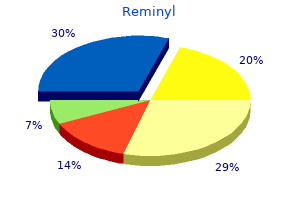
Reminyl
"Order reminyl line, treatment 10".
By: I. Curtis, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Creighton University School of Medicine
Multiphasic pills contain variable amounts of estrogen and progestin for 21 days medications list template reminyl 4mg without prescription, also followed by a 7-day placebo phase treatment trichomoniasis cheap reminyl 4 mg with visa. There are no published data demonstrating increased safety or efficacy with the multiphasic tablets compared to monophasic tablets. The inclusion of 3 additional days of active pills to shorten the pill-free interval has been shown to reduce hormone fluctuation between menstrual cycles. No significant differences have been found with regard to bleeding and spotting in those with extended use. In the first 21 days postpartum (when the risk of thrombosis is higher), estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives should be avoided (see Table 79-3). Continuous combination regimens provide a shortened pill-free interval, from the traditional 7 days to 2 to 4 days. These various extended-cycle regimens may be beneficial for women with symptoms such as dysmenorrhea, severe premenstrual syndrome, or menstrual migraines. Patient education and early reevaluation within 3 to 6 months are necessary to identify and manage adverse effects, in an effort to improve adherence. Women on extended-cycle regimens should be counseled to expect this during the first 6 months. For women experiencing bleeding irregularities beyond the recommended time-frame, then several different methods, including on the first day of bleeding during the menstrual cycle, on the first Sunday after the menstrual cycle begins or on the fifth day after the menstrual cycle begins. The most popular "Sunday start" method is to begin pills on the first Sunday after the menstrual cycle begins, as this may provide for weekends free of menstrual periods. It may be preferable to have women use additional contraception for the entire first cycle, due to user failure in the first month. Of all antibiotics, rifampin is the one with a true documented pharmacokinetic interaction. Women should be given the package insert that accompanies all estrogen products and instructed to read it. Although several transient self-limiting side effects often occur, the patient should be Patient Instructions with Oral Contraceptives 4 aware of the danger signals that require immediate medical attention (see Table 79-5). Patients should be told the importance of routine daily administration to ensure consistent plasma concentrations and improve adherence. If one tablet is missed or late then take the tablet as soon as remembered and continue taking the rest of the tablets as prescribed (for most women that means two tablets taken on the same day). If two or more consecutive tablets are missed then take one missed tablet as soon as remembered and discard the remaining missed tablets. If tablets were missed in the last week of hormonal tablets then omit the hormone-free interval by finishing tablets containing hormones and then starting a new pack. Counsel to use additional nonhormonal contraception until tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days. If a woman forgets a tablet or is more than 3 hours late then additional nonhormonal contraception should be used for 48 hours. Evidence suggests that higher exposure to estrogen may lead to increased thromboembolic risk, and the labeling for the contraceptive patch now contains a warning of this risk. If there is delayed application for less than 48 hours since patch should have been applied or detachment less than 24 hours, a new patch should be applied immediately, or the detached patch can be reapplied, with no additional nonhormonal contraception necessary. If there is delayed application for 48 hours or more since the patch should have been applied or detachment for 24 hours or more, a new patch should be applied as soon as possible, and additional nonhormonal contraception should be utilized until the patch has been worn for 7 consecutive days. If the delayed application or detachment occurs in the third patch week, the hormone-free week should be omitted and a new patch should be applied immediately. If vomiting or diarrhea persists greater than 48 hours then continue taking tablets and use additional nonhormonal contraception until tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days after the vomiting or diarrhea subsides. If this scenario occurs during the last week of the hormonal tablets, then finish the tablets, skip the hormone-free tablets and begin a new pack. Additional nonhormonal contraception should be used until 7 consecutive days of tablets are taken without gastrointestinal symptoms. If amenorrhea does continue beyond 6 months, women should be counseled to see a physician for further fertility work-up.
