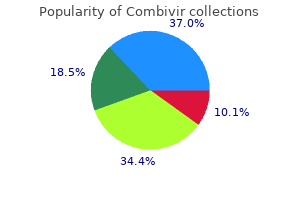
Combivir
"Purchase combivir in india, treatment management company".
By: I. Moff, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, Alpert Medical School at Brown University
It occurs when bones are forced out of alignment and usually is involved with a sprain treatment of strep throat buy discount combivir 300mg online. The most commonly dislocated joints are those of the jaw medications information generic combivir 300 mg with amex, fingers, thumbs, and shoulders. This means the ends of the bones must be returned to their proper positions by a physician. Usually, the meniscus receives a compression and shear stress simultaneously, resulting in tearing. Cartilage usually remains torn because it cannot usually and sufficiently 212 Chapter 8 Articulations repair itself. Loose bodies (fragments of cartilage) interfere with joint function because they cause binding or locking of the joint. Fortunately, the patient is usually able to leave the hospital the same day as the surgery. An arthroscope is used, which is very small, containing a miniscule lens and fiberoptic light source. Ligaments can be repaired or fragments of cartilage removed through one or several small slits. If only part of the meniscus is removed, mobility is not severely impaired, but the joint becomes much less stable. If the entire meniscus is removed, osteoarthritis usually develops in the joint earlier than normal. A meniscal transplant may be used for younger patients when cartilage is extensively damaged. Conditions such as arthritis and rheumatism are among the most prevalent complaints of elderly people. These conditions involve pain and stiffness in the joints, which may lead to immobility. Causes of arthritis include bacterial or viral infections, joint injuries, severe physical stress, and metabolic conditions. Arthritis Arthritis is a term that signifies more than 100 inflammatory or degenerative diseases, all of which damage the joints. Arthritis is the most common disease that results in crippling of movement in the United States, affecting one in five people. Acute arthritis usually develops from bacterial infections, whereas chronic arthritis includes the forms known as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gouty arthritis. Gouty Arthritis Gouty arthritis is a condition based on excessive, abnormal levels of uric acid deposited as needle-like urate crystals in soft tissues of joints. An inflammatory response is triggered and an extremely painful gouty arthritis occurs. Men experience gouty arthritis much more than women because of their naturally higher blood levels of uric acid. Medications include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, glucosteroids, and others. Dietary changes include increased water intake, avoiding alcoholic beverages, and avoiding foods such as kidneys, liver, or sardines, which are high in purine-containing nucleic acids. In people with osteoarthritis, more cartilage is destroyed than can be normally replaced. Most commonly, the joints of the cervical or lumbar spine, fingers, knuckles, knees, and hips are affected. Osteoarthritis develops slowly, is irreversible, and causes pain, joint stiffness, and inflammation. Treatments include pain relievers, moderate activity, capsaicin, and nutritional supplements. Degenerative joint disease occurs more commonly in women, usually affecting the knees and other weight-bearing joints and the distal finger joints. The skin at the inferior of the metatarsal-phalangeal joint has broken down and white granular material-the tophus-is extruding from the deft.
Divergence: the spread of information from a neuron to several other neurons or from one neuronal pool to additional neuronal pools medications like lyrica 300 mg combivir with visa. This means the postsynaptic neuron can be affected by several patterns of activity in the presynaptic neurons medications janumet combivir 300 mg visa. Some motor neurons can be under both conscious and subconscious control as a result of convergence. Serial processing: Information is relayed from one neuron to another or from one neuronal pool to another. For example, the relay of sensory information from one part of the brain to another. Parallel processing: When several neurons or neuronal pools process the same information at the same time. Reverberation: this resembles a positive feedback loop, because collateral axon branches along the circuit extend back to the source of an impulse and stimulate presynaptic neurons again. A reverberating circuit functions until it is broken by inhibitory stimuli or synaptic fatigue and can occur in one or more neuronal pools. Therefore, agents that block the voltage-gated sodium channels such as local anesthetics are extremely effective. Impulse conduction is also impaired by continuous pressure and cold temperatures, which interrupt blood circulation, slowing oxygen and nutrient delivery to neuron processes. This is why a body part goes to sleep if it receives pressure from the rest of the body and then recovers when the pressure is removed (causing a prickly feeling that is uncomfortable). Effects of Aging on the Nervous System Processing of Impulses Neurons and axons within the brain and spinal cord affect impulse processing. If the net effect of an input is excitatory, a threshold may be reached, triggering an outgoing impulse. If the net effect is subthreshold (but still excitatory), an impulse is not triggered but the neuron is more excitable to incoming stimulation than the neural tissues arise from the ectoderm, in response to its adjacent layer, the mesoderm. After birth, up to the age of three years, the brain triples in weight and establishes approximately 1,000 trillion nerve connections. Development of the frontal lobe increases greatly between six and 12 months of age. The prefrontal cortex portion of the frontal lobe is the final brain area to mature, resulting in developmental changes as late as adolescence. This area is the location of cognitive functions that include attention, motivation, and goal-directed behavior. Beginning at age 30, anatomic and physiological changes begin to affect the nervous system. As fatty deposits accumulate in the blood vessels, there is a decrease in blood flow to the brain. This can increase the chances that an affected vessel will rupture, leading to symptoms of a stroke (cerebrovascular accident). Cerebrovascular diseases are more common in long-term smokers or when conditions such as hypertension, high cholesterol, or diabetes mellitus are present. If no neurologic disorders are present, intellectual performance is usually maintained until about age 80. Because the brain processes nerve impulses more slowly, performance of certain tasks and reaction times often become slower. Other disorders that affect the nervous system due to aging include depression, hypothyroidism, and degenerative brain disorders. An elderly person who exercises (both mentally and physically) often loses fewer nerve cells in the brain. The spine is also affected by aging, and pressure increases on the spinal cord and spinal nerve roots. Peripheral nerve conduction slows because the myelin sheaths degenerate with aging.
As action potentials stimulate cardiac muscle fiber contraction treatment restless leg syndrome combivir 300 mg without prescription, a specific pattern appears-it is not the same as individual action potentials treatment 20 buy cheap combivir online. Typically, 12 leads or electrodes are used that respond to weak electrical changes by moving a pen or stylus on a moving strip of paper. The regular movement of the paper allows the distance between the pen movements to record the time between phases of the cardiac cycle. They measure voltage differences between both arms or between one arm and one leg. The total of 12 leads provides a complete picture of the electrical activity of the heart. A normal electrocardiographic pattern includes several waves or deflections during each cardiac cycle. The atria and ventricles are not connected by gap junctions even though they meet each other. Right and Left Bundle Branches the A-V bundle soon splits into the right and left bundle branches. These branches move along the interventricular septum toward the apex of the heart. Purkinje Fibers Nearly halfway down the septum, the right and left bundle branches spread into enlarged Purkinje fibers, extending into the papillary muscles. The Purkinje fibers have numerous small branches that become continuous with cardiac muscle fibers and irregular whorls. Purkinje fiber stimulation causes the ventricular walls to contract in a twisting motion to force blood into the aorta and pulmonary trunk. The Purkinje fibers are also referred to as the subendocardial conducting network. As the impulse reaches ventricular fibers, they quickly depolarize, showing a greater electrical change because of the thicker ventricular walls. Atrial repolarization is missing from the pattern because atrial fibers repolarize at the same time the ventricular fibers are depolarizing. The P-R interval includes atrial depolarization, contraction, and the passage of the depolarization wave through the remainder of the conduction system. The S-T segment occurs when the action potentials of the ventricular myocytes are in their plateau phases. It is the period from the start of ventricular depolarization through ventricular repolarization. Speed of Conduction From the time the S-A node generates an impulse until depolarization of the final ventricular muscle cells takes only 220 ms in a healthy heart. After the ventricular depolarization wave, ventricular contraction is nearly immediate. Some contained blood is ejected superiorly into the large arteries that leave the ventricles. The heart normally beats 75 times per minute because of the actions of the S-A node. If the S-A node was not there, the A-V node would depolarize approximately 50 times per minute. If the A-V node was not providing input, the A-V bundle and remainder of the conduction system would depolarize only approximately 30 times per minute, even though their conduction speed is extremely rapid. Instead of moving several meters per second in most areas, they would move only 0. Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Innervation When the body requires more blood, such as during exercise, the heart rate increases to pump more blood to the body. Parasympathetic fibers that innervate the heart arise from neurons in the medulla oblongata of the brain. Nerve impulses reach nerve fiber endings, secreting acetylcholine, decreasing S-A and A-V node activity, and decreasing heart rate. The cardioacceleratory center of the medulla oblongata projects to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in levels T1 to T5 of the spinal cord. These neurons synapse with postganglionic neurons located in the cervical and upper thoracic sympathetic trunk. Postganglionic fibers then run through the cardiac plexus to the heart, innervating the S-A and A-V nodes as well as the heart muscle and coronary arteries.
Syndromes
- Heavy menstrual cycles
- Arterial blood gases
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) II
- Poor muscle coordination that usually develops after age 10
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention - http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/CleftLip.html
- Fortified cereals
- Constipation
- Narrow bifrontal skull
It affects about 13% of the female population symptoms zollinger ellison syndrome order 300 mg combivir visa, arising from the epithelial cells of the smallest breast ducts severe withdrawal symptoms order combivir 300 mg with amex. Risk factors include family history, early onset menstruation, late menopause, no pregnancies, first pregnancy later in life, and no periods or only short periods of breastfeeding. Unfortunately, more than 70% of women who develop breast cancer have no known risk factors. It is diagnosed by skin texture changes, puckering of the skin, and nipple leakage. Simple, regular breast selfexaminations can find abnormalities before they have progressed significantly. Mammography, the X-ray examination that detects very small breast cancers, should be performed in women over 40 years of age every year. When diagnosed, breast cancer is treated with radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and/or surgery. Surgically, most physicians now recommend lumpectomy, which removes just the cancerous lump, or simple mastectomy, which removes only breast tissue and sometimes a portion of the axillary lymph nodes. Physiology of the Female Reproductive System Females release egg cells only from puberty to menopause, which occurs on average at around age 51. Although today we know that egg stem cells continue to survive throughout life, it has not yet been proven that the cells are viable for reproduction. Physiology of the female reproductive system includes the processes of oogenesis, the ovarian cycle, hormonal regulation, the uterine or menstrual cycle, and the female sexual response. Oogenesis Oogenesis is the process of egg cell formation, producing female sex cells. During the fetal period, the diploid stem cells of the ovaries or oogonia multiply quickly via mitosis. Eventually, primordial follicles appear, whereas the oogonia change into primary oocytes. However, they stall in the late part of prophase I and do not complete their division. Although there were seven million oocytes originally, at birth about one million have survived programmed death. Primordial follicles change into an enlarging collection of primary follicles over time. This process starts during the fetal period and continues until there are no more primordial follicles. In rare conditions, menopause occurs before age 40 and is known as premature menopause. During this time, some primary oocytes continue meiosis, with 23 chromosomes in their nuclei like their parent cells. In every cycle, one of these follicles becomes the dominant follicle and continues meiosis I. This eventually produces two haploid cells, with each having 23 replicated chromosomes, which are very different in size. A spindle forms at the edge of the oocyte, and a small nipple-like structure also appears. This produces a tiny second polar body and a large fertilized egg cell called a zygote. They allow for production of egg cells with massive amounts of cytoplasm and abundant organelles that carry the zygote through its first cell divisions, still with the right number of chromosomes. Ovarian Cycle the ovarian cycle is the monthly series of events linked to maturation of an egg. In the follicular phase, the dominant follicle is selected and starts to secrete significant amounts of estrogens. When this is the case, there are variations in the length of the follicular phase and the timing of actual ovulation. In younger females, estrogens stimulate development of the secondary sex characteristics.