Cleocin Gel
"Purchase cleocin gel online, acne cleanser".
By: M. Zarkos, M.S., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of Colorado School of Medicine
Stool studies for leukocytes the skincare shop 20gm cleocin gel, ova and parasite examination acne 5dpo purchase cleocin gel without a prescription, Giardia antigen, and Clostridium difficile antigen are all negative. A glucose hydrogen breath test is positive, with a rise in breath hydrogen excretion of >20 ppm within 30 minutes of ingesting 50 g of glucose. Within a week, she experiences a dramatic improvement of her symptoms, including bloating, flatus, and diarrhea. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and orocecal transit time in patients of inflammatory bowel disease. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in irritable bowel syndrome: association with colon motility, bowel symptoms, and psychological distress. Clinical predictors of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth by duodenal aspirate culture. Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: a meta-analysis. Jejunal bacterial overgrowth and intestinal permeability in children with immunodeficiency syndromes. Ileocecal valve dysfunction in small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: a pilot study. The relationship between small-intestinal bacterial overgrowth and intestinal permeability in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Restless legs syndrome in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: response to small intestinal bacterial overgrowth therapy. Restless legs syndrome is associated with irritable bowel syndrome and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Antimicrobial surveillance in idiopathic parkinsonism: indication-specific improvement in hypokinesia following Helicobacter pylori eradication and non-specific effect of antimicrobials for other indications in worsening rigidity. Frequency and factors associated with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with cirrhosis of the liver and extra hepatic portal venous obstruction. Small-intestinal bacterial overgrowth in cirrhosis is related to the severity of liver disease. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: histopathologic features and clinical correlates in an underrecognized entity. Breath tests for gastrointestinal disease: the real deal or just a lot of hot air Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in irritable bowel syndrome: are there any predictors Using breath tests wisely in a gastroenterology practice: an evidence-based review of indications and pitfalls in interpretation. A comprehensive metatranscriptome analysis pipeline and its validation using human small intestine microbiota datasets. Rifaximin versus chlortetracycline in the short-term treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Prevalence of small bowel bacterial overgrowth and its association with nutrition intake in nonhospitalized older adults. Clinical trial: the combination of rifaximin with partially hydrolysed guar gum is more effective than rifaximin alone in eradicating small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Case A 50-year-old Caucasian man presents with involuntary loss of weight, diarrhea, and fatigue 3 months after a visit to southern Mexico, where his diarrhea began acutely. Antibodies against endomysial and tissue transglutaminase are negative and the level of total immunoglobulin A is normal, making celiac disease unlikely. Giardia antigen and three stool samples are negative for the presence of cysts and trophozoites. Clinical Features Celiac disease has protean manifestations of variable severity that are summarized according to the "celiac iceberg" model as classical, atypical, silent, or latent [5]. In the iceberg model, some atypical cases, but most especially silent and latent celiac disease, are below the waterline [5]. Currently, non-classical symptoms are the clinical presentation in more than 50% of American patients with celiac disease [1]. Diagnosis Celiac Disease Definition and Epidemiology Celiac disease is an immune-mediated enteropathy induced by the ingestion of gluten (present in wheat, barley, and rye) in genetically susceptible individuals, which reverts to normal after the exclusion of gluten from the diet.
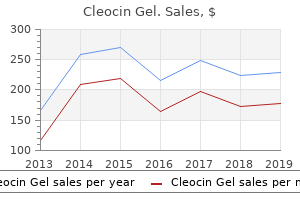
The cannula should be advanced to the level of the right atrium to allow good decompression of the right heart acne extraction dermatologist buy cleocin gel pills in toronto. If the femoral arteries are occluded bilaterally acne tips cheap cleocin gel 20 gm otc, it may be necessary to use an external iliac artery. Rather than following the femoral vessels up under the inguinal ligament, it is preferable to use an iliac fossa retroperitoneal approach. It should be exceedingly rare that axillary artery cannulation is required, although it is now being used regularly for adult cardiac surgery. Carotid artery cannulation is not recommended other than in extreme situations because there is a risk that cerebral blood flow will be compromised. On the other hand, innominate artery cannulation is often helpful, particularly when the femoral vessels are unavailable. The previous skin scar is usually excised and the sternal wires are cut and removed. The xiphoid process is divided and the linea alba is opened to allow a plane to be developed behind the lower end of the sternum. Rake retractors are used to elevate the lower end of the sternum off the heart and to provide a counter pressure to the oscillating sternal saw. Short segments of bone are cut through sequentially up to , but not through, the posterior table which is then divided with heavy scissors while visualizing the space behind the sternum. If a conduit is known to be close to the left side of the sternum it may be advisable to free up only the right half of the sternum until the retractor is placed. This will allow the pleural cavities to be drained at the completion of the procedure, but more importantly it allows the heart to be moved around more freely, thereby improving exposure without having to retract the chambers of the heart itself with undue force. When the bone incision has been completed and the sternal retractor is in place, dissection is begun using the electrocautery. Dissection should be begun in the space between the diaphragm and the inferior surface of the heart which is almost always a free space. Grasping the diaphragm with forceps and moving it up and down helps to identify the correct plane. Sufficient inferior right atrial free wall is cleared to allow placement of at least one venous cannula. Decompression of the right atrium allows dissection in this area to proceed more rapidly and safely. If the sternum is very narrow, it may be advisable to place the wires through the costal cartilage to increase the depth of the bite. If hemodynamic instability is severe and the surgical team has determined that there is no remediable anatomic cause, it may even be advisable to stent open the sternum. This can be done with the malleable Logan bow used for cleft palate surgery, although there are many innovative alternatives, such as a partial syringe. An iodoform impregnated adhesive plastic drape is then placed widely over the surgical site covering both the silastic patch and the exiting chest tubes, monitoring lines and temporary pacemaker wires. Bleeding can be reduced by accurate dissection in the less vascular planes that almost always exist between structures, no matter how many previous procedures have been performed. There is probably no single skill in the field of congenital surgery which seems to be as innate as the ability to see these tissue planes. Every surgeon will learn to find a blend of cutting and coagulation current that suits his or her dissecting style. For example, the woody edematous planes that are found in the child who has had a bidirectional Glenn shunt are best developed with a predominantly coagulation current with appropriate countertraction developed between the surgeon and assistant to open the plane. A strong coagulation current is often useful when taking lung adhesions down because very vascular adhesions will have developed, particularly to the heart itself, but also to the chest wall. However, once the pericardial cavity has been entered, it is often best to change to sharp dissection with curved tip Metzenbaum scissors. The curved tip is used to gently push the planes apart and to develop the adhesions which can then be cut.
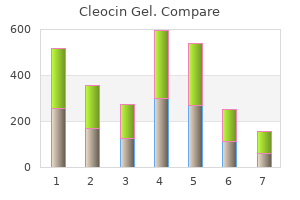
Surgical options include proctocolectomy with permanent ileostomy or total colectomy with ileal pouch anal anastomosis skin care brand crossword order 20gm cleocin gel. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Incidence acne zyme purchase cleocin gel, prevalence, and environmental influences. Indeterminate colitis: definition, diagnosis, implications and a plea for nosological sanity. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of iron deficiency and anemia in inflammatory bowel diseases. Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults (update): American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. European consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis: current management. American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and infliximab in inflammatory bowel disease. Increased risk of lymphoma among inflammatory bowel disease patients treated with azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine. The incidence and severity of this infection have increased in the last decade, probably related to the emergence of a highly toxigenic strain associated with hospital outbreaks. Recurrent infection usually responds to retreatment with these antibiotics, or to pulse-tapered therapy. Control measures to minimize the risk of hospital-acquired infections remain an important preventative strategy. Case A 68-year-old woman presents to the office complaining of a 2-week history of loose stool and abdominal cramps. She was treated by her primary care physician with amoxicillin for a sinus infection 1 month ago. These spores are resistant to heat and antibiotics, and widely contaminate the hospital environment. These alterations lead to apoptosis and disintegration of the epithelial barrier function. These effects result in colonic mucosal inflammation, microulceration, and, in some patients, pseudomembrane formation. Since 2000, Practical Gastroenterology and Hepatology Board Review Toolkit, Second Edition. The loose stool is usually non-bloody, and urgency or incontinence may develop in elderly patients. Peripheral edema or ascites has been observed, due to a secondary protein-losing enteropathy and hypoalbuminemia [13]. The development of fulminant colitis or megacolon will manifest as ileus and abdominal distension, accompanied by hypotension, diffuse guarding, and rebound tenderness or rigidity if perforation occurs. Associated features include dehydration, hypokalemia, colonic hemorrhage, perforation, and sepsis [16]. Once the patient starts treatment, stools may remain toxin-positive both during and after clinical recovery. We do not recommend repeat toxin assays to confirm elimination of toxin at the end of successful therapy, as many cured patients will be convalescent carriers. In some patients, the rectosigmoid may be spared, with signs of colitis only in the right or transverse colon. The risk of perforation is increased in patients with extensive ulceration or a dilated colon.
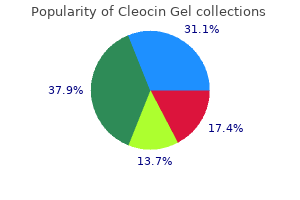
Midterm results of Ross aortic valve replacement: a single-institution experience acne 911 effective cleocin gel 20 gm. Inhibition of aortic wall calcification in bioprosthetic heart valves by ethanol pretreatment: biochemical and biophysical mechanisms skin care 9 discount cleocin gel express. Hydrodynamic characteristics of porcine aortic valves cross-linked with glutaraldehyde and polyepoxy compounds. Transcatheter aorticvalve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. Congenital mitral stenosis resulting from anomalous arcade and obstructing papillary muscles: Report of correction by use of ball valve prosthesis. Late results of mitral valve replacement with the Bjork-Shiley prosthesis in children under 16 years of age. Aortic root replacement in 372 Marfan patients: evolution of operative repair over 30 years. Long-term results of arterial switch repair of transposition of the great vessels. Since coronary blood flow occurs during diastole, there is a risk that coronary blood flow will be importantly compromised. If the communication is large and if pulmonary resistance is low, these anomalies can result in a severe degree of congestive heart failure. Aortoventricular tunnel is a closely related anomaly that shares some of the pathophysiologic features of these anomalies. In term infants, ductal closure usually occurs within the first 24 hours after birth. In preterm neonates, the immature ductal tissue is much less reactive to oxygen and persistent patency of the ductus is therefore much more likely. Relationship of the Ductus to the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Embryologically the ductus represents persistence of the distal component of the left sixth aortic arch. It is important to recall that the left sixth aortic arch originates in the neck (branchial = gill). Therefore, the left recurrent laryngeal nerve is carried down into the thoracic cavity as the heart and proximal great vessels migrate from a more cervical to a thoracic position. On the right side, there is usually resorption of the right sixth aortic arch, as well as the right fifth aortic arch. Thus, the right recurrent laryngeal nerve comes to pass around the remnant of the fourth aortic arch which persists as the right subclavian artery. Usually ductal closure occurs initially by constriction of smooth muscle within the wall of the ductus. There is subsequently fibrosis over several weeks and months and the ductus evolves to become the ligamentum arteriosum. During fetal life, the patency of the ductus is maintained by both local and circulating prostaglandin. After birth, increased pulmonary blood flow metabolizes prostaglandin and absence of the placenta removes an important source of prostaglandin. Subsequently, there is a marked decrease in the circulating level of prostaglandin. It is also 267 268 Comprehensive Surgical Management of Congenital Heart Disease, Second Edition arch at the junction of the arch with the proximal descending aorta. The ductus subsequently passes anteriorly to join the origin of the left pulmonary artery, thereby completing a vascular ring. However, the ductus does not always arise from the diverticulum of Kommerell in cases of right-sided aortic arch. When there is mirror image branching, that is, the first branch of the rightsided arch is an innominate artery which branches into a left subclavian artery and left common carotid artery, the ductus often arises more distally from the left subclavian artery or the innominate artery itself.