Although each measurement has a normal range (see Table 52-3) medicine 54 543 reminyl 4mg with amex, it is often easiest to consider the midpoint of each range as the normal value treatment deep vein thrombosis purchase cheap reminyl on-line. Under normal circumstances, the pH difference between arterial and mixed venous blood is not clinically significant. However, the oxygenation difference between arterial and mixed venous blood is always substantial. This value is lower than the value of 12 mEq/L (mmol/L) cited in the literature in the past because of changes in the instrumentation for measurement of serum electrolytes. The metabolic acidosis observed in patients with kidney disease is initially hyperchloremic but can progress to an anion-gap acidosis as kidney disease progresses and sulfates, phosphates, and other anions accumulate. Hyperaldosteronism predisposes to the development of hyperkalemia, which results in further impairment of ammoniagenesis. Treatment to control the hyperkalemia is usually sufficient to reverse the metabolic acidosis, and mineralocorticoid replacement is frequently unnecessary. Patients with this defect have impaired tubular potassium secretion in addition to impaired urinary acidification (urine pH more than 5. Normally, more than 85% of filtered bicarbonate is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. Defects in proximal tubular bicarbonate reabsorption result in increased delivery of bicarbonate to the distal nephron, which has a limited capacity for bicarbonate reabsorption. As a result, at a normal serum bicarbonate concentration, the filtered bicarbonate load is incompletely reabsorbed, and is lost in the urine. As the serum bicarbonate concentration decreases, the filtered load of bicarbonate is proportionately decreased. A new equilibrium is established in which the kidney is able to reabsorb the filtered bicarbonate load, albeit at a reduced serum bicarbonate concentration. These patients are able to acidify their urine in response to an acid load, but develop bicarbonaturia at a reduced serum bicarbonate concentration following bicarbonate loading. The impaired bicarbonate reabsorption results in salt wasting and secondary hyperaldosteronism. Hypokalemia, which can be severe, usually develops as a result of the hyperaldosteronism and bicarbonaturia. The renal potassium wasting decreases considerably if bicarbonate therapy is administered. States of enhanced metabolic activity (eg, grand mal seizures, strenuous exercise, or hyperthermia), decreased tissue oxygen delivery (eg, severe anemia, hypoxia, circulatory shock, or carbon monoxide poisoning), or impaired oxygen utilization (eg, cyanide toxicity) all are associated with lactic acidosis. Impaired hepatic clearance of lactate, as seen in hypoperfusion states, liver failure, and alcohol intoxication, can also result in lactic acidosis. Cardiovascular and septic shock, with resultant tissue hypoperfusion, are the most common causes of lactic acidosis. The mortality rate of this type of lactic acidosis can be as high as 80% and correlates with the degree of hyperlactatemia. Lactic acidosis associated with liver disease, toxins, and congenital enzyme deficiency can be caused by deranged oxidative metabolism or impaired lactate clearance. Lactic acidosis in neoplastic disease is uncommon and reported mostly in patients with myeloproliferative disorders. In the case of a large tumor or tightly packed bone marrow, oxygenation can be decreased, favoring the accumulation of lactate. Lactic acidosis has been reported in patients with massive liver tumors, and it has been postulated that the liver uptake of lactate is decreased in these patients. Lactic acidosis associated with seizures is usually transient and occurs because of excessive muscle activity. The primary suspected mechanism for metformin-induced lactic acidosis is inhibition of liver gluconeogenesis as the result of its inhibitory effects on pyruvate carboxylase, which is necessary for the conversion of pyruvate to glucose. Metformin should be discontinued during periods of tissue hypoxia (eg, myocardial infarction, sepsis), for 3 days after contrast media has been administered or 2 days before general anesthesia administration. Linezolid inpairs mitcochondrial function and has been rarely reported to cause lactic acidosis, usually after prolonged (more than or equal to 4 weeks) therapy. The normal plasma lactate concentration in healthy subjects is approximately 1 mEq/L (mmol/L). Lactic acidosis is considered to be present when lactate concentrations exceed 4 to 5 mEq/L (mmol/L) in an acidemic patient.
The appropriate use of medications-and antipsychotics in particular-for the management of behavioral disturbances in patients with dementia continues to be controversial treatment kawasaki disease order 8 mg reminyl otc. Nonpharmacologic approaches are considered first-line therapy medicine 2 discount reminyl 4mg mastercard, but evidence for individual nonpharmacologic strategies is often lacking. Additionally, commonly cited institutional barriers to implementing nonpharmacologic approaches include education and training, staffing resources and time, and availability of necessary supplies or equipment. When nonpharmacologic approaches fail, selected antipsychotics and antidepressants have been useful for effective management of behavioral, psychotic, and depressive symptoms, thereby easing caregiver burden and allowing the patient to spend additional time at home. All too often, however, nonpharmacologic measures are not implemented appropriately and medication overuse is an ongoing problem. Recommendations for patients with renal or hepatic dysfunction or low body weight are detailed in Table 54-6. The potential for adverse events due to drug interactions increases as the number of medications increases. Cognitive status, physical status, functional performance, mood, and behavior all need to be evaluated before initiation of drug therapy. The clinician should interview both the patient and the caregiver to assess response to drug therapy. These could include, for example, "striking at spouse because patient believes spouse is an impostor," "verbal threats and refusal to allow clothes to be changed," and so on, as opposed to documenting vague symptoms such as "aggression" or "delusions. The patient should be observed carefully for potential side effects of drug therapy. The specific side effects to be monitored and the method and frequency of monitoring should be documented. Patients should be monitored for therapeutic effect 8 weeks after initiation of therapy and at least every 6 months thereafter. The effects of cognition-enhancing medications will not necessarily be obvious, and a treatment period of several months to a year may be necessary before it can be determined whether therapy is beneficial. Cognitive effects of the drug are often noticed only as a plateauing during treatment or as deterioration following drug discontinuation. In general, cognitive agents should be continued if the patient is demonstrating no change in clinical status. However, if there is doubt, the medication can be slowly tapered and discontinued, and the patient monitored off the drug for 4 to 6 weeks to determine the need for continued therapy. Alzheimer disease in the United States (2010-2050) estimated using the 2010 census. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1996. Cumulative use of strong anticholinergics and incident dementia: A prospective cohort study. Translating research into practice: Case study of a community-based dementia caregiver intervention. Non-pharmacological interventions for behavioral symptoms of dementia: A systematic review of the evidence. Mild cognitive impairment in clinical care: A survey of American Academy of Neurology members. Effect of treatment gaps in elderly patients with dementia treated with cholinesterase inhibitors. A Risk-Benefit Assessment of Dementia Medications: Systematic Review of the Evidence. The cognitive benefits of galantamine are sustained for at least 36 months: A long-term extension trial. Dual use of bladder anticholinergics and cholinesterase inhibitors: Long-term functional and cognitive outcomes. Memantine treatment in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer disease already receiving donepezil: A randomized controlled trial. A 24-week open-label extension study of memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. Open-label, multicenter, phase 3 extension study of the safety and efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer disease. Position statement of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry regarding principles of care for patients with dementia resulting from Alzheimer disease. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association.

Teriflunomide carries a black-box warning because of the risk of hepatotoxicity and teratogenicity (based on animal data) medicine interactions order 4mg reminyl mastercard. Animal studies have found that oral teriflunomide resulted in fetal malformations and embryolethality in female rats as well as reduced sperm count in male rats treatment quincke edema proven reminyl 4 mg. Therefore, teriflunomide is contraindicated in pregnancy and in women of childbearing potential not using reliable contraception. Patients who become pregnant during therapy or within 2 years after discontinuation of therapy should enroll in the Aubagio Pregnancy Registry and consider a cholestyramine washout. Additionally, men taking this medication with partners who wish to become pregnant may consider a cholestyramine washout to reduce serum drug levels, as this drug may remain in the blood for up to 2 years after discontinuation. Teriflunomide may activate tuberculosis so a negative skin test or treatment of the disease must be documented prior to starting therapy. Dimethyl fumarate is dosed initially at 120 mg (delayed release) orally twice daily. After 7 days, the dose should be increased to 240 mg (delayed release) orally twice daily. The medication works by inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase to prevent the proliferation of peripheral lymphocytes (T and B cells). Teriflunomide is the active metabolite of leflunomide, an agent approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; however, teriflunomide is dosed as 7 or 14 mg orally once daily. Patients receiving 7 or 14 mg daily of teriflunomide had a statistically significant reduction in annualized relapse rate compared with placebo (relative risk reductions: 31. The risk of disability progression was statistically significantly reduced for those receiving 14 mg of teriflunomide daily (hazard ratio reduction: 29. A statistically significant reduction in the primary endpoint was reported for both 7 and 14 mg of teriflunomide compared with placebo (0. Moreover, there are single case reports of spirochetal gingivitis, pyogenic granuloma, esophageal candidiasis, tuberculosis, and listeria meningitis; the latter leading to dietary advice to avoid, for example, unpasteurized cheese. Secondary autoimmune disease affects approximately 30% to 40% of patients, predominantly impairing thyroid function. Thyroid autoimmune disease mainly comprised hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, goiter, and thyroiditis. This complication can occur at any time ranging from 1 to 34 months post-alemtuzumab administration. Additionally, glomerulonephritis and single cases of autoimmune neutropenia, hemolytic anemia, and type 1 diabetes have been reported. According to the labeling information, 12 mg of alemtuzumab are infused for five consecutive days in the first course and for 3 days in the second course 1 year later. Currently, alemtuzumab therapy is 6 Neurologic Disorders Remaining Questions for Disease-Modifying Therapy 9 Despite encouraging results from well-conducted clinical trials, several relevant issues remain. Key recommendations regarding treatment and access considerations are summarized in Table 55-5. Clearly, these drugs slow the course of the illness but do not suppress it completely, and in some individuals, there is no apparent benefit. There is now, however, overwhelming evidence that the vast majority of untreated patients will have progressive disease over time. Pathologic data clearly show that even in acute lesions there is significant axonal damage that is essentially irreversible. There are no general consensus guidelines regarding when to test for neutralizing antibodies, which assay to use, or what titer cutoff to apply to patients in clinical settings. A second option is addition of an immunosuppressant agent, such as monthly methylprednisolone,113 azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate. This section addresses the primary symptoms in which pharmacologic management may be of benefit (Table 55-6). Gait Difficulties and Spasticity Problems with gait can be caused by spasticity, weakness, ataxia, defective proprioception, or a combination of these factors. Spasticity often presents late in disease and is amenable to pharmacologic intervention, whereas physical therapy may be required in treating gait disturbances caused by other factors. Spasticity is encountered commonly and tends to affect the legs more markedly than the arms. Spasticity can result in falls; however, in the later stages of the disease, the increased muscle tone of a spastic limb often lends pseudo strength to patients with underlying weakness. Therefore, when using muscle relaxants, one must be careful not to decrease the tone to an extent that ambulation is actually hindered.
Intraurethral alprostadil is generally reserved as a treatment of last resort for patients who do not respond to other less invasive and more effective forms of therapy symptoms gerd discount reminyl 4mg online, and who refuse surgery medicine river animal hospital purchase reminyl 4 mg with visa. Pharmacokinetics Intracavernosal injection should be administered into only one corpus cavernosum. From this injection site, the drug will reach the other corpus cavernosum through vascular communications between the two corpora. Local 15-hydroxy dehydrogenase in the corpora cavernosum quickly converts alprostadil to inactive metabolites. Any alprostadil that escapes into the systemic circulation is deactivated on first pass through the lungs. Hence, the plasma half-life of alprostadil is approximately 5-10 minutes, and the potential for systemic adverse effects is negligible. The usual dose of intracavernosal alprostadil is 10 to 20 mcg, with a maximum recommended dose of 60 mcg. Doses greater than 60 mcg have not produced any greater improvement in penile erection, but may cause hypotension or prolonged erections lasting more than 1 hour. The manufacturer recommends that patients be slowly titrated up to the minimally effective dosage to minimize the likelihood of hypotension. Thus, many physicians start the patient on 10 mcg and move quickly up the dosage range to identify the best dose for the patient. To avoid adverse effects, patients should receive not more than one injection per day and not more than three injections per week with a 24-hour interval between doses (see Table 83-3). A tuberculin syringe or a syringe prefilled with diluent as supplied by the manufacturer should be used to ensure precise measurement of doses. Patients with needle phobia, poor vision, or poor manual dexterity can use commercially available autoinjectors to facilitate administration of intracavernosal alprostadil. Intracavernosal injections require that the patient or the sexual partner practice good aseptic techniques (to avoid infection), have good manual skills and visual ability, and be comfortable with injection techniques. When practicing self-injection, the patient should use one hand to firmly hold the glans penis against his thigh to Dosing Intracavernosal Alprostadil Efficacy the overall efficacy of intracavernosal alprostadil is 70% to 90%. The mean duration of erection is directly related to the dose of alprostadil administered and ranges from 12 to 44 minutes. A higher percentage of patients with psychogenic and neurogenic erectile dysfunction respond to alprostadil at a lower dose compared to patients with vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. Tolerance does not appear to develop with continued use of intracavernosal alprostadil at home. Depending on the study and the length of observation, 30% to 50% of patients voluntarily discontinue therapy, usually during the first 6 to 12 months, and this increases to 54% and 67% 1329 with large doses and repeated administration of papaverine, penile scarring secondary to alprostadil appears to be unpredictable. The pain has been described as a burning discomfort or dull pain near the injection site or during the erection, which generally does not persist after the penis becomes flaccid. The pain usually is mild, generally does not require discontinuation of therapy, and often abates even with continued treatment. However, 2% to 5% of patients discontinue taking alprostadil because of severe pain. One investigator has recommended adding procaine to intracavernosal alprostadil, but this may mask the signs of more serious adverse effects of the drug or of penile injury during intercourse and is not recommended. Alprostadil is acidic, and the commercially available Caverject formulation is buffered with sodium citrate, a weak base, to reduce pain on injection. Priapism, a prolonged, painful erection lasting more than 1 hour, occurs in 1% to 15% of treated patients. Blood sludging in the corpora can lead to tissue hypoxia and irreversible cavernosal fibrosis and scarring. The risk for this complication is greatest for erections that persist beyond 4 to 6 hours. Patients are advised to seek medical attention immediately when drug-induced erections last more than 4 hours, as this may progress to a urologic emergency. Its management includes supportive care, including analgesics for pain and sedatives for anxiety.