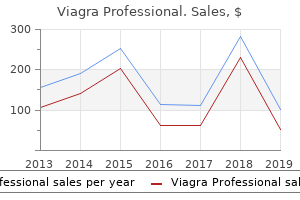
Viagra Professional
"Order viagra professional from india, erectile dysfunction causes psychological".
By: Z. Sven, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Program Director, Howard University College of Medicine
The ship subsequently spent 4 days in an Asian port during which time the crew had the opportunity to meet local prostitutes and barmaids impotence is the effective viagra professional 100mg. After leaving port impotence by smoking buy cheap viagra professional 50 mg, a sample of 537 men were again examined for gonorrhoea infection and 54 were now positive. This important piece of extra Measuring Infectivity 153 information was provided from the clinic that the registered prostitutes had to attend for bimonthly check-ups. About 511 out of the approximately 8000 prostitutes in the area attended this clinic during the days when the ship was in port and they were all examined for gonorrhoea. The next step in the calculations requires two assumptions: the first is that the 511 women examined constituted a representative sample of all the women that the crew could have met. The second is that the men chose women randomly as regards the infectious status: the women who were infected should not have higher or lower probability of becoming a partner than the ones who were not infected. This is a good place to introduce a parenthesis about the calculation of risk in such situations. Risks cannot be added like that, and the problem is somewhat similar to the discussion of risks and rates in Chapter 10. The reason for this is that the way of becoming infected in, say, the third intercourse is to escape infection in the first two, and then being infected in the third. The simplest way to estimate the total risk is as follows: first calculate the probability of not being infected at all during the four intercourses. This is equal to the chance of escaping infection the first time, which is 75%, multiplied by the chance of not being infected the second time, which is again 75%, and so on. Dose Another important aspect of infectivity concerns the dose of the pathogen that a susceptible person receives. In most real-life situations, it becomes almost impossible to measure the infective dose, counted as number of bacteria or viruses. How do we know exactly how many virus particles a measles case spreads when coughing How many of these must enter a susceptible individual to cause infection and/or disease We know that the blood of an acute case of hepatitis B may contain up to 109 virus particles per millilitre, but in the study of percutaneous, accidental transmission in the hospital, how do we know the exact volume of blood inoculated into a susceptible person Several such trials took place in the United States in the 1950s and 1960s, and used prisoner volunteers as subjects. It is doubtful that they would have passed the scrutiny of an ethics committee today. In one such experiment [5], controlled doses of Salmonella bareilly were dissolved in water and given to three groups of six volunteers. A possible error in calculations such as these is that some of the ill subjects were not infected in the experiment, but that they became secondary cases to some real primary case. Changes in agglutination titres (a serological, rather crude test for salmonella infection) were also measured in all subjects, but only showed any rise in four of the seven cases. That is, two of the subjects only excreted Salmonella on the day of the trial, three of them continued to excrete Salmonella during the next day, but not longer, and so on. Most of the subjects who did not fall ill thus excreted the bacteria for a day or two only which may have been just those bacteria they had ingested. In a similar study of typhoid [6], volunteers were given controlled doses of Salmonella typhii with a 106 variation in number of bacteria given (Table 14. Another example of experimental infection comes from a study of gonorrhoea in male volunteers in the United States in the early 1990s [7]. A controlled dose of gonococci, ranging from 104 to 106 bacteria, was instilled in the urethra with a catheter in 47 men. For bacterial enteric infections this becomes possible if some part of the infected food item remains and can be tested after the outbreak has been discovered. One example comes from an outbreak of Salmonella eastbourne in North America in 1974 [8]. Shortly after the detection of the outbreak, a telephone-based case control study was undertaken, interviewing 28 cases in different states. Only primary cases in each family were interviewed and each family was asked to name two controls.
Enrichment methods may be used to isolate and cultivate specific soil microorganisms for the production of industrial products such as steroids erectile dysfunction world statistics order generic viagra professional line, enzymes erectile dysfunction pills free trial buy viagra professional online from canada, and vitamins. Likewise, a beneficial environmental application may involve the isolation by enrichment of petroleum-utilizing microorganisms, such as Pseudomonas, that would be capable of degrading environmentally destructive oil spills in waterways. In this experimental procedure, a compost or a rich garden soil sample will be used to isolate Pseudomonas species by means of the enrichment culture procedure. Members of the genus Pseudomonas can utilize mandelic acid aerobically as their sole carbon and energy source. Therefore, this compound is the most important factor in the enrichment broth, which also contains a number of inorganic salts. The pseudomonads are gram-negative, motile organisms that generally produce a diffusible yellow-green pigment. By increasing the number of bacteria present in a media that is enriched, thus lowering competition, bacterial species with low numbers may increase their percentage of the population and increase the chances of their identification. Equipment Sterile 10-ml, 5-ml, and 1-ml pipettes, mechanical pipetting device, microspatula, Bunsen burner, staining tray, glass slides, lens paper, bibulous paper, inoculating loop, and glassware marking pencil. Inoculate an appropriately labeled Erlenmeyer flask containing the enrichment broth by adding an amount of the soil sample equivalent to the size of a pea with a microspatula. If growth is not present, return the flask to the incubator for an additional 24 hours. If growth is present, aseptically transfer 1 ml of the primary culture to an appropriately labeled Erlenmeyer flask containing fresh enrichment medium. Aseptically perform a four-way streak inoculation on an appropriately labeled agar plate of the enrichment medium. Record your observations of cellular morphology and Gram reaction in the Lab Report. Pick a discrete colony and aseptically inoculate a Trypticase soy agar slant by means of a streak inoculation. If growth is present in the secondary broth culture, aseptically perform a four-way streak inoculation on the appropriately labeled agar plate of the enrichment medium (refer to Experiment 2). Using the Trypticase agar slant culture, aseptically inoculate the appropriately labeled tubes of Trypticase nitrate broth and litmus milk by means of a loop inoculation. Record your observations of the cultural characteristics of these colonies in the Lab Report. Determine the type of reaction that has taken place (refer to Experiment 26), and record in the Lab Report. Perform the nitrate reduction test on the Trypticase nitrate broth culture (refer to Experiment 27). Nitrate reduction Test Record whether or not the organism was capable of nitrate reduction (+ or -) below. A patient is afflicted with a disease that generates a large volume of gelatinous abdominal ascites. The use of a microbial enzyme capable of degrading this viscous ascites is suggested. Explain how you would go about isolating an organism that is enzymatically competent to act on this unusual substrate. Their haploid genetic state, which allows the phenotypic, observable expression of a genetic trait in the presence of a single mutant gene. Their rapid rate of growth, which permits observation of transmission of a trait through many generations. The availability of large test populations, which allows isolation of spontaneous mutants and their induction by chemical and physical mutagenic agents. Their low cost of maintenance and propagation, which make it possible to perform a large number of experimental procedures. In the following experiments, bacterial test systems are used to demonstrate enzyme induction, screening for chemical carcinogens, and the genetic phenomena of mutation and genetic transfer.
Severe phosphorus depletion can result in respiratory depression erectile dysfunction treatment in thane cheap generic viagra professional uk, muscle weakness impotence caused by medication trusted 50mg viagra professional, hemolytic anemia, and cardiac dysfunction. Acetoacetate and -hydroxybu yrate are the primary ketones that cause the anion gap acidosis. The nitroprusside test for ketone detection in serum or urine measures acetone and acetoacetate bu not -hydroxybutyrate. Physical exam reveals a fruity odor on her breath, diffuse tenderness to palpation in her abdomen, and costovertebral angle tenderness. Labs/Tests: Her glucose is 440 mg/dL and her bicarbonate is 12 mEq/L with an elevated anion gap. Serum glucose and electrolytes are monitored every 2 hours until the anion gap closes. She ates that both her hands, her right knee, and her left ankle have been bothering her and ar swollen at times. When the arthritis is acute (lasting a few days or less), one must immediately consider septic arthritis or crystal-induced arthritis. Septic arthritis can occur secondary to organisms of bacterial, viral, or fungal origin. An arthrocentesis should be immediately performed to rule out this possibility as well as to evaluate for crystal-induced arthritis. When symptoms have been present for more than a few days but less than 6 to 8 weeks, one should consider subacute types of infectious or parainfectious arthritides such as poststreptococcal arthritis or viral arthritis such as parvovirus B19 arthritis. Be mindful that arthritis due to tuberc lous or fungal infections may fall into the chronic category if not detected early on. What is meant by the term oligoarthritis, and why is the number of joi ts i volved in arthritis important Arthritis is usually categorized into monoarthritis, oligoarthritis or polyarthritis. These terms refer to the number of joints involved in arthritis Oligoarthritis refers to 4 affected joints, whereas polyarthritis refers to five or more affected joints. The number of joints involved is important because the differential diagnosis for each class of arthritis is a bit different (although there can be overlap) Ta le 9. She reports 2 hours of morning stiffness and has been having trouble opening jars and closing buttons on her clothes. When trying to determine what is causing chronic arthritis, it is important to determine whether a patient is suffering from an inflammatory arthritis or a noninflammatory arthritis. Inflammatory arthritis is associated with at least 30 minutes and often greater than 1 hour of morning stiffness. Patients with osteoarthritis can also have morning stiffness, but it usually lasts less than 20 minutes. The right knee has a moderate effu ion, and there is synovitis at the left tibiotalar joint. Synovitis is the physical exam term used to indicate the finding of active inflammatory arthritis. A joint with synovitis may have bogginess, swelling, tenderness, and ay o may not have a palpable effusion. Synovitis is not specific to any particular type of nflammatory arthritis; any type may have this finding. When an effusion is present with synovitis and no diagnosis has been made, arthrocentesis is critical to perform to help estab ish a diagnosis. In this case, arthrocentesis may be necessary to differentiate inflammatory versus noninflammatory arthritis. A patient with severe inflammatory ar hritis will have difficulty making a complete fist (this is a particularly helpfu finding i someone with an equivocal exam for synovitis [i. In summary, this is a young female who presents with a chronic, polyarticular, symmetric arthritis affecting both small and large joints. Axial joint involvement refers to spinal or sacroiliac joint involvement, which the patient does not have.
On pathological examination erectile dysfunction vacuum device viagra professional 50 mg online, most ruptured coronary plaques have fibrous caps measuring less than 65 m doctor for erectile dysfunction buy generic viagra professional 100 mg, and therefore, this threshold has been used to define thick- versus thin-cap fibroatheroma. Although all imaged lesions in this study were culprit lesions, plaque rupture as an underlying mechanism correlated positively with the number of spotty calcium deposits and inversely with the number of large calcium deposits. The longitudinal view (middle panel) depicts pull-back imaging of a 54-mm segment of the vessel, with the distal vessel oriented toward the left and the proximal vessel oriented toward the right. Cross-sectional images (1 to 8) correspond to different points along the longitudinal view (horizontal dotted lines). The most distal cross-section (1) shows the three-layered structure of a normal coronary artery segment. A small side branch can be seen on both cross-sectional imaging (arrow in 2) and on the longitudinal view (arrow in middle panel). Cross-sectional images reveal a ruptured plaque with fibrous cap disruption and cavity formation (arrow in 5) and multiple features associated with plaque vulnerability, including macrophage accumulation (arrow in 3), intracoronary thrombus (arrow in 4), lipid-rich plaque with a thin fibrous cap (arrow in 6), microchannels (arrows in 7), spotty calcium (arrow in 8), and cholesterol crystals (dotted arrow in 8). These factors, along with a greater risk of intraplaque hemorrhage, may contribute to more rapid plaque progression. The authors speculated that there was an incremental effect of inflammation and intimal neovascularization on atherogenesis, in which intimal neovascularization increased vascular wall blood flow and facilitated the penetration of inflammatory cells into the developing plaque, and activated macrophages to promote further angiogenesis and additional macrophage recruitment. Penetration depth is important for the evaluation of plaque burden and arterial remodeling, because these parameters require measurement of the vessel area delineated by the external elastic membrane (see Chapter 3). Plaque area is calculated as the difference between vessel and lumen areas, and plaque burden is calculated as the proportion of vessel area composed of plaque. In addition, the direction and degree of arterial remodeling is determined by comparing the area bounded by the external elastic membrane at the culprit site with that of reference vessel segments. Volume expansion during cholesterol crystallization is hypothesized to cause disruption and perforation of neighboring fibrous tissue, thereby contributing to plaque vulnerability for rupture. Interestingly, no angiographic variables were strongly associated with subsequent events. Although this pilot study suggests that intensive statin therapy can rapidly reduce the lipid content of obstructive lesions, no significant differences in clinical endpoints between the standard and intensive therapy groups could be detected because of the low number of adverse events and short follow-up period. Intraluminal thrombi and intimal disruption can be readily assessed, and neointimal strut coverage can be evaluated in stented coronary segments. Angioscopy has been studied for its potential usefulness in identifying vulnerable plaques, because the color of the endoluminal surface overlying a plaque may provide indirect information on its composition. Studies have correlated yellow coloration with an underlying lipid pool covered by a thin fibrous cap and white coloration with fibrous plaques or a lipid pool covered by a thick fibrous cap. Intracoronary thermography was developed around the hypotheses that plaque temperature may serve as a marker for local inflammation and that the detection of thermal heterogeneity may therefore provide a functional assessment of plaque vulnerability. Studies have shown a correlation among measured temperature, macrophage density, and systemic inflammatory markers. In addition, because of the cooling effects of blood flow, perturbations to blood flow or pressure may confound thermal heterogeneity measurements in atherosclerotic vessels. Lastly, some temperature measuring techniques require direct contact between the thermal sