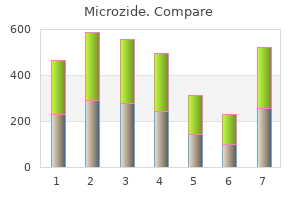
Microzide
"Order microzide visa, blood pressure chart kpa".
By: P. Ashton, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Professor, The Ohio State University College of Medicine
Analgesia implies sensory blockade only blood pressure medication cause weight gain buy generic microzide 12.5mg on-line, usually for postoperative pain management or labor analgesia low pressure pulse jet bag filter generic 25mg microzide with visa, and may be achieved with dilute local anesthetic or epidural opioids or a combination of the two. To provide adequate surgical blockade with an epidural anesthetic, it is necessary to know the innervation of the structures stimulated during the procedure. For example, a transurethral resection of the prostate requires a T8 level because the bladder is innervated by T8 through its embryologic origins. A laparotomy such as a cesarean delivery requires a T4 level to cover the innervation of the peritoneum. The block is most intense near the site of catheter insertion and diminishes with distance. The needle and catheter should be placed as close to the site of surgery as possible. In labor, the lower limit of block can be kept above the sacral nerve roots until the second stage of labor to preserve pelvic floor tone and the perineal reflex. The extent of epidural blockade is determined primarily by the volume of local anesthetic; more dermatomes are blocked by more milliliters of local anesthetic. To achieve a T4 level from a lumbar epidural catheter, 20 to 30 ml of solution is required. In some surgical procedures, controlled ventilation may be safer or more comfortable for the patient or may be necessary for the surgical procedure. Because these procedures often result in moderate to severe postoperative pain, an epidural anesthetic can be an ideal way to provide pain relief and aid in postoperative mobilization to prevent pulmonary and thromboembolic complications. By using the epidural catheter intraoperatively, smaller amounts of general anesthetic agents are required, which may result in fewer hemodynamic effects and faster awakening. A specific example of improved outcomes with this combined technique is for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in whom epidural analgesia contributes to lower postoperative pulmonary complications through faster ventilator weaning and decreased splinting. New evidence also supports that use of epidural anesthesia during breast, ovarian, and colon cancer surgery may improve patient survival. Any of these complaints requires a thorough neurologic examination to localize the deficit. This helps in confirming correct needle placement and giving an early warning of local anesthetic toxicity. The clinician must have knowledge of the anatomy, technique, and equipment necessary to perform the most appropriate block for a given situation. The use of aseptic technique, correct equipment (B-bevel needles, nerve stimulators, ultrasound), and basic physiologic monitoring is mandatory. Examples include direct trauma to the nerve or spinal cord by intraneural injection of local anesthetic, nerve laceration, vascular injury with resulting hematoma formation, or pneumothorax. Ester local anesthetics are derivatives of p-aminobenzoic acid, a known allergen, and therefore are more likely to cause allergic reactions than the amide local anesthetics. Any local anesthetic injected intravascularly has the potential for systemic reactions, including seizures and cardiovascular collapse. Knowledge of the anatomy of the target region and the surrounding structures is necessary. Knowledge of the equipment and of the pharmacology of local anesthetics is also required. Continuous aspiration is mandatory while advancing the needle; flow of blood or cerebrospinal fluid is an obvious sign that the needle needs to be redirected and the landmarks reevaluated. A paresthesia indicates close proximity to a nerve; and, depending on the technique being used, it might constitute the end point. Once it is determined that the needle is correctly positioned, a 1-ml test dose is administered.
Pheochromocytoma: Recommendations for clinical practice from the First International Symposium hypertension with cardiac involvement buy 12.5 mg microzide otc. Prolonged treatment with - and -blockers and sometimes metyrosine may be needed to palliate the symptoms of catecholamine excess arrhythmia tachycardia purchase microzide from india, which can be severe. Next, we will examine excess of cortisol or deoxycorticosterone as other adrenal causes of hypertension. Plasma chromogranin A or urine fractionated metanephrines follow-up testing improves the diagnostic accuracy of plasma fractionated metanephrines for pheochromocytoma. Rhabdomyolysis and acute myoglobinuric renal failure in a patient with bilateral pheochromocytoma following open pyelolithotomy. Clinical and genetic characteristics of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 and pheochromocytoma. Pheochromocytoma of the urinary bladder: A systematic review of the contemporary literature. Pheochromocytoma: Current perspectives in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Left ventricular thrombus and embolic stroke caused by a functional paraganglioma. Catecholamine metabolism: A contemporary view with implications for physiology and medicine. Current progress and future challenges in the biochemical diagnosis and treatment of pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. When should genetic testing be obtained in a patient with pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma in children: A review of medical and surgical management at a tertiary care center. Pheochromocytoma crisis induced by glucocorticoids: A report of four cases and review of the literature. Clozapine use presenting with pseudopheochromocytoma in a schizophrenic patient: A case report. A pheochromocytoma with normal clonidine-suppression test: How difficult the biochemical diagnosis Sympathoadrenal function in patients with paroxysmal hypertension: Pseudopheochromocytoma. Diagnosis of endocrine disease: Biochemical diagnosis of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Bilateral adrenal incidentalomas differ from unilateral adrenal incidentalomas in subclinical cortisol hypersecretion but not in potential clinical implications. A current review of the etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of pediatric pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Diagnosis and treatment of pheochromocytoma in an academic hospital from 1997 to 2007. Diagnosis and management of pheochromocytoma in an academic hospital 3 years after formation of a pheochromocytoma interest group. Subclinical Cushing syndrome is the most common hormonal disturbance arising from adrenal incidentalomas found by adrenal scans (Starker et al. Moreover, as milder and cyclical forms of Cushing syndrome have been recognized (Manenschijn et al. Hypertension is present in more than 75% of patients with Cushing syndrome (Feelders et al. In addition, adrenocortical cells may harbor "illegitimate" receptors, responding to unusual ligands (Bertherat et al. As many as 20% of these adrenal incidentalomas when initially recognized secrete cortisol in a partially unregulated manner, often in association with hypertension, diabetes, and generalized obesity (Rossi et al. Over 5 years, as many as 7% of those with initially normal cortisol regulation develop subclinical hyperfunction (Barzon et al.
Cortical blindness in severe preeclampsia: Computer tomography blood pressure medications with the least side effects order microzide 12.5mg amex, magnetic resonance imaging 7th hypertension discount microzide 12.5 mg online, and single-photon-emission computed tomography findings. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring for the early identification of hypertension in pregnancy. Prevalence, trends, and outcomes of chronic hypertension: A nationwide sample of delivery admissions. The relationship between pre-eclampsia and peripartum cardiomyopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. However, estrogen will continue to be used since nothing else will effectively prevent hot flushes (North American Menopause Society, 2012). In a prospective study of 1,000 postmenopausal and premenopausal untreated women followed for a median of 5. The maternal, cerebral circulation in pre-eclampsia: Investigations using Laplace transform analysis of Doppler waveforms. Potassium regulation and progesterone-aldosterone interrelationships in human pregnancy: A prospective study. Prevention of preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction with aspirin started in early pregnancy: A meta-analysis. Preeclampsia is associated, with the presence of transcriptionally active placental fragments in the maternal lung. Antihypertensive medication use during pregnancy and the risk of cardiovascular malformations. Adverse perinatal outcomes and risk factors for preeclampsia in women with chronic hypertension: A prospective study. Prospective study of oral contraceptives and hypertension among women in the United States. Calcium supplementation prevents endothelial cell activation: possible relevance to preeclampsia. Metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women: the influence of oral or transdermal estradiol on inflammation and coagulation markers. Accuracy of mean arterial pressure and blood pressure measurements in predicting preeclampsia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovascular and metabolic characteristics 40 years after hypertensive pregnancies: a longterm follow-up study of mothers. Effect of magnesium sulfate given for neuroprotection before preterm birth: A randomized controlled trial. Systematic review, and meta-analysis of preterm birth and later systolic blood pressure. Aldosterone, vascular endothelial growth factor, and preeclampsia: a mystery solved Kidney disease is an independent risk factor for adverse fetal and maternal outcomes in pregnancy. Clinical morbidities, trends, and demographics of eclampsia: A population-based study. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and cardiometabolic health in adolescent offspring. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A and aldosterone: Relevance to normal pregnancy and preeclampsia. Low-to-moderate alcohol consumption during pregnancy and child development-moving beyond observational studies. Cardiovascular risk factors in women who had hypertensive disorders late in pregnancy: a cohort study. Reproducibility of the tolerance-hyperbaric test for diagnosing hypertension in pregnancy. Calcium supplementation during pregnancy for preventing hypertensive disorders is not associated with changes in platelet count, urate, and urinary protein: A randomized control trial. Association between maternal alcohol consumption in early pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes.
Most of the reported mutations are gain-of-function missense mutations causing increased calcium influx blood pressure kit target buy microzide with american express, which may play a role in the regulation of actin polymerization blood pressure which arm buy microzide uk. Patients typically present with nephrotic syndrome in the third or fourth decade, with progressive renal failure over the next 10 years. Patients display either ambiguous external genitalia or normal-appearing female external genitalia. In Frasier syndrome, there is an increased risk of developing gonadoblastoma, but not Wilms tumor. The second, postzygotic mutation occurs in nephrogenic rests, resulting in the loss of heterozygosity and the development of Wilms tumors. These cases may present with isolated congenital or infantile nephrotic syndrome and have normal-appearing external genitalia. Karyotyping is recommended in all children with diffuse mesangial sclerosis to rule out male pseudohermaphroditism. The expanded matrix has a reticulated spongy appearance, which is best appreciated with silver stains, without increase in cellularity. Shrunken, sclerotic glomeruli surrounded by a corona of hypertrophied podocytes and immature glomeruli are commonly seen. A corticomedullary gradient of involvement is present, with more severe changes in the outer cortex and milder features in the inner cortex. Missense mutations and small in-frame deletions have a higher mean age at onset of renal disease and absence of neurologic abnormalities, suggesting that at least some of these may represent hypomorphic alleles (210). Most mutations are nonsense or frame-shifting mutations that lead to loss of function. Biallelic mutations are present in over 50% of cases and patients with two missense mutations have a milder phenotype (216). It is likely that this chromatin bundling protein causes altered transcription of other vital podocyte genes. The major integrin expressed by podocytes is 31, but there are also lower levels of other integrin heterodimers, such as 64. Renal manifestations include Fanconi syndrome, proteinuria or nephrotic syndrome, tubulointerstitial nephritis, cystic kidney disease, myoglobinuria, and renal failure (218). Although the prevalence of renal disease associated with the A3243 mutation is unknown, it may be relatively common because of its association with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The association of maternally inherited diabetes mellitus and deafness is seen in 0. When neurosensory deafness is present, progressive renal disease in patients with mitochondrial cytopathy is distinguished clinically from Alport syndrome by the absence of hematuria, severity of renal involvement in females, the lack of ultrastructural findings of Alport syndrome, steroid-induced diabetes mellitus, and neurologic findings (226,227). The clinical course is one of progressive renal failure in some but not all affected individuals (220,222,223,226). In nine patients with the mutation and prominent renal manifestations diagnosed as adults (mean age 35 years), Guery et al. Several investigators have noted the presence of a vasculopathy with hyalinosis of small arteries and myocyte necrosis (221,228). Electron microscopy shows podocyte injury manifested by cell body attenuation, pseudocyst formation, and binucleate forms and variable changes in the mitochondria including increased numbers, variations in size, shape, and outline, and disorganization and loss of cristae. Tubular epithelium also displays increased numbers of dysmorphic mitochondria, giving rise to a granular appearance by light microscopy, which may be a clue to the presence of a mitochondrial disease (229). One other patient presented at 5 days of life with oliguric kidney failure, renal biopsy showed severe extracapillary proliferation and death ensued at the age of 6 months from progressive epileptic encephalopathy (231). Interestingly, the renal symptoms in patients improved following oral coenzyme Q10 treatment. Possible mechanisms may include increased apoptosis, impaired nucleotide metabolism, loss of antioxidant function, and increased autophagy, all of which have been linked to CoQ10 deficiency.
Assisted reproductive technology and pregnancy-related hypertensive complications: a systematic review prehypertension heart attack discount microzide 12.5mg. Maternal hypertensive disorders in pregnancy and self-reported cognitive impairment of the offspring 70 years later: the Helsinki Birth Cohort Study blood pressure chart for age 50+ order microzide with a visa. Early and late preeclampsia: Two different maternal hemodynamic states in the latent phase of the disease. Blood pressure in 12-year-old children is associated with fatty acid composition of human milk: the prevention and incidence of asthma and mite allergy birth cohort. New gestational phasespecific cutoff values for the use of the soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1/placental growth factor ratio as a diagnostic test for preeclampsia. Differential effects of oral versus transdermal estrogen replacement therapy on C-reactive protein in postmenopausal women. Soluble (pro)renin receptor and blood pressure during pregnancy: a prospective cohort study. Maternal caffeine consumption during pregnancy and the risk of miscarriage: A prospective cohort study. This chapter will describe the features of hypertension in children and adolescents and will also examine the increasingly strong evidence that the genesis of adult cardiovascular disease has its origins in childhood (Expert Panel, 2011). Initially, the thresholds used for defining hypertension in the young were the same as those used in adults. Unsurprisingly, hypertension was found to be exceedingly rare in young children but could affect up to 2% of adolescents Table 16-1). The impact of the childhood obesity epidemic on the prevalence of hypertension in the young can be seen in several recent studies from the Houston Screening Project (McNiece et al. In multiple publications, these investigators have demonstrated an increased prevalence of hypertension among obese children-as high as 4. According to this analysis, the prevalence of prehypertension has now reached 10% and the prevalence of hypertension nearly 4%. Similar findings have been seen in screening studies performed in other countries, including China (Cao et al. The significance of hypertension in the young is further underscored by the many studies documenting the occurrence of hypertensive target organ damage in children and adolescents. However, the strength of tracking appears to decrease with longer periods of follow-up (Chen & Wang 2008; Toschke et al. In view of the higher prevalence of hypertension in black adults than in white adults, comparisons of the tracking phenomenon in black and white children have been made (Lane & Gill, 2004). While longstanding hypertension has long been recognized as a risk factor for the development of cognitive impairment and even dementia in the elderly (Paglieri et al. In a recent follow-up study, hypertensive children were found to have decreased executive function that was associated with decreased cerebrovascular reactivity in response to hypercapnia (Ostrovskaya et al. Fewer pediatric data are available on the other major target organ effect of hypertension, namely renal damage. Taken together, these data indicate that over time, adult morbidity and mortality will be more tightly connected with childhood precursors and emphasize the need for early intervention (Expert Panel, 2011). The Critical Role of Obesity Obesity is growing at an alarming pace among children and adolescents in all developed societies, with-as in many other aberrant behaviors-the U. Unfortunately, adolescent obesity tracts closely with adult obesity (Kvaavik et al. Some factors are either genetic or environmental, but most have contributions of both. The pathophysiologic links between childhood obesity and the development of hypertension, including the crucial role of sympathetic nervous system activation, have recently been reviewed (Flynn, 2013). Whether there is more to breastfeeding than a reduced rate of excess weight gain (Grummer-Strawn & Mei, 2004) is uncertain, but slower early growth appears to be beneficial for longterm cardiovascular health (Singhal et al. Recently published studies have demonstrated that a large percentage of children and adolescents with primary hypertension have positive family histories of hypertension in a parent or grandparent (Flynn & Alderman, 2005; Robinson et al.