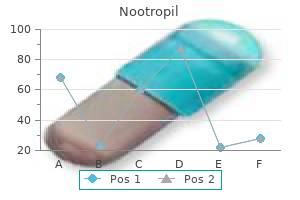
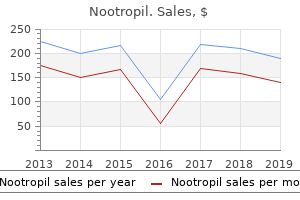
Nootropil
"Buy discount nootropil 800 mg on-line, symptoms indigestion".
By: O. Baldar, M.A., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
In those cases treatment nail fungus buy generic nootropil on line, an ileostomy is usually required because there is a high chance that if a new pouch is created treatment 20 initiative order nootropil 800mg amex, similar problems will occur again. They worry that, after going to all of the trouble and taking on the pain and risk of surgery, they might be back at "square one" within a year or two of having undergone surgery. When surgery is finally carried out, this can lead to increased infections and complications and slower recovery times. This may lead to the need for multiple operations and removal of additional intestinal segments at each operation. This produces symptoms of pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting after meals and can even lead to bowel obstruction. Small intestinal resections may also be required when a fistula or an abscess has arisen from an affected segment of intestine or when symptoms of active inflammation in the small intestine (abdominal cramping, diarrhea, weight loss) do not respond to drug therapies. This is called an ileocecal resection: the last part of the ileum and the first part of the colon are taken out together as a single piece of intestine. Ultimately, this can result in the removal of so much intestine that it leaves patients unable to keep themselves nourished and to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance through the intake of food and liquids. Because the diseased bowel and associated narrowing usually extends right up to the junction between the small and large intestine (ileocecal valve), it is technically impossible for the surgeon to remove just the small intestine, making it necessary to remove the ileocecal valve and an adjacent portion of the large intestine. The amount of large intestine resected is determined by whether or not it, too, is affected. Small Intestinal Resection When there is a normal segment of small intestine between the lowermost extent of the affected small intestine and the ileocecal valve, it is technically possible to remove only the affected segment of small intestine and not remove any of the large intestine. Anastomosis In all of these operations, the removal of a segment of intestine leaves two unattached, or open, ends of small intestine or one open end of small intestine and one of large intestine. These ends are sewn or stapled together to reestablish the continuous flow of intestinal contents all the way through the gastrointestinal tract. However, in some situations, the surgeon may decide to create a temporary stoma above the surgical hookup site (anastomosis) in order to divert the intestinal contents away from the anastomosis so that it has the best chance of healing fully. This is usually done when there has been an abscess or uncontrolled infection in the area of the anastomosis prior to surgery and the risk of poor healing is higher. In most cases, the stoma is closed during another surgical procedure several months later. Strictureplasty Patients who have had multiple previous intestinal resections or who have multiple segments of affected small intestine are at risk of developing short bowel syndrome if they have more of their bowel removed surgically. A strictureplasty is a method of avoiding removal of additional segments of intestine. There are a number of methods of performing strictureplasty, but they all involve opening up the affected and narrowed segment of the intestine and creating a larger internal passageway for food to pass through without causing symptoms of obstruction. Strictureplasty Strictureplasty is not always done whenever there is a narrowed segment of small intestine, for several reasons. The affected segment is often too long - multiple short segments of narrowing are ideal for strictureplasty. The segment is sometimes too diseased and thickened, making it difficult to work with surgically. There may be only a single short segment of narrowing, and the risk of the strictureplasty procedure (leak, infection, recurrent obstruction) is not worth the potential benefit of avoiding a resection, which is generally much easier to perform. In the situation where the affected segment is very short, then resection of that segment carries very little risk of complication or of future development of short bowel syndrome. Reducing Risk Strictureplasty involves trying to open up narrow segments of small intestine in order to avoid having to remove them. By conserving the affected segments of intestine, it may be possible to reduce the future risk of short bowel syndrome that might occur if the affected intestine was simply removed. Occasionally, the operation is performed because of one or more strictures in the colon or because of a fistula or abscess arising out of the colon. There are a few common segments of colon that may be removed, and each of these operations has its own name describing the part of the colon that has been removed: the right half of the colon in a right hemicolectomy, the left half of the colon in a left hemicolectomy, and the sigmoid colon in a sigmoid resection. In a partial colectomy, only a portion of the large intestine is removed and usually the two cut ends of the intestine are sewn together. Subtotal Colectomy A subtotal colectomy involves removal of all of the large intestine, with the exception of the rectum and perhaps the lower end of the sigmoid colon. In this operation, the last part of the small intestine (ileum) is connected to the rectum to form an ileorectal anastomosis or to the sigmoid colon to form an ileosigmoid anastomosis. Total Proctocolectomy If the entire colon and rectum are removed, the operation is called a total proctocolectomy.
Because this is an artificial way to provide nutrition medications used for anxiety order nootropil 800 mg without a prescription, your body often has difficulty processing the nutrients treatment lupus purchase 800 mg nootropil mastercard, and you could develop problems with your liver or gallbladder or abnormalities of cholesterol, triglycerides, and sugar levels in the blood as a result. Synbiotics "Synbiotics" refers to both prebiotics and probiotics, which contribute to maintaining the health of the intestinal bacteria and keep a sufficient number of "good" bacteria in the intestine. The inflammatory response is actually a natural protective mechanism, but can be damaging if it is overactive or uncontrolled. It is thought that some of the "good" bacteria normally present in the intestine contribute to maintaining the appropriate balance of the immune response. There are food and supplement sources of both prebiotics and probiotics, but how much and how often you should eat these foods to experience benefits is not known. Prebiotics Prebiotics are nondigestible carbohydrates that are fermented by colonic bacteria. The process of fermentation provides energy for the growth of "good" bacteria, which, in turn, produce short-chain fatty acids, which are a fuel source for the cells lining the large intestine. Some nutrition companies are adding these prebiotics to their food supplement drinks and puddings. More recently, food companies have been adding a prebiotic named inulin (a soluble fiber processed from chicory root) to dairy products, chocolate, and beverages. Interestingly, most soluble fibers, including psyllium fiber, are considered prebiotics. Limits As with all fermentable foods, be sure to limit your intake of prebiotics to only a few grams a day in order to avoid gas and cramping. When foods are fermented by bacteria in the intestine, gas is produced as a normal by-product. Although not abnormal, gas may be uncomfortable or difficult to manage in some social situations. Probiotics Probiotics are any number of different "good" live bacteria that are administered by mouth, in a capsule or in a drink or food, and confer a health benefit. The bacteria then establish themselves and grow within the intestine, a process called colonization. Live bacteria are most easily found in yogurts and kefir, where active bacterial cultures have been added. Similarly, the amount of remaining live bacteria when you consume the product will be affected by the processing, transport, and storage conditions. Probiotics must also arrive alive in the gut, so they must be acid- and bile-resistant. It is important to know the strain of bacteria because not all strains in a given group have the same benefit. By eating more antiinflammatory fats, we can directly influence production of these anti-inflammatory mediators. Anti-Inflammatory Fats Omega-3 fats are anti-inflammatory, while omega-6 are proinflammatory. In North America, our balance between these two essential fats is skewed, and we generally consume too much omega-6 and not enough omega-3 fats. For the general public, some recommendations in the medical literature suggest an intake of 400 to 500 mg per day as being optimal. Some of these products have added costs, so be sure to read the label to determine whether the additional omega-3 is significant enough to add to your daily totals. Still, it is considered worthwhile to include plant sources of omega-3 along with marine sources because this can improve the balance of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids in the diet. Functional foods are conventional foods (fish, for example) or those similar in appearance to a conventional food (omega-3 eggs, for example) that are part of a usual diet and that demonstrate a physiological health benefit. Eventually, he was placed on an immunosuppressant drug, azathioprine, to try to keep his colitis in remission and avoid the need for more courses of prednisone. Overall, azathioprine seemed to reduce how frequently he experienced flares but did not completely eliminate them. James was not entirely satisfied with the results of his medical treatment and wanted to consider other options, such as diet, for controlling his condition. He booked an appointment with his gastroenterologist, who told him there was no role for diet in treating ulcerative colitis and said he should simply stick with the prescribed medication.
More Hyperglycemia-Mediated Effects Apart from the above distinct pathways medications 2 times a day discount generic nootropil uk, hyperglycemia can promote redox state via other mechanisms treatment brachioradial pruritus buy discount nootropil 800mg on-line. Antioxidant systems seem the last resort of the organism, although they are also compromised in diabetics. Last but not least, vasa vasorum display an accelerated but faulty angiogenetic process resulting in intraplaque hemorrhages and thus enlargement of the core [48]. Prothrombotic State Platelet Activation and Aggregation It has been demonstrated that hyperglycemia promotes platelet activation and aggregation via surface protein glycation and interference with intraplatelet calcium homeostasis. Dyslipidemia Dyslipidemia is one of the strongest risk factors for the development of atherosclerotic disease. Incorporation of oxidized 58 Coronary Artery Disease cholesterol transforms the latter into foam cells, the hallmarks in plaque formation. The result is suppression of the inflammation by an increased ratio of Treg/T1 helpers [51,53]. Homocysteine is a nonessential, sulfur-containing amino acid provided by demethylation of the essential amino acid methionine. Hyperhomocysteinemia is classified as moderate (15e30 mmol/L), intermediate (31e100 mmol/L), and severe (>100 mmol/L) [61]. Hyperhomocysteinemia is caused by genetic defects, vitamin deficiencies, drugs, renal dysfunction, chronic hepatic disease and other systemic diseases [61]. Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Dysfunction Elevated plasma levels of homocysteine are associated with a significant deterioration of redox state. However, we know that cysteine, which is found in plasma at much higher concentrations and gets easily auto-oxidized is not correlated with endothelial dysfunction. Another way that high homocysteine levels disrupt the normal endothelial function is through the impairment of endothelial cell growth cycle. Research has demonstrated that homocysteine interferes with the expression of cyclin A, thus intercepting normal growth and replacement of damaged endothelial cells [65]. The proposed mechanism involves the overexpression of c-myb and c-fos genes, which interfere with protein kinase C cascade [65]. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Endoplasmic reticulum includes a specialized network of proteins, called chaperones, which functions as a quality control system. Interactions With Plasma Lipids It has recently been shown that higher levels of homocysteine (>100 mmol/L) are associated with an otherwise unexpected increase in the plasma levels of total cholesterol, free cholesterol and cholesteryl ester accompanied by a decrease in ApoE expression. Lipoprotein aggregates invade the endothelial barrier and get easily incorporated by macrophages. Foam cells that include these aggregates are more atherogenic due to increased oxidative potential. The aforementioned homocysteinylated lipoproteins can also aggregate with microorganisms. The resulting complex particles are believed to be responsible for obstructions of vasa vasorum. The latter disrupt the integrity of arterial wall and destabilize the atherosclerotic plaque by causing microischemias, microhemorrhages, and microabscesses [59,66]. Risk Factors of Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiological Mechanisms 61 Prothrombogenic Effects Elevated plasma levels of homocysteine have recently been associated with a wide spectrum of prothrombotic adverse effects. Homocysteine interferes with arachidonic acid in platelets and enhances thromboxane-mediated platelet aggregation. Their difference is the binding of glycoprotein apo(a) to B-100 by a single disulfide bridge. Normal function of Lp(a) is not yet fully elucidated; however, it is speculated that it contributes to tissue healing by binding fibrin and delivering cholesterol. Prothrombotic Effects of Lp(a) Elevated plasma levels of Lp(a) account for the promotion of a prothrombotic state involving three main mechanisms [1,71,72]: 1. Lp(a) displays a unique structural resemblance to plasminogen resulting in the competitive inhibition of the latter. Consequent inhibition of plasmin formation significantly impairs the fibrinolytic process. It exerts both atherogenic and prothrombotic direct effects contributing to the development and aggravation of atherosclerotic disease.
Syndromes
- Poor gag reflex in people who are not alert (unconscious or semi-conscious) after a stroke or brain injury
- Warm the formula slowly by placing it in hot water. DO NOT boil the water and DO NOT use a microwave. Always test the temperature of the formula on yourself before feeding your baby.
- Impotence
- Corneal abrasion
- Talk therapy (psychotherapy) can help adolescents understand issues that may be causing their behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
- Difficulty reasoning and solving problems
- Decreased appetite
- Biliary stricture
Non-pharmacologic management can include encouraging airflow over the face (open window treatment stye quality 800 mg nootropil, use of a fan) and distraction (reading medications without a script purchase nootropil 800 mg overnight delivery, relaxation, company, music). Energy conservation with pacing of exertion, controlled breathing exercises and psychological support can also be beneficial (112). If anxiety contributes to breathlessness, anxiolytics such as low-dose benzodiazepine (in the United Kingdom typically lorazepam 0. Ambulatory oxygen can be prescribed if there is exertional desaturation below 90% and clear evidence of benefit from its use. Assessing this benefit depends on evidence of increased quality in life as a result of increased walk distance. More studies may be useful, as there are potential disadvantages of using oxygen treatment. Oxygen prescription may be prohibited in households where ongoing smoking habits increase the risk of fire. Gabapentin has been used successfully in refractory chronic cough and is attractive as a non-opiate agent with relatively favourable side effect and interaction profiles (124). While there is an understandable push to institute such therapies, patient-centred care aiming to improve quality of life must remain a priority. In such a system it is, therefore, important for specialist centres to build relationships with referring units, primary care and community services to improve referral pathways and patient experience. Under times of financial pressures within healthcare systems, it can be challenging to develop such roles to effectively treat a sizeable patient group in whom comorbidities and frailty are common issues. It can be a major cause of symptom burden and impact very negatively on quality of life (120). The evolving role of integrated care respiratory physicians providing clinical support for these services can allow this to be safely developed. Partnership of these caregivers with palliative care practitioners may optimize provision of appropriate symptom relief and support in achieving preferred place of death. Establishing evidence-based standards of such collaborative practice may enable more consistent, high-quality care. They may provide a means to measure service provision against patient-centred, performance-related outcome measures. Most strikingly, patients who adhered to the treatment protocol had a marked reduction in mortality on co-trimoxazole (hazard ratio of 0. It is possible that benefit may have accrued from beneficial effects of co-trimoxazole counteracting adverse consequences of immunosuppression. The triple therapy arm was stopped early due to an interim review that detected an increase in mortality, hospitalization and adverse events in this group without any detectable treatment benefit to offset such serious harm. As a consequence the dominant mechanism(s) of therapeutic action are not entirely clear beyond generally anti-fibroproliferative effects. This is particularly the case for pirfenidone, which appears to be highly pleiotropic with multiple effects upon cytokines, growth factors and collagen secretion in vitro (137). A wide range of novel therapeutic approaches currently in development, therefore, target molecules involved in crosstalk between epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells and in mesenchymal cell recruitment and potentiation. It is implicated in epithelial cell apoptosis, fibroblast activation, transition of epithelial cells to those with characteristics of mesenchymal cells and differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. However, the pleiotropic effects of this pathway mean that this approach risks side effects that may underlie its lack of success to date (142,143). Galectin-3 is found at the cell surface in alveolar epithelial cells and lung fibroblasts (146). Synthetic galectin-3 ligands can protect lung tissue from fibrotic responses to bleomycin. The lebrikizumab trial will assess the effects of the drug compared with placebo, both alone and in combination with pirfenidone (ClinicalTrials. Moreover, the lungs of aged Nox4 knockout mice retain the ability to recover from a fibrotic insult with resolution of fibrosis; this ability to recover from such injury is characteristic of young mice and is lost in aged wild-type mice.