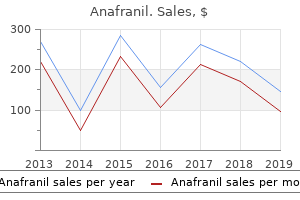
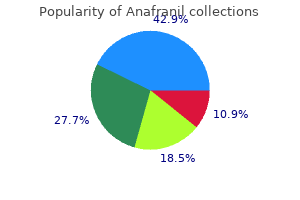
Anafranil
"Best 50 mg anafranil, mood disorder nos dsm criteria".
By: E. Connor, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Program Director, Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine
Benign nephrosclerosis is the term used to describe the kidney of benign phase of hypertension mood disorder unspecified dsm 5 code cheap 50 mg anafranil visa. Mild benign nephrosclerosis is the most common form of renal disease in persons over 60 years of age but its severity increases in the presence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus depression game 25mg anafranil otc. Grossly, both the kidneys are affected equally and are reduced in size and weight, often weighing about 100 gm or less. Less common causes are: amyloidosis of the kidney, myeloma kidney and diabetic nephropathy. There is variable elevation of the blood pressure with headache, dizziness, palpitation and nervousness. Malignant Nephrosclerosis Malignant nephrosclerosis is the form of renal disease that occurs in malignant or accelerated hypertension. Microscopically, most commonly the changes are superimposed on benign nephrosclerosis. The two characteristic vascular changes seen are as under: a) Necrotising arteriolitis develops on hyaline arteriolosclerosis. The vessel wall shows fibrinoid necrosis, a few acute inflammatory cells and small haemorrhages. The patients of malignant nephrosclerosis have malignant or accelerated hypertension with blood pressure of 200/140 mmHg or higher. Approximately 90% of patients die within one year from causes such as uraemia, congestive heart failure and cerebrovascular accidents. The vascular changes are hyaline arteriolosclerosis and intimal thickening of small blood vessels in the glomerular tuft. The parenchymal changes include sclerosed glomeruli, tubular atrophy and fine interstitial fibrosis. Causes of thrombotic microangiopathy of renal microvasculature are listed in Table 22. The injured endothelial surface causes the following effects: Passage of plasma constituents to the subendothelial zone of microvasculature. The medulla, the juxtamedullary cortex and a rim of cortex under the capsule are usually spared. The obstruction may be unilateral or bilateral, partial or complete, sudden or insidious. Before describing these conditions, an account of the most common and important cause of obstructive uropathy, urolithiasis, is given below. Urinary calculi are worldwide in distribution but are particularly common in some geographic locations such as in parts of the United States, South Africa, India and South-East Asia. The mechanism of calcium stone formation is 691 explained on the basis of imbalance between the degree of supersaturation of the ions forming the stone and the concentration of inhibitors in the urine. Most likely site where the crystals of calcium oxalate and/or calcium phosphate are precipitated is the tubular lining or around some fragment of debris in the tubule acting as nidus of the stone. Calcium stones are usually small (less than a centimeter), ovoid, hard, with granular rough surface. Struvite stones are formed as a result of infection of the urinary tract with urea-splitting organisms that produce urease such as by species of Proteus, and occasionally Klebsiella, Pseudomonas and Enterobacter. Types of Urinary Calculi There are 4 main types of urinary calculi-calcium containing, mixed (struvite), uric acid and cystine stones, and a few rare types (Table 22. They may be pure stones of calcium oxalate (50%) or calcium phosphate (5%), or mixture of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate (45%). Sectioned surface shows dilated pelvicalyceal system with atrophied and thin peripheral cortex. The pelvis of the kidney contains a single, large, sof t yellow white stone t aking the contour of the pelvi-calyceal system (arrow). Type Calcium stones Incidence 75% Etiology Hypercalciuria with or without hypercalcaemia; idiopathic Urinary infection with ureasplitting organisms like Proteus Hyperuricosuria with or without hyperuricaemia.
Sarcomas mark with antibody to vimentin rain depression definition anafranil 50mg without prescription, an 54 E Synovial sarcomas account for 10% of all adult sarcomas and can be found around a joint or in deep soft tissues because they arise from mesenchymal cells depression geometry definition cheap anafranil 10mg without prescription, not synovium. Leiomyosarcomas do not have a biphasic pattern microscopically and are rarely seen in soft tissues. A mesothelioma can be biphasic, but it more typically arises in the pleura, or less commonly the mesothelial surface of peritoneum or pericardium. The tumor has infiltrated the overlying soft tissue, and the surgeon must remove a portion of the facial nerve to obtain an adequate margin. Which of the following best describes the most likely outcome during the first week after surgery Acute inflammatory cells around the graft Formation of a traumatic neuroma Recurrent tumor along the nerve graft Segmental demyelination and axonal loss of the nerve proximal to the graft E Fragmentation of distal axons and myelin sheaths C Ganglion D Myofiber E Schwann cell 4 A 41-year-old man had an influenza-like illness for 1 week, followed 4 days later by rapidly progressive, ascending motor weakness requiring mechanical ventilation. On physical examination, he is now afebrile and has 3/5 motor strength in his extremities. A lumbar puncture is done and yields clear, colorless cerebrospinal fluid under normal pressure. This fluid has a slightly elevated protein concentration, but a normal glucose level, and a cell count with only a few mononuclear cells. On physical examination, he has loss of sensation in the lateral left foot and movement in the left foot. The wound is surgically repaired, including nerve, and he receives physical therapy. Over the next month there is increasing weakness of the left pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, and triceps muscles. A lesion involving which of the following structures is most likely to be present in this man Nerve conduction studies show findings consistent with demyelination and remyelination. She is treated with acyclovir, and partial resolution of the skin lesions occurs, but the pain persists for the next 3 months. Aging Diabetes mellitus Multiple sclerosis Somatoform pain disorder Varicella-zoster virus infection Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency Peripheral Nerve and Skeletal Muscle 425 10 A 41-year-old woman has noted marked pain in the right foot for the past 2 months. The pain makes it difficult for her to wear high-heeled shoes and seems to be worse at the end of the day. On physical examination, she has severe pain on palpation of the interdigital space between the second and third toes. Beriberi Type 2 diabetes mellitus Entrapment neuropathy Lead poisoning Wallerian degeneration 7 A 66-year-old man receiving hemodialysis for chronic renal failure has noted increasing loss of sensation in his legs for the past 4 years. On physical examination, there is symmetrically decreased sensation over both lower extremities. Cerebral astrocytoma Diabetes mellitus Hansen disease Multi-infarct dementia Multiple sclerosis Uremia 11 A 58-year-old man has experienced worsening double vision and eyelid drooping, particularly toward the end of the day, for 1 month. On physical examination, he has 5/5 motor strength in his extremities that decreases to 4/5 strength with repetitive movement. Physical examination shows a 2-cm shallow, nonhealing ulceration of the left medial malleolus. There is symmetric decreased sensation in the distal regions of the lower extremities. He has a history of multiple urinary tract infections resulting from difficulty in completely emptying the bladder. Which of the following pathologic findings is most likely to be present in the peripheral nerves Acute inflammation Axonal neuropathy Onion bulb formation Segmental demyelination Wallerian degeneration 12 A 72-year-old man has had a 7-kg weight loss, proximal muscle weakness, and difficulty with urination for the past 4 months. On physical examination, he has 4/5 muscle strength in his proximal extremities that does not diminish with repetitive motion. Laboratory studies show that he does not have serum antibodies to acetylcholine receptor. Chronic hepatitis C Diabetes mellitus Duchenne muscular dystrophy Lead poisoning Small cell lung carcinoma 9 A 24-year-old woman has had episodes of numbness and tingling in both hands for 5 months. The problem is worse near the end of the day and makes it difficult for her to use the computer keyboard. There is no pain or swelling, and she does not recall any trauma to the upper extremities.
The prognosis is good in most cases depression zoloft order anafranil overnight delivery, even with metastases mood disorder nos 504 plan anafranil 10 mg sale, because seminomas are radiosensitive. Fragile X syndrome is associated with bilaterally enlarged testes and mental retardation. Klinefelter syndrome is associated with bilaterally decreased testicular size and reduced fertility. An abnormally positioned or anchored testis in the scrotum is a risk factor for this condition. Testicular carcinomas do not obstruct the blood flow, and are not likely to produce an acute event. Parasitic infestation, typically filariasis, obstructs the flow of lymph, leading to gradual enlargement of the scrotum with thickening of the overlying skin. Tuberculosis can spread from the lung through the bloodstream, producing miliary tuberculosis, seen as multiple pale, millet-sized lesions, most often involving the epididymis. A previous vasectomy may lead to a small leakage of fluid and sperm, producing a localized sperm granuloma. Some patients have gynecomastia caused by androgenic or estrogenic hormone production (or both) by the tumor. Most patients are young to middle-aged men; sexual precocity may occur in the few boys who have such tumors. Choriocarcinomas are grossly soft and hemorrhagic masses that have large bizarre syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast cells and are aggressive. Embryonal carcinomas are large, aggressive tumors that have a variegated gross appearance and primitive cells with large, hyperchromatic nuclei. Gonadoblastomas are rare testicular tumors that arise in the setting of gonadal dysgenesis. A pure seminoma can be uniformly brown on cut surface, but often has a lymphoid stroma, and is not likely to secrete androgens or estrogens. Yolk sac tumors have cells that organize into primitive endodermal sinuses (SchillerDuval bodies). The infection typically starts in the epididymis and spreads to the body of the testis. Chancroid caused by Haemophilus ducreyi leads to ulcerated nodules of the external genitalia. Mumps produces patchy orchitis with minimal inflammation, which heals with patchy fibrosis. Syphilis involves the body of the testis, and there can be gummatous inflammation with neutrophils, necrosis, and some mononuclear cells. The most common form of testicular neoplasm combines multiple elements; the term teratocarcinoma is sometimes used to describe tumors with elements of teratoma, embryonal carcinoma, and yolk sac tumor. It is unusual for a tumor to metastasize to the testis; this patient is of an age at which a primary cancer of the testis should be considered when a testicular mass is present. On examining more histologic sections from the mass, the pathologist would find the malignant elements. Pure yolk sac tumors are rare in adults, but yolk sac components are common in mixed nonseminomatous tumors. Cytotrophoblasts do not produce a serum marker, but they may be present in a choriocarcinoma along with syncytiotrophoblasts, which do produce human chorionic gonadotropin. Embryonal carcinoma cells are common in nonseminomatous tumors, however, and are often mixed with other cell types. Lymphoblasts may be seen in high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphomas, which do not produce hormones. Elephantiasis is a complication of parasitic filarial infections involving the inguinal lymphatics; it is typically bilateral. Orchitis involves the body of the testis without marked enlargement, but with tenderness.
