurs when host defense mediators released into the circulation to combat the infection elicit systemic inflammatory responses throughout the body [1]. About 20% of patients with sepsis die within the hospital, and severe sepsis leads to a mortality rate of approximately 40% [3, 4]. Hemorrhage is due to consumption and subsequent depletion of coagulation factors and platelets, caused by ongoing activation of the hemostatic system [10]. Levi Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome, typically observed during fulminant meningococcal septicemia, although many other microorganisms may cause this clinical situation as well [11]. Commonly, platelet count drops in the first 4 days following admission to the hospital [16]. The severity of sepsis correlates markedly with the decrease in platelet count [17]. Critical factors that cause thrombocytopenia in sepsis are decreased platelet production, enhanced consumption, obliteration, or sequestration in the spleen. Platelet consumption is presumably also significant in sepsis, due to platelet activation secondary to continuous formation of thrombin. Platelet activation, consumption, and destruction take place at the endothelial surface as a result of the widespread endothelial cell-platelet interaction in sepsis, although the extent may differ between various vascular beds of different organs [20]. Other coagulation assay changes include high fibrin degradation products (in more than 95% of patients with sepsis) [22, 23] and low levels of physiological anticoagulants, such as antithrombin and protein C (90% of sepsis patients) [23, 24]. It is clear that various mechanisms in the coagulation system act simultaneously toward a prohemostatic state. Apparently the most important factors that mediate this derangement of the coagulation system during sepsis are cytokines. Ample evidence indicates an extensive cross talk between inflammation and coagulation, where besides inflammation-induced coagulation activation, coagulation also markedly influences inflammatory activity. Expression of tissue factor in mononuclear cells and subsequent exposure to blood results in thrombin generation followed by fibrinogen to fibrin conversion. Simultaneously, platelet vessel wall interaction and activation of platelets contribute to (micro)vascular clot formation. Levi Gram-negative sepsis, ex vivo tissue factor expression on monocytes of patients was demonstrated [30]. An alternative source of tissue factor may be its localization on other blood cells [32], although it is not likely that these cells themselves produce tissue factor in substantial quantities [33]. Based on the assessment of transfer of tissue factor from mononuclear cells to activated platelets in an ex vivo perfusion setting, it was postulated that this "blood-borne" tissue factor is shuttled between cells through microparticles [34]. Platelets have a central role in the development of coagulation abnormalities in sepsis. Platelets can be triggered directly by pro-inflammatory mediators, such as plateletactivating factor [35]. Activation of platelets may also stimulate fibrin formation by alternative mechanism. The expression of P-selectin on the platelet membrane not only mediates the adherence of platelets to leukocytes and endothelial cells but also enhances the expression of tissue factor on monocytes [36]. P-selectin can be shed from the surface of platelet membrane, and soluble P-selectin levels are indeed increased during systemic inflammation [36]. Due to a combination of impaired synthesis, ongoing consumption and proteolytic degradation. In addition, at the time of the greatest activation of coagulation in sepsis, endogenous fibrinolysis is largely turned off. Most proinflammatory cytokines have been demonstrated to initiate coagulation activation 4 the Coagulation System in Sepsis 49 in vitro. In sepsis high levels of cytokines can be found in the circulation of affected patients and investigational infection or experimental endotoxemia results in the transient increase in plasma levels of these cytokines [27]. Coagulation factors and anticoagulant proteins do not only play a role in hemostatic activation but also interact with specific cell receptors leading to activation of signaling pathways.
While so-called low-dose hydrocortisone may help to restore responsiveness to vasoconstrictive substances and shorten shock duration spasms in your sleep purchase imitrex on line, their impact on outcome remains controversial muscle relaxant education generic imitrex 100 mg online. The recommended hydrocortisone dose is 200 mg per day, eventually as a continuous infusion to improve glycemic control, and it is suggested by the Surviving Sepsis Campaign as a weak recommendation, with low quality of evidence [27]. Two ongoing large-scale double-blind randomized trials will provide new information in close future and may clarify these controversies on the use of hydrocortisone in septic shock. Conclusions Prompt correction of hypotension seems desirable as both severity and duration of hypotension are associated with a poor outcome. Norepinephrine, an alphaadrenergic agent, is considered as first-line vasopressor agent. When the patient fails to respond to norepinephrine, alternative agents acting on different receptors should be considered as second-line agents rather than adding another adrenergic agent. Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: for the Third International Consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). Cytokine-mediated downregulation of vasopressin V(1A) receptors during acute endotoxemia in rats. Impaired pressor sensitivity to noradrenaline in septic shock patients with and without impaired adrenal function reserve. Increasing mean arterial blood pressure in sepsis: effects on fluid balance, vasopressor load and renal function. The significance of non-sustained hypotension in emergency department patients with sepsis. Flow redistribution during progressive hemorrhage is a determinent of critical O2 delivery. Early-phase cumulative hypotension duration and severe-stage progression in oliguric acute kidney injury with and without sepsis: an observational study. Dobutamine increases cerebral blood flow velocity and jugular bulb hemoglobin saturation. Apoptosis of neurons in cardiovascular autonomic centres triggered by inducible nitric oxide synthase after death from septic shock. Microcirculatory alterations in patients with severe sepsis: impact of time of assessment and relationship with outcome. Norepinephrine increases cardiac preload and reduces preload dependency assessed by passive leg raising in septic shock patients. Restoring arterial pressure with norepinephrine improves muscle tissue oxygenation assessed by near-infrared spectroscopy in severely hypotensive septic patients. Effects of dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine on the splanchnic circulation in septic shock: which is best Norepinephrine plus dobutamine versus epinephrine alone for management of septic shock: a randomised trial. For many patients, the simultaneous or sequential failure of multiple organ systems triggered by the infection poses a greater threat to life and health than the primary infection. Multiple scores exist [8], with most rating pulmonary, cardiovascular, and renal function and many also rating neurologic, hepatic, and hematologic function (Table 10. Scoring systems mainly describe the extent of organ dysfunction rather than predict patient outcomes [9]. Nevertheless, and regardless of the specific criteria, the number of organ failures predicts mortality [10, 11]. Brown a factor of six if the biological-but not the adoptive-parent died early from infection [30]. Similarly, familial risk of influenza mortality appears independent of viral factors or shared environment [32]. Pulmonary failure was most common (75%), followed by cardiovascular (59%) and renal (40%). Early descriptions emphasized a characteristic sequence of organ failures, beginning with respiratory and progressing to hepatic, neurologic, and cardiac failure [2, 4, 36], but later studies deemphasized this concept. Relevant pathways include microvascular hypoperfusion, direct cell injury, inflammation, and cell hibernation/stunning [38]. Clusters were not synonymous with sepsis etiology, preexisting conditions, or sepsis 10 Management of Multiorgan Failure in Sepsis 143 severity but nevertheless predicted distinct mortality patterns. Meanwhile, the leukocyte transcriptome displays two distinct "sepsis response signatures," one of which is characterized by immune tolerance, T cell "exhaustion," and higher mortality [41]. Importantly, the host response to infection behaves as a complex nonlinear system [42]. So far, none have clear efficacy, even when restricted to biomarker-identified subgroups.
The activation of this system leads to vasoconstriction muscle relaxant gabapentin buy imitrex 100 mg on line, plasma volume expansion spasms after hysterectomy buy imitrex 50mg with mastercard, activation of the sympathetic nervous system, and increased blood pressures. The interaction between the fetal antigens and maternal immune cells allows immune tolerance to be established for normal placentation to occur. This association was recently reproduced in Chinese Han [31] and sub-Saharan [32] populations. Therefore, genetic studies examining genes involved in the oxidative stress pathway. Nevertheless, more individual studies actually show null associations of these genes, compared to those that do [25]. Genome-wide linkage mapping or positional cloning studies are performed using family pedigrees to ascertain, without bias, any genetic loci that are associated with the condition. The entire genome is first scanned in a process termed "chromosome walking" to identify and localize disease susceptibility loci to specific chromosomal regions. These regions are then subjected to further genetic investigation to identify plausible candidate genes. Table 2 Genome-wide linkage and association studies performed in the study of preeclampsia Population American Australian Australian Study type Association Linkage Linkage Sample size 293 unrelated individuals 15 families 26 families 34 families 34 families 34 families 34 families 34 families 74 families 74 families 1078 unrelated individuals 74 families and 1095 unrelated individuals 35 families 67 families 24 families 24 families 15 families 248 unrelated individuals 15 families Study authors Zhao et al. All loci contain regions for maternal susceptibility, with the exception of the fetal 18q21 susceptibility locus. Modified from Adler [70] A summary of the susceptibility loci identified thus far and their chromosomal locations is presented in. A potential linkage at the 7q36 locus was also demonstrated in the Australian/New Zealand and Icelandic population linkage analyses [55, 67]. The lack of replication between these early studies as explained by Harrison et al. A subsequent reanalysis of the original Australian/New Zealand scan, using an alternative variance component-based linkage approach, showed novel susceptibility loci on chromosomes 5q and 13q [14]. An additional case-control analysis in the Finnish population demonstrated a nominal association at the 2p13 locus [64]. A meta-analysis of these multiple population genome scans confirmed linkage with seven of the loci and revealed an additional six novel loci [69]. These studies show further associations with the 2q14 locus in an Australian/New Zealand cohort [47] and the 19q31. Hence, to test for imprinting effects, the Dutch group examined gene expression in androgenetic placentas, where all genes are derived solely from the father. Another issue is that populations will have different genetic backgrounds and likely have a diverse range of causal gene variants, thus lowering study reproducibility of a single causal gene variant. Yet another confounder is that most of the earlier studies were inadequately powered with small sample sizes, which results in more false positives. Effect sizes of causal gene variants are also likely to be small, further reducing the ability of past studies, which are designed to identify larger effect sizes, to detect them. While the use of meta-analyses may improve statistical power by combining past studies, they are reliant on the quality of the original studies. Activin A and its related receptors belong to the transforming growth factor -family [88], and are ubiquitously expressed throughout the body, where they mediate numerous cellular functions such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis [89]. To identify novel interactions and possible functions of susceptibility genes, and prioritize efforts for future functional studies, we previously pursued a novel integrative bioinformatics approach based on transcriptome profiling [94]. Genetic Approaches in Preeclampsia enzymes at 15 weeks gestation in nulliparous women who subsequently develop preeclampsia. Accessed 2015 Wang Q, Wang G, Guo C, Cao X, An L, Du M, Qiu Y, Yang Y, Wang Y, Wang S, Wang X, Ma X (2015) Single nucleotide polymorphisms near the inhibin beta B gene on 2q14 are associated with preeclampsia in Han Chinese women. Women who develop hypertensive disorders during pregnancy are considered to have "failed" the cardiovascular stress test of pregnancy and likely represent a subpopulation with inadequate cardiovascular accommodation. Preeclampsia is a serious complication with a myriad of manifestations in both mother and offspring. This pregnancy syndrome is a polygenic disease and has now been linked to a greater incidence of cardiovascular disease. Moreover, offsprings born to preeclamptic mothers exhibit an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and mental disorders during adulthood.
Therefore muscle relaxant 5658 generic 50 mg imitrex, once the decision has been made to remove the device spasms throughout my body discount 25 mg imitrex overnight delivery, cultures of the pocket tissue, deep pocket swab, and device surface swab should be obtained at the time of extraction. In the case of pocket site infections, culture of tissue from the pocket has a higher yield than swabs from the pocket site [48]. Also, lead tip cultures are not always reliable in the presence of a pocket infection as lead tips can potentially get contaminated during extraction through an infected pocket environment [49]. Sonication of the extracted device to disrupt biofilm on the device surfaces can improve the microbiological diagnosis of infection. In the infected group, significant bacterial growth was observed in 54 % of sonicate fluids, significantly greater than the sensitivities of pocket swab (20 %), device swab (9 %), or tissue (9 %) culture. Of note, majority of patients had received antibiotics prior to device removal in this study. Therefore, sonication may be the only way to confirm lead infection in patients who have positive blood cultures but no signs of pocket infection and no lead vegetations noted on echocardiography. Management No randomized clinical trials have been conducted to compare medical management only versus device removal along with antimicrobial therapy. Overall treatment failure (death, infection recurrence) was more common in cases with device retention (52 %) versus complete device removal (25 %). Infected device removal should be done if the patient is hemodynamically stable to tolerate lead extraction procedure. However, a plan on how the patient will be "bridged" prior to re-implantation should be in place. Empiric gram-negative coverage with an anti-pseudomonas agent may also be considered in patients who present with severe sepsis or shock. A antimicrobial therapy can then be modified on the basis of culture and in-vitro susceptibility data as they become available. If the cultured organism is oxacillin susceptible and the patient does not have a beta lactam allergy, then vancomycin can be discontinued and cefazolin or nafcillin inititated. For gram negative and other organisms the therapy needs to be modified accordingly. In patients with prosthetic valve involvement, gentamicin for first 2 weeks of therapy and rifampin for the entire duration of therapy should be added to the regimen if infection is caused by staphylococci. There are limited data looking at the optimal duration of antibiotic therapy in this patient population. It is generally recommended that the patient should be treated for at least 2 weeks after removal of the infected cardiac device. The antimicrobial therapy should also be prolonged if the patient has evidence of valvular endocarditis, osteomyelitis or septic emboli. Lead Extraction Extraction of infected leads is a procedure that electrophysiologists and cardiac surgeons are encountering with a higher frequency in their practice today. However, leads that have been in place for longer periods of time tend to develop a fibrotic encasement and their removal is more complex. Attempts to remove these leads using stylus and manual traction alone can result in lead breakage, leftover lead fragments and potential damage to the heart. These older leads are now removed using extraction dilators and power sheaths [30]. These power sheaths employ a radio-frequency probe or laser, attached to the tip of the sheath that is threaded transvenously over the lead. This helps in breaking scar tissue and enables subsequent removal of the lead [59, 60]. Regardless of equipment used, lead extraction is an intricate procedure that can be associated with serious complications such as bleeding, stroke, pulmonary embolism and even death [59, 60]. Complicated device removal is associated with an increase in 30-day patient mortality [52, 56]. However, the benefit of device removal outweighs the risks associated with retention of device in most circumstances. As power sheaths are advanced over the leads, vegetations attached to lead break off and embolize to the pulmonary vasculature. In our experience, most infected leads can be safely removed percutaneously even if the vegetation size is up to 2 cm [12]. Few patients may experience transient hypotension during the procedure or post-operatively but clinically significant pulmonary embolism is rare.