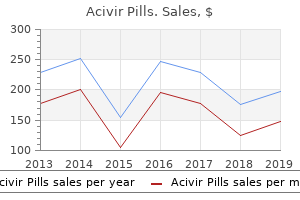
Acivir Pills
"Generic 200mg acivir pills overnight delivery, antiviral rx".
By: D. Marik, M.A., M.D.
Associate Professor, Noorda College of Osteopathic Medicine
Factors such as ventricular interactions kleenex anti viral discontinued order acivir pills amex, positive airway pressure anti viral foods list generic 200mg acivir pills visa, and intrinsic cardiac disease may decrease ventricular compliance and lead to an overestimation of ventricular preload. Echocardiographic techniques can provide a more accurate assessment of ventricular loading conditions, while dynamic indicators such as pulse pressure variation, stroke volume variation, changes in caval diameter, and passive leg raising may provide greater insight into fluid responsiveness. The first component is intravascular volume, which regulates mean circulatory pressures and venous return to the heart. Decreases in intravascular volume limit venous return to the heart and cardiac output. Cardiac output is determined by heart rate, contractility, and loading conditions. Impaired cardiac contractility decreases effective ventricular ejection and compromises stroke volume. The third component is the resistance circuit; it consists of the arteriolar bed, where the major decreases in vascular resistance occur. Arteriolar tone plays an important role in ventricular loading conditions, arterial pressure, and distribution of systemic blood flow. Excessive decreases in arteriolar tone lead to hypotension and limit effective organ perfusion, whereas excessive increases in arteriolar tone impede cardiac ejection by increasing ventricular afterload. Differences in arteriolar tone between organs can result in maldistribution of blood flow and mismatching of blood supply with tissue metabolic demands. They are the site of nutrient exchange and fluid flux between the intravascular and extravascular spaces. Increases in capillary permeability result in tissue edema and loss of intravascular volume. Decreases in capillary cross-sectional area, secondary to either obstruction or impairment in endothelial cell function, compromise nutrient blood flow. The opening of arteriovenous connections, which bypass the capillary network, may play a role in tissue hypoperfusion. They are the site of the lowest shear stress in the circulatory system and are thus the site most prone to occlusion from alterations in cell rheology. Increases in venular tone increase capillary hydrostatic pressures, thereby promoting the extravascular movement of fluid. Increases in venous tone decrease venous capacitance, redistributing blood volume centrally and thereby increasing venous return to the heart. Decreases in venous tone increase venous capacitance and decrease effective arterial blood volume and venous return. Echocardiographic measurements and esophageal Doppler can be used to assess ventricular ejection and also provide diagnostic information regarding the presence of pericardial tamponade and valvular function. The response of stroke volume to changes in ventricular loading during fluid infusion is also useful to assess cardiac contractility. A good response indicates preserved cardiac function, while lack of response may be related to either cardiac dysfunction or inadequate fluid volumes. However, the adequacy of cardiac output in meeting tissue metabolic demands must be assessed independently by monitoring indices of tissue perfusion and oxygen metabolism. A low cardiac output may be adequate when metabolic requirements are decreased-for example, in deep sedation or hypothermia. In contrast, an increased cardiac output may not be adequate when metabolic requirements are increased or maldistribution of blood flow exists, such as in septic shock. Systemic vascular resistance is an indicator of arterial tone; it is calculated from cardiac output and arterial pressure. Increases in systemic vascular resistance are due to vasoconstriction and represent compensatory mechanisms directed at maintaining blood pressure in the setting of a decreased cardiac output. Excessive increases in vascular resistance increase ventricular afterload and the impedance to ejection. Decreases in vascular resistance are due to vasodilation, decreases in blood viscosity, or presence of arteriovenous connections. Vasodilation may be pathologic, as occurs in septic shock and liver disease, or it may be adaptive, as occurs in hyperdynamic stress following major surgery and traumatic injury. Modest increases in central venous pressures in the setting of large-volume infusion and the absence of intravascular volume loss suggest decreased venous tone.