There is a deficiency of myophosphorylase enzyme in McArdle disease depression symptoms on the body order anafranil with mastercard, leading to muscle pain and cramping with vigorous exercise mood disorder with anxiety icd 9 discount 10mg anafranil mastercard. Antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor cause the muscular weakness in myasthenia gravis. Cholestyramine binds bile acids in the intestine and disrupts enterohepatic bile acid circulation to increase conversion of cholesterol to bile acids in the liver. These abnormal genes can lead to mitochondrial myopathies, encephalopathies, and deafness. An abnormal voltage-gated calcium channel is seen in one of the channelopathies; it causes hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Antibodies to acetylcholine receptor cause myasthenia gravis; its sole manifestation is muscle weakness. Decreased sarcolemmal dystrophin is present in Becker muscular dystrophy; dystrophin is absent in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In keeping with the diagnosis of Becker muscular dystrophy, the patient is older and not severely affected. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a denervation atrophy seen in adults, with loss of anterior horn cells in the spinal cord and cranial nerve nuclei. Myasthenia gravis results from antibodies to acetylcholine receptors, and there is minimal structural change to the muscle. Onset is at birth, and it results from a genetically determined loss of anterior horn cells. Congenital myopathies are often named for their characteristic histologic features. Channelopathies typically present as periodic paralysis with abnormalities in serum potassium. Neuropathies affect muscle through denervation, leading to groups of atrophic muscle fibers. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis are inflammatory myopathies that are accompanied by myalgia and fiber degeneration with increased serum creatine kinase. Mitochondrial myopathies may appear in childhood but are usually progressive, and often other organs such as heart or brain are involved. The biopsy specimen shows variation in muscle fiber size and increased connective 22 F Werdnig-Hoffman disease is a form of spinal muscular atrophy resulting from loss of motor neurons in infancy, so the biopsy specimen shows grouped atrophy of myofibers. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a progressive disease with a neurogenic form of muscle atrophy resulting from loss of motor neurons. McArdle disease is an autosomal recessive condition resulting from a deficiency in muscle phosphorylase and does not produce progressive weakness. Myasthenia gravis results from acetylcholine receptor antibody and leads to progressive weakness. Myotonic dystrophy is characterized by facial and upper body weakness, cataracts, gonadal atrophy, cardiomyopathy, and dementia. Thick filaments include the myosin contractile protein; -myosin mutations are found in some cases of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In patients with mutations in the ryanodine receptor, there is impaired reuptake of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum with increased intracellular calcium leading to hypermetabolism. Motor end plates include acetylcholine and acetylcholine receptors that are involved with myasthenia gravis. Actin is one of the contractile proteins of muscle and its absence is not compatible with life. Cardamom is an aromatic spice from the ginger family of plants, used in traditional medicine for oral and intestinal conditions. Caveolin is an intracellular vesicle transport protein, and mutations involving this protein may be present in some forms of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. Dystrophin stabilizes sarcolemmal membranes, and its absence leads to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Troponin is part of the myofiber unit and is used to detect striated muscle injury, specifically myocardial ischemia and infarction. One cell type in the hippocampus is noted to exhibit intense cytoplasmic eosinophilia, central chromatolysis, spheroidal swellings, and nuclear pyknosis. The only abnormalities on physical examination are bruits over the carotids in the neck. At autopsy there is an area of necrosis and microscopically these lesions are noted to have increased numbers of cells distributed around the central zone of necrosis.