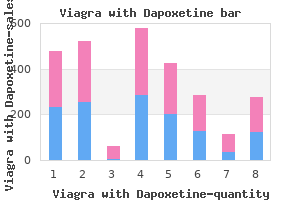
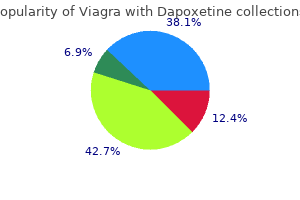
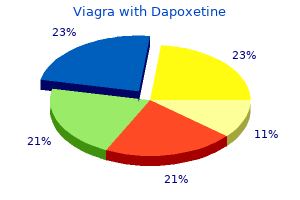
Viagra with Dapoxetine
"Order cheap viagra with dapoxetine line, erectile dysfunction 4xorigional".
By: S. Gunock, M.A., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, San Juan Bautista School of Medicine
Neuroendocrine differentiation in non-small cell lung cancer and its relation to prognosis and therapy kidney transplant and erectile dysfunction treatment generic viagra with dapoxetine 100/60 mg with amex. Prognostic implications of neuroendocrine differentiation and hormone production in patients with Stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma erectile dysfunction due to diabetic neuropathy buy generic viagra with dapoxetine online. Neuroendocrine differentiation in poorly differentiated lung carcinomas: a light microscopic and immunohistologic study. Subtyping of undifferentiated non-small cell carcinomas in bronchial biopsy specimens. A reevaluation of the clinical significance of histological subtyping of non: small-cell lung carcinoma: diagnostic algorithms in the era of personalized treatments. The use of electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis and understanding of lung neoplasms. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical features of common lung tumors: an overview. Invasion of lung tissue by bronchogenic squamouscell carcinomas: interaction of tumor cells and lung parenchyma in the tumor periphery. Value of immunohistochemical markers in preinvasive bronchial lesions in risk assessment of lung cancer. Multiple gene methylation of nonsmall cell lung cancers evaluated with 3-dimensional microarray. Loss of histone H4K20 trimethylation occurs in preneoplasia and influences prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Gene expression-based classification of nonsmall cell lung carcinomas and survival prediction. A 10-gene classifier for distinguishing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma. Retrospective evaluation of the clinical and radiographic risk factors associated with severe pulmonary hemorrhage in first-line advanced, unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer treated with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab. Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care for nonsmall-cell lung cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma following head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: metastasis or second primary Genomic and mutational profiling to assess clonal relationships between multiple non-small cell lung cancers. Distinguishing second primary tumors from lung metastases in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Gene expression profiling allows distinction between primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinomas in the lung. Heterogeneity of prognostic profiles in non-small cell lung cancer: too many variables but a few relevant. Prognostic markers in resectable non-small cell lung cancer: a multivariate analysis. Prognostic factors obtained by a pathologic examination in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Clinical significance of biological differences between cavitated and solid form of squamous cell lung cancer. Tumor location is not an independent prognostic factor in early stage nonsmall cell lung cancer. The histologic spectrum and 1112 Chapter 28: Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung significance of clear-cell change in lung carcinoma. Small cell squamous and mixed small cell squamous: small cell anaplastic carcinomas of the lung. P63 in pulmonary epithelium, pulmonary squamous neoplasms, and other pulmonary tumors. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: a rare tumour with a rare clinical presentation. Basal cell (basaloid) carcinoma of the lung: a new morphologic and phenotypic entity with separate prognostic significance. Fine needle aspiration cytodiagnosis of basaloid-squamous cell carcinoma metastatic to a cervical lymph node. Distinction of basaloid squamous cell carcinoma from adenoid cystic and small cell undifferentiated carcinoma by immunohistochemistry. Large cell carcinomas are poorly differentiated tumors diagnosed in the absence of glandular or squamous features. Large cell carcinoma Variants Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma Combined large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma Basaloid carcinoma Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma Clear cell carcinoma Large cell carcinoma with rhabdoid phenotype Source: reference 2.
Diseases
- Quadriceps sparing myopathy
- Staphylococcus epidermidis infection
- Motor neuron disease
- Urbach Wiethe disease
- Lichstenstein syndrome
- Infantile dysphagia
- Fara Chlupackova syndrome
- Otosclerosis, familial
- Chlamydia pneumoniae
- Light chain disease
Influenzavirus is spread by large droplets buy erectile dysfunction injections cheap viagra with dapoxetine on line, small aerosol particles erectile dysfunction fertility treatment order 100/60 mg viagra with dapoxetine visa, and contact with fomites. Shedding persists for 5:10 days, or longer in immunocompromised hosts and in young children. The onset of "flu" is abrupt, with prominent systemic symptoms including fever, myalgias and fatigue. But symptoms may also be limited to rhinorrhea, sore throat, fever, conjunctival injection and non-productive cough. The early onset of dyspnea is a poor prognostic sign, as it may progress rapidly to respiratory failure. Acute influenza causes diffuse inflammation of the larynx, trachea and bronchi, with mucosal injection and edema. Rates of serious morbidity and death are highest among persons older than 65 years, children aged less than 2 years and persons of any age who have medical conditions that place them at increased risk for complications from influenza. Immunocompromised hosts tend to develop disease earlier in the fall, but the bulk of disease occurs in the winter and early spring. Influenza pneumonia tends to develop in elderly, non-vaccinated or immunocompromised individuals, and bacterial superinfection is common in these settings. Diagnosis rests predominantly on the immunological detection of viral antigens in respiratory secretions. Antiviral medications are an adjunct to vaccination and may be effective when administered as treatment or used as chemoprophylaxis following an exposure to influenzavirus. Oseltamivir and zanamivir are the only antiviral medications that are currently recommended for use in the United States. The pathology of seasonal influenza includes an acute diffuse tracheobronchitis/bronchiolitis in which the normal ciliated respiratory epithelial lining is sloughed. Bacterial infection can mask evidence of a previous influenza infection, and there may be multiple bacterial pathogens in some cases. Virions form along the endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi apparatus and next bud into cisternae, where they acquire a lipid envelope. Subsequent transmission took place largely in the hospital setting, where transmission was by droplet spread and required close contact. After 2:7 days, patients develop a dry cough and progressive dyspnea over 4:7 days. Upper respiratory viral symptoms of rhinorrhea or sore throat are uncommon and most patients develop pneumonia. Chest radiographs show unilateral or bilateral infiltrates, either ground-glass opacities or consolidation, progressing to bilateral airspace consolidation. Laboratory findings include elevations in lactate dehydrogenase, transaminases and creatine kinase, with lymphopenia and thrombocytopenia. However, in one study, viral antigens could not be detected in situ, probably as a result of the prolonged interval (> 2 weeks) between the primary infection and death. Respiratory syncytial virus causes most cases of viral bronchiolitis and pneumonia in children. Surface fusion proteins, F and G, mediate attachment and multikaryon formation by infected cells. Ribavirin, administered via either intravenous or aerosol routes, has been used to treat immunocompromised hosts with lower tract disease. The efficacy of antiviral therapies remains uncertain, and hyperimmune globulin or monoclonal antibodies may alternatively provide treatment for severe disease. Adenovirus is an uncommon cause of acute bronchiolitis, but must be considered in the setting of severe disease. Children may develop inspiratory stridor and wheezing when lower respiratory tract involvement ensues. Both the cough and stridor are signs of inflammation, while edema of the larynx and trachea is primarily localized at the subglottic level. However, it is not routinely performed, as the clinical syndrome is generally characteristic, and management does not depend on identification of the specific agent. Croup must be distinguished from other serious causes of airway obstruction, such as bacterial epiglottitis and tracheitis. Epiglottitis, most often due to vaccine-preventable Hemophilus influenzae type B or to alpha hemolytic streptococci, causes acute respiratory distress and drooling without cough. Stridor can result from peritonsillar or retropharyngeal abscess, diphtheria or the aspiration of a foreign body.
Hopefully does erectile dysfunction get worse with age buy viagra with dapoxetine uk, the recognition of the serious hazards posed by exposure to asbestos erectile dysfunction 3 seconds purchase 50/30 mg viagra with dapoxetine mastercard, the reduction in asbestos consumption, the improvements in regulation, occupational and industrial hygiene, and the scientific understanding of asbestos-associated illness down to the molecular level will result in the removal of this scourge. Statistical modeling indicates that asbestosis deaths are not due to decrease sharply over the next 10:15 years. The disease will claim the lives in excess of 29 000 individuals between the years 2005 and 2027. Cases reporting this association were first published in 1935,102,103 and the relationship was confirmed in epidemiological studies in 1955. Experimental animal studies provided additional support for the association between asbestos and lung cancer. These include the interaction between asbestos and cigarette smoking in increasing lung cancer risk, differences in fiber types with respect to potency in the production of lung cancer, and the role of asbestos dose versus asbestosis as the underlying etiological factor. Finally, one must consider the role of fiber analysis of lung tissue in determining the cause of lung cancer in an individual case. Cigarette smoking inhibits clearance mechanisms in the lower respiratory tract and thus can increase the effective dose of asbestos. Furthermore, carcinogens from cigarette smoke, adherent to the surface of asbestos fibers, may be more readily delivered to the respiratory epithelium. Berman and Crump reached a similar conclusion in their extensive literature review. The result must be correlated with the range of values observed in bona fide cases of asbestosis. In everyday practice, fiber burden analysis cannot substitute for or overrule the histological diagnosis of asbestosis. The immunosuppressive therapy which constitutes the mainstay of medical intervention for other forms of pulmonary interstitial fibrosis is ineffective. Historically, deaths result from intractable respiratory failure, with the expected association of decreased life expectancy in proportion to disease severity. Other causes of death include cor pulmonale, carcinoma of the lung and mesothelioma. Studies from the United Kingdom and Finland document considerable and excessive mortality from carcinoma of the lung in workers with asbestosis. Risk differential for lung cancer for chrysotile alone versus amphibole fibers appears to be between 1:10 and 1:50 Modified from reference 111. One of the most controversial areas with respect to asbestos and lung cancer is whether asbestosis is an obligatory precursor of asbestos-related lung cancer (fibrosis/cancer hypothesis), or whether asbestosis and lung cancer are two independent endpoints, each related to the dose of asbestos (fiber burden hypothesis). Proponents of the fibrosis/cancer hypothesis note the oncogenic potential for severe interstitial lung fibrosis, and the tendency for carcinomas to develop in animal models only in cases of asbestosis. Proponents of the fiber burden hypothesis consider asbestos both an initiator and promoter of carcinogenesis, and regard fibrogenesis and carcinogenesis as distinct effects of asbestos exposure. The pro and con arguments in this regard have been presented in detail elsewhere, and have included the fundamental disagreements between experts on the criteria for the diagnosis of asbestosis, laboratory-specific variance in fiber burden analyses and criticisms of the imprecision of epidemiological studies. Asbestosis is primarily a disease of the lung periphery with greatest severity typically in the lower lobes, whereas asbestos-related bronchogenic carcinoma is a more central process and commoner in the upper lobes. Some have argued that epidemiological studies favor asbestosis as the precursor to asbestos-induced lung cancer. This is because 85 to 95% of lung cancers are related to cigarette smoking, whereas asbestos is a causative factor in fewer than 5% of lung cancer cases. Although some studies have reported that asbestosrelated lung cancers are commoner in the lower lobes, others have found that they are more frequent in the upper lobes (similar to cigarette-smoking related lung cancers in the absence of asbestos exposure). Analysis of lung tissue fiber content plays an increasing role in determining the causation of lung cancer in an individual case. This observation was supported by the consensus of experts that met in Helsinki, Finland, in 199788 but is disputed by others. Our studies show one asbestos body per cm2 of an iron-stained lung tissue section is equivalent to approximately 400 asbestos bodies per gram of wet lung tissue. In this regard, there is considerable variation in results analyzing the same sample by different laboratories, since different laboratories follow different protocols. This difference is almost entirely due to the detection of chrysotile (Karjalainen, personal communication, academic dissertation, University of Helsinki 1994). Specifically, when comparing groups of patients with asbestosis, parietal plaques but not asbestosis, and groups with neither, the asbestos body count in the asbestosis cohort was more than 35 times greater than the cohort with plaque only, and more than 300 times greater than the group with neither plaques nor asbestosis.
It appears as a mixture of mucus with granular eosinophilic material trazodone causes erectile dysfunction viagra with dapoxetine 100/60 mg with amex, often containing small yellow "meconium bodies" erectile dysfunction treatment honey order viagra with dapoxetine 50/30 mg mastercard. The ventilation/perfusion mismatch associated with meconium aspiration produces an acidosis and hypoxia, causing vasoconstrictive pulmonary hypertension. Some authors argue that the excessive muscularization of pre-acinar pulmonary arterioles and the extension of muscle into the normally muscle-free intra-acinar arterioles found in these infants is an in utero development. As such, the pulmonary hypertension is less a complication of the meconium aspiration but 112 Chapter 3: Congenital abnormalities and pediatric lung diseases, including neoplasms both conditions share a common etiology of chronic intrauterine stress and hypoxia. It has long been recognized that acute hypoxia can lead to a deep form of gasping type of fetal breathing. As noted above, obstruction of airways with distal collapse, hypoxia and a "ball-valve effect" causing emphysema and pneumothorax can occur from the simple physical presence of meconium. Meconium is largely composed of water, lanugo, desquamated cells, minerals, small quantities of various enzymes, and bile pigments, including bile acids. There is experimental evidence to suggest pneumonias develop from bacteria inhaled with the meconium. The former is suggested by an umbilical arterial (postductal blood) PaO2 that is significantly lower than the PaO2 in the right radial artery (pre-ductal blood). Severe hypoxia due to intrapartum asphyxia and meconium aspiration may cause intense pulmonary vasoconstriction. The pulmonary vascular bed is reduced in pulmonary hypoplasia, so prolonged membrane rupture, possibly associated with both the oligohydramnios:pulmonary hypoplasia sequence and sepsis, is a risk factor in preterm infants. In these cases it is appropriate to consider the pulmonary hypertension idiopathic or primary. Pathologically, pre-acinar and intra-acinar pulmonary arteries and arterioles demonstrate grossly thickened walls due to an increase in vascular smooth muscle. In some instances, muscularization of these vessels is so complete that lumina are almost obliterated. Diffuse interstitial lung disease in children this category comprises a varied set of diseases manifesting with impaired gas exchange and diffuse radiographic infiltrates. In the former group, genetic factors, especially those associated with surfactant production, are prominent. The infant group of diseases also includes those conditions that interfere with normal growth. The groups of conditions, which usually occur after infancy, are poorly understood. Further, these conditions are rare, thus clinical characteristics are not as well defined in the pediatric population. It tends to be more aggressive than in adults but while some cases are idiopathic many are associated with surfactant-related disorders (see above). Most of the infant-associated conditions are related to processes and conditions interfering with normal postnatal growth or development512 and have already been discussed. However, there are two relatively recently described conditions that present post-natally, whose cause is less clear. Five of the infants presented on the first day and all within the first month of life. Subsequent reports have largely confirmed that this early presentation is typical and presentation after 6 months rare. Periodic acid-Schiff stains may show prominent glycogen, while electron microscopy readily reveals the glycogen. Pulmonary interstitial glycogenosis may be associated with other conditions, especially where there is a lung growth disorder, and it has been seen in association with meconium aspiration and cardiac abnormalities. Recently it is considered that these cells may modulate lung growth and differentiation in the fetus, and act as postnatal stem cells. The mean age at presentation was 4 months (range 0:11 months) and 80% of cases were term gestations. Increased numbers of bombesin-positive cells in greater than 70% of bronchioles are also noted. Although long-term oxygen may be required to support infants with this condition, possibly for many years, no deaths have yet been reported. Ascending infection In utero fetal infection is due mainly either to ascending infection, through the maternal os, or transplacentally.