While the diagnosis is being made hiv infection and stds generic acivir pills 200mg on line, therapy may include the use of diuretics hiv infection blood count discount acivir pills 200mg line, inotropic agents, and nitroprusside or other vasodilators in an attempt to stabilize hemodynamics. If acute aortic regurgitation is due to aortic dissection, acute surgical intervention is needed. Rheumatic mitral stenosis is a slowly progressive disease with an insidious decline in exercise tolerance and symptom onset over many years. Because mitral stenosis is more common in women (80% of cases) and occurs during the reproductive years, the most common emergency presentation of mitral stenosis is a pregnant woman with heart failure. Many of these patients are unaware of the underlying valve disease and are initially diagnosed during pregnancy. The clinical presentation may also be due to or exacerbated by the onset of atrial fibrillation. A large atrial myxoma may mimic the clinical presentation of mitral stenosis, presenting with acute hemodynamic compromise due to the obstruction of the mitral valve orifice by the tumor mass. When the valve leaflets are normal, some centers will preserve the native valve by the resuspension of the leaflets in the prosthetic conduit (called the David procedure). Beta blockers should be avoided when acute aortic regurgitation complicates an aortic dissection. When acute aortic regurgitation is due to endocarditis, surgical options include a mechanical valve, a heterograft tissue valve such as a porcine aortic valve or bovine pericardial valve, or a cryopreserved homograft aorta valve. Rarely, the patient may undergo valve repair if there is a simple perforation with adjacent normal leaflet tissue. Rheumatic aortic stenosis is less common and is invariably accompanied by mitral valve involvement. In younger adults, congenital aortic stenosis may be encountered; some of these patients have restenosis after prior commissurotomy in childhood. Like mitral stenosis, aortic valve stenosis is a chronic, slowly progressive disease that presents acutely only in patients who have not been receiving regular medical care. Young women with congenital aortic stenosis may present with angina or heart failure during pregnancy. In older adults, asymptomatic patients with moderate to severe valve obstruction may present with heart failure in the setting of pneumonia, anemia, or other conditions with increased metabolic demands. If atrial fibrillation is present, rate control is essential, preferably with conversion back to sinus rhythm. Even when sinus rhythm is present, beta blockers may improve ventricular diastolic filling by prolonging the duration of diastole as the heart rate is decreased. In patients who do not respond to conservative therapy, emergency intervention should be considered. However, in patients who have denied symptoms or have not been receiving medical care, the first presentation of severe aortic stenosis may be syncope or pulmonary edema. In these patients, aortic stenosis is the cause of decompensation, as evidenced by very severe valve obstruction, often with a low ejection fraction. The cautious use of nitroprusside may improve hemodynamics prior to valve replacement in severe decompensated aortic stenosis, if the mean arterial pressure is above 60 mm Hg,36,37 and some patients can be managed by careful diuresis. However, in unstable patients who are surgical candidates, it is more prudent to proceed promptly to valve replacement. For prohibitive and high-risk surgical patients, transcatheter aortic valve implantation can be performed in experienced centers. Tricuspid valve stenosis is rare and usually accompanies rheumatic mitral valve disease. Tricuspid valve endocarditis often results in acute severe regurgitation; pulmonic valve endocarditis is rare. Cases of acute traumatic disruption of the tricuspid valve with blunt chest trauma have been described, although myocardial contusion or thoracic aorta disruption is more common. However, while a grade 4 murmur (palpable thrill) with a single S2 and diminished carotids is specific for severe stenosis, these findings are very insensitive for the diagnosis.
Forensic aspects of water intoxication: four case reports and review of relevant literature hiv infection in adolescent generic acivir pills 200 mg amex. The effect of pre-existing medical conditions on heat stroke during hot weather in South Korea hiv infection fever order generic acivir pills from india. Plasma hyperosmolality augments peripheral vascular response to baroreceptor unloading during heat stress. Body temperature modification of osmotically induced vasopressin secretion and thirst in humans. The normal range for total serum calcium must be established for each laboratory, and it varies according to the method used. Total serum calcium concentration is a combination of protein-bound calcium, ionized calcium, and nonionized calcium. These organelles are endowed with their own calcium pumps that help preserve the very low levels of free cytosolic calcium. Calcium-dependent intracellular signaling generally requires a 10-fold increase in free cytosolic calcium. Elevation in cytosolic calcium is mediated by the activation of calcium channels, which allows passive calcium flux down electrochemical gradients. Variations in serum protein proportionately alter the concentration of the protein-bound and total serum calcium. An increase in serum albumin concentration of 1 g/dL increases protein-bound calcium by 0. However, the validity of this correction in critical illness has been questioned, with multiple authors emphasizing the importance of directly measuring serum ionized calcium concentrations in this patient population. Changes in pH also affect protein-bound calcium, and an increase or decrease of 0. Intestinal absorption of calcium depends primarily on 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2, which stimulates calcium absorption from all parts of the small intestine. Acidosis decreases protein binding, thereby increasing the ionized fraction of calcium. Because vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, poor intake of food products containing fatty substances results in nutritional osteomalacia. Low Nonionized Calcium the nonionized form of calcium is also called complexed calcium. Calcium complexes are formed with bicarbonate, phosphate, and acetate and constitute approximately 13% of the total serum calcium. Cytosolic Free Calcium the normal concentration of cytosolic calcium is about 100 nM/L, which is 10,000-fold lower than the concentration of extracellular calcium. In certain types of cells, a Na+/Ca++ exchanger, energized by the Na+ gradient, helps drive cytosolic calcium into the extracellular space. Hypothetically, this mechanism may account for vitamin D deficiency in clinical states of calcium malabsorption, including gastrointestinal diseases, anticonvulsant therapy. Likewise, increased intake of foods rich in phytate, oxalate, and citrate that chelate calcium in the gastrointestinal tract and render it nonabsorbable may cause vitamin D deficiency. It is manifested by early hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, severe secondary hyperparathyroidism, and severe rickets. However, mild chronic hypoparathyroidism may cause hypocalcemia so gradually that the only symptoms may be visual impairment from cataracts after years of hypoparathyroidism. Hypoparathyroidism may be either an acquired abnormality designated as secondary hypoparathyroidism or primary hypoparathyroidism, also known as idiopathic hypoparathyroidism. Postoperative hypoparathyroidism may result from the removal of the parathyroid glands or the traumatic interruption of their blood supply. Hypocalcemia following parathyroid adenoma excision results from the functional suppression and hypofunctioning of the remaining normal glands and is usually transient. This results in profound hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, and elevated alkaline phosphatase. Similarly, hypocalcemia has been reported to occur in 15% of patients after thyroidectomy. In the last two disorders, the deposition of iron and copper, respectively, in the parathyroid glands are the likely underlying mechanisms. It is speculated that magnesium depletion may impair the activity of calcium pumps and thus alter the distribution of calcium between the extracellular and the intracellular spaces.
Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone in postoperative scoliosis patients: the role of fluid management hiv infection rate by country order 200 mg acivir pills with mastercard. Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone in a postsurgical pediatric population rate of hiv infection in jamaica order 200 mg acivir pills fast delivery. Postoperative hyponatremia despite near-isotonic saline infusion: a phenomenon of desalination. Hypotonic versus isotonic maintenance fluids after surgery for children: a randomized controlled trial. A detailed study of electrolyte balances following withdrawl and reestablishment of therapy. Hyperglycemia-induced hyponatremia-calculation of expected serum sodium depression. Severe hyperglycemia: effects of rehydration on endocrine derangements and blood glucose concentration. Importance of timing of risk factors for cerebral oedema during therapy for diabetic ketoacidosis. Incidence and outcome of diabetic cerebral oedema in childhood: are there predictors The Pediatric Emergency Medicine Collaborative Research Committee of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Cerebral oedema during treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis: are we any nearer finding a cause Preventing a drop in effective plasma osmolality to minimize the likelihood of cerebral edema during treatment of children with diabetic ketoacidosis. Validity and reliability of clinical signs in the diagnosis of dehydration in children. Detection of electrolyte abnormalities in children presenting to the emergency department: a multicenter, prospective analysis. A prospective study of the usefulness of clinical and laboratory parameters for predicting percentage of dehydration in children. High antidiuretic hormone levels and hyponatremia in children with gastroenteritis. Clinical and laboratory evaluation and management of children with vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration. Reduced osmolarity oral rehydration solution for treating dehydration due to diarrhoea in children: systematic review. Pocket Book of Hospital Care for Children: Guidelines for the Management of Common Childhood Illnesses. Acute hyponatraemia in children admitted to hospital: retrospective analysis of factors contributing to its development and resolution. Management of hyponatremic seizures in children with hypertonic saline: a safe and effective strategy. Treatment of acute hyponatremia: ensuring the excretion of a predictable amount of electrolyte-free water. Comparison of isotonic and hypotonic intravenous maintenance fluids: a randomized clinical trial. Extrapontine myelinolysis caused by electrolyte imbalance during the management of suprasellar germ cell tumors. Central pontine myelinolysis in a 6-month-old infant with rapidly corrected hyponatremia. Experimental studies of gross anatomic changes and alterations of chemical composition of the tissues. A clinical study of 59 infants with observations of respiratory and renal water metabolism. Fluid resuscitation and hyperchloremic acidosis in experimental sepsis: improved shortterm survival and acid-base balance with Hextend compared with saline. Rapid saline infusion produces hyperchloremic acidosis in patients undergoing gynecologic surgery. The value of the chloride: sodium ratio in differentiating the aetiology of metabolic acidosis. If renal tubular and glomerular function is intact, but solute clearance is limited by factors compromising renal perfusion, the injury is termed prerenal azotemia. If renal dysfunction is related to an obstruction of the urinary outflow tract, it is termed postrenal azotemia.