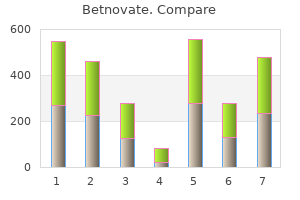
Betnovate
"Cheap betnovate 20gm free shipping, skin care during pregnancy home remedies".
By: U. Ilja, M.S., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Marist College
Peter Drucker was famous for saying "You cannot manage what you cannot measure-and if you cannot manage it acne inversa images buy cheap betnovate on-line, you cannot improve it acne light mask order 20gm betnovate free shipping. Developing these feedback loops will allow your center to better understand your operation, the quality of your service, and identify areas of opportunity for improvement. The elements that we measure with our patient satisfaction survey include the following: 1. My provider seemed familiar with my medical history 235 Third-Party Reporting Who Owns the Patient Experience Will they ask the physician to wait until answering the patient, or will they ask the patient to wait while answering the physician Shaping the corporate culture so that everyone feels ownership of the patient experience requires transparency of patient satisfaction results; it also requires a nonpunitive, curiosity-rewarding approach to issues that may arise with patient care. We implemented an incident reporting feedback system on our company intranet that allows any employee to report a patient incident where they felt an opportunity for improvement exists. If we had rolled out this program without first establishing a patientcentric, quality improvement culture-the initiative would have fallen flat for fear of the tool being used punitively. What has made this system so successful, however, has been a culture that is committed to improving the patient experience. There is a natural curiosity that occurs when something goes awry, and a desire to determine why the unexpected outcome occurred-without placing blame on any individual. The culture reveals an organizational commitment to the collective success regarding the patient experience. So, if an individual creates an error-the questions are as follows: Where did the process break down Meeting Patient Needs Successfully meeting patient needs requires a broad understanding of those needs: emotional, physical, and experiential. Oftentimes, clinicians will emphasize outcomes, nursing staff will emphasize operational excellence and care, and administrators will focus on the business aspects, including access and branding. While different roles can better meet specific patient needs-what matters most to patients, and how you define it, should be understood by everyone within your organization. Moving to a patient-centered care model may require thinking outside of the "operations" box and investment of resources. I call them investments because each has come with a cost; however, the return on these investments has yielded better patient retention, lower dropout rates, and positive patient reviews. Our team approach to patient care has allowed the company to grow dramatically, but the patient remains at the center-with individualized care and a small dedicated team. For example, patients with a prenatal scan resulting in no heartbeat, or disappointing egg retrieval or fertilization results can see a psychologist within an hour at the expense of the Center. Thus, investing in the patient experience may not only reduce dropout but as we have seen it can attract new patients to your center as well. Continuous Quality Improvement Our goal is to achieve a 95% overall patient satisfaction score. We publish the results to our employees monthly via our company intranet because we want the patient experience to be front-of-mind for all of staff. Once we have identified issues, we commit to conducting a root-cause analysis-the results of which are presented at the subsequent monthly meeting. Together with an interdepartmental team, including clinicians and staff from each department, preferably at an off-site location (as not to be distracted with the day-to-day business), list on a whiteboard every single patient interaction. While one of the goals of this exercise is to ensure that the information patients receive will prepare them for a seamless clinical experience, another objective is to assess the "brand" of your practice. Once you have completed this exercise, you should make modifications to improve communication gaps and brand issues that have been revealed (Table 24. The level of care your patients receive-as well as their ultimate success-go hand in hand in their journey to parenthood. Further, as an organization, you have created expectations, which are viewed as promises by your patients.
The clinical examination should focus on assessing attention as well as noting other cognitive or perceptual disturbances acne 7 months postpartum purchase betnovate without prescription. Methods for assessing attention vary acne problems order betnovate online from canada, because there is no generally accepted means. Obtaining collateral information through chart review or discussion with staff and family is essential for establishing the acuity of symptoms, determining the existence of fluctuation in symptoms, and obtaining information regarding additional symptoms that may not be observed at the time of examination of the patient. Known or suspected comorbid dementia can complicate the evaluation for possible delirium. The core feature of delirium is impairment in attention, regardless of the presence of dementia. Inattention, disorientation, and noncognitive symptoms are more severe in individuals with delirium superimposed on dementia than in those with dementia alone (Meagher et al. When compared with persons with delirium alone, individuals with delirium superimposed on dementia manifest more psychomotor agitation, disorganized thinking, and disorientation (Cole et al. Identification of Etiologies Once the diagnosis of delirium has been made, a thorough medical evaluation is necessary to identify all potential causes of delirium. Updated vital signs, physical examination, and basic laboratory studies, including a complete blood count, comprehensive metabolic panel, and urinalysis, are appropriate. Additional aspects of the initial evaluation should be tailored to the specific risk factors and exposures of the patient. The medication list review is recommended, because medications, including many commonly used medications possessing anticholinergic properties, frequently contribute to the development of delirium (Han et al. Specifically, avoidance of new prescriptions of benzodiazepines, opioids, dihydropyridines, and histamine1 antagonists is recommended in those at risk of delirium, and caution is recommended with histamine2 antagonists, tricyclic antidepressants, antiparkinsonian medications, steroids, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, and muscarinic agents (Clegg and Young 2011). For situations in which a plausible etiology is not identified after initial investigation, additional evaluation is indicated. Additional laboratory studies, including, among other possibilities, serum medication levels, toxicology, cortisol, and thyroid-stimulating hormone, as well as imaging of head, chest, or other areas pertinent to the specific patient, should be considered. A more exhaustive search may be indicated, especially if the course of delirium is worsening, because worsening of the delirium suggests offending etiologies have yet to be addressed. Continuous electroencephalographic monitoring in older patients without an identifiable cause is reasonable. Evaluation for delirium etiologies Primary assessment Vital signs Interval physical examination (including neurological exam) Complete blood count Comprehensive metabolic panel Urinalysis with microscopy and culture Prescription drug levels Other studies focusing on known or suspected areas of pathology Secondary assessment Thyroid function Ammonia level Vitamin B12 Cortisol level Blood cultures Urine drug screen Arterial blood gas Sputum culture Posteroanterior and lateral chest radiograph Computed tomography of head Electrocardiogram Electroencephalogram Magnetic resonance imaging of brain Lumbar puncture Management There is no cure or definitive treatment for delirium. Management is often categorized into nonpharmacological and pharmacological interventions. A few professional organizations, such as the Society of Critical Care Medicine (Barr et al. As summarized and synthesized from these guidelines here, the goals of management are focused on secondary and tertiary prevention, such as reducing the duration and severity of delirium and minimizing any adverse sequelae. Nonpharmacological Interventions Many of the approaches used in delirium prevention are also useful as nonpharmacologic management interventions for continued use after delirium has been diagnosed (see section "Risk Factors and Prevention" earlier in this chapter). These nonpharmacological interventions focus on reducing the impact of predisposing factors and optimizing physiological conditions for the brain. Additionally, they aim to treat the syndrome itself through providing a stable and reassuring environment, avoiding complications such as aspiration pneumonia and prolonged immobility, providing rehabilitation, and promoting effective communication with families (Maclullich et al. Pharmacological Interventions Excluding alcohol withdrawal delirium, no medication is approved for or recognized by experts for treatment of delirium, nor does any medication have convincing evidence that supports its beneficial effects in treating delirium. On the basis of the anticholinergic theory of delirium, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors have been considered a potential pharmacological intervention that might act as a treatment, yet studies remain inconclusive. Although short-term use of low-dose antipsychotics may result in decreased severity scores of delirium symptoms in up to 75% of patients, it is unclear whether the medication serves to manage the symptoms or to treat the underlying syndrome (Meagher et al. Despite this lack of evidence, antipsychotic medications remain the most commonly used medications for managing symptoms of delirium.
Educational differences in cancer mortality among women and men: a gender pattern that differs across Europe skin care clinique buy betnovate with paypal. Measures of racial/ethnic health disparities in cancer mortality rates and the influence of socioeconomic status skin care owned by procter and gamble generic 20 gm betnovate overnight delivery. Impact of socioeconomic status on cancer incidence and stage at diagnosis: selected findings from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results: National Longitudinal Mortality Study. Determinants of late stage diagnosis of breast and cervical cancer: the impact of age, race, social class, and hospital type. Geographic remoteness, arealevel socioeconomic disadvantage, and advanced breast cancer: a crosssectional, multilevel study. Differences in socioeconomic status and survival among white and black men with prostate cancer. Cervical cancer mortality by neighbourhood income in urban Canada from 1971 to 1996. Early evidence of this came from studies documenting that cancer rates in successive generations of migrants shifted toward those of the host country. For example, colorectal cancer rates in 1950 in the third generation of Japanese immigrants to California approached those of white Californians [1, 2]. However, the cancer pattern in economically developing countries is changing; cancers associated with smoking, unhealthy diet, and overweight and obesity, such as lung, breast, and colorectal cancers, are becoming more common due in part to increasingly sedentary lifestyles associated with urbanization, as well as targeted advertisements by the tobacco and the food/beverage industries. The cancer burden in developing countries also is increasing because of the aging and growth of the population. This article provides an overview of the global descriptive epidemiology of commonly diagnosed cancers. Issues affecting global cancer information include lack of cancer registries and/or vital registration in many countries, incomplete coverage of the population, or inadequate quality of registration. Although the overall cancer incidence rate in economically developed countries in both males and females is nearly twice as high as the rate in economically developing countries, overall cancer mortality rates are generally similar between economically developed and developing countries. Reasons for this pattern include differences in awareness, detection practice, completeness of case reporting, and survival. Further, the most commonly diagnosed cancers in economically developing countries are more likely to be fatal. International Cancer Data Sources Major sources of data for research on global cancer include national or regional cancer registries for incidence and national or regional vital registration for mortality. Lung Cancer Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in men and the second leading cause of cancer death in women, with an estimated 1,099,000 deaths in men and 491,000 deaths in women in 2012 (Table 4. Smoking is the predominant cause of lung cancer, accounting for 80% of lung cancer deaths in men and 50% in women [3]. In men, the highest lung cancer mortality rates (per 100,000) are found in Eastern Europe and the lowest in SubSaharan Africa, ranging from 0. In females, rates are highest in Eastern and Northern Europe and North America and lowest in Sub Saharan Africa, ranging from fewer than three in most countries of Africa to 28. In addition to smoking and air pollution, other factors that increase lung cancer risk include environmental and occupational exposures to radon, asbestos, arsenic, certain metals.
Drug-induced changes combined with genetic vulnerabilities can produce craving that leads to relapse months or years after acute withdrawal resolves acne body wash cheap 20gm betnovate otc. Other brain areas acne under chin discount 20gm betnovate amex, such as the hippocampus and amygdala, create a lasting memory called conditioned association that links these good feelings and later craving with the circumstances and environment in which they occur. These cravings occur when the drug user reencounters those persons, places, or things that were associated with their drug use. Finally, the action decisions that lead to substance users making poor decisions and seeking out more drugs in spite of many obstacles and adverse health consequences involve a reduction in prefrontal cortex activity that otherwise inhibits drug craving leading to relapse (Goldstein and Volkow 2011). Thus, medication development to address abnormalities in the neurocircuitry for various substance use disorders is of primary importance. Positive subjective effects through brain reward circuitry are the primary reason that some people continue to take drugs, particularly in the early stages of drug use. However, the continued drive and the compulsion to use drugs build over time and extend beyond simple pleasure seeking. Chronic drug administration eventually leads to abnormal synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission that contributes to continued drug use. Overall, patient history and corroborating family member information are critical, and questions must be asked with nonjudgmental empathy and caring professional interest rather than confrontational challenging. Finally, the emergence of agitation, confusion, or delirium due to an unanticipated withdrawal syndrome is not rare and requires both an accurate diagnosis and institution of appropriate medical treatment for the withdrawal and for a follow-up that will reduce or prevent relapse to drug taking. Laboratory tests that assess biomarkers known to reflect drug consumption are very helpful. For example, laboratory tests can augment alcohol use disorder questionnaire screens. The Patient Placement Criteria algorithm developed by the American Society of Addiction Medicine attempts to match patients to their optimal intensity of care as defined within five levels of care (with sublevels) based on six dimensions (Mee-Lee et al. Individuals placed in treatments that are based on this algorithm have shown better outcomes than mismatched patients. First, a cross-tolerant, less harmful, and usually longer-acting medication can be substituted for the abused drug, such as lorazepam for alcohol or methadone or buprenorphine for heroin. The dosage is adjusted until withdrawal symptoms are minimized, and then the medication is gradually tapered off over several days. Second, non-cross-tolerant medications can be used to reduce withdrawal symptoms, such as clonidine for opioid withdrawal or carbamazepine for alcohol withdrawal. These medications can be particularly useful for outpatient procedures where the cross-tolerant medications have their own misuse potential. Craving has been newly added as a fourth criterion of impaired control, and this is manifested by an intense desire or urge for the drug that is more likely when in an environment where the drug previously was obtained or used. Risky use occurs in situations that are physically hazardous and involves continued use despite the knowledge of having a persistent or recurrent physical or psychological problem due to the substance. Neuropsychiatric Syndromes by Drug Class Alcohol the 2013 National Survey on Drug Use and Health indicated that half of people age 12 and older were current alcohol drinkers, 60. Intoxication Binge drinking frequently leads to intoxication, depending on numerous factors such as body weight, amount and type of alcoholic beverage, duration over which the alcohol was consumed, individual tolerance, metabolism, sex, and genetic makeup. However, other lethal complications of intoxication during chronic alcohol use may be associated with cerebral atrophy, predisposing individuals to subdural hematomas and disordered coagulation, rendering them liable to intracerebral hemorrhage after a fall. Withdrawal Withdrawal symptoms generally occur within 8 hours after stopping heavy or prolonged drinking and reach maximal intensity on day two and typically resolve by day four or five. Uncomplicated withdrawal with tremor, vascular headache, photophobia, irritability, and mild autonomic excitation generally does not require mediation. More severe early-stage withdrawal includes hyperreflexia and transient hallucinations. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures and postictal confusion and disorientation are more obvious severe signs and can be associated with disorientation and fluctuating levels of consciousness. For treatment of the signs and symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal, comorbid psychiatric and medical conditions related to nutritional and vitamin deficiencies need to be considered.
Patients with any kind of infertility diagnosis acne hoodie order betnovate on line, including endometriosis acne meaning 20 gm betnovate with visa, ovarian dysfunction, advanced age, male factor, premature ovarian failure, recurrent miscarriage, tubal blockage, and unexplained infertility, may attend. The groups include married heterosexual women, single women, lesbian women, and women with secondary infertility (although secondary patients may only have one child, women with more than one child are referred for individual counseling since their presence would be likely to upset the primary patients). Each session incorporates relaxation training, social support, and a new stress management strategy. Despite the fact that the first half-hour of social support is optional, virtually all participants choose to attend. This is their time to share their stories, compare experiences, and complain about their husbands/mothers-in-law/doctors. The next one is focused on self-nurturance, after which lifestyle habits are addressed. The next sessions are dedicated to cognitive approaches to stress reduction, such as cognitive restructuring, journaling to express negative emotions, and effective communication strategies. Group leader and peer counselor introductions, research on the stress/infertility connection, the physiology of the relaxation response, participant and partner introductions, program mechanicsa 2. Physiology of diaphragmatic breathing, mini-relaxation exercises, effective communication 3. The impact of lifestyle behaviors on fertility: weight, smoking, alcohol, exercise. All day Sunday session-couples yoga, the use of humor to reduce stress, goal setting, couples communicationa 8. Assertiveness, goal-setting, summary, goodbyes a Husbands/partners attend these sessions. At the first session, each participant is asked to describe what they hope to get out of the program, i. Then, at the 10th session, patients are asked whether or not they reached their goal. This tends to be a very emotional time, since each patient recounts her emotional state a mere 10 weeks ago and thanks the group, and group leader, for helping her get to such a much healthier place. At the 10th session, participants complete a similar but shorter questionnaire to the one they completed before the intake. Each patient is offered an appointment with the group leader to review their progress, compare their pre- with their post-program status, and set goals for their continued improvement. Patients consistently experience statistically significant reductions in all measured physical and psychological symptoms. As opposed to their sole identity as an infertile woman at the intake, they leave being a healthy active woman who happens to be experiencing infertility. Mind/Body Approaches versus Pharmacotherapy the most common treatment for depressive symptoms is medication. Recent research has shown that antidepressant medication is associated with a reduced probability of conceiving in women attempting to conceive naturally [38] and a negative impact on semen parameters in men [39]. Summary Women experiencing infertility report significant levels of emotional distress. Their distress can make them difficult to treat, may make treatment less effective, and increases their tendency to drop out of treatment, which might have been successful. Psychological interventions can decrease symptoms of anxiety and depression and are associated with increases in pregnancy rates. The psychological impact of infertility: A comparison to women with other medical conditions. Prevalence and predictors of major depressive disorder for fertility treatment patients and their partners. Suicidal risk among infertile women undergoing in vitro fertilization: Incidence and risk factors. Addressing the needs of fertility treatment patients and their partners: Are they informed of and do they receive mental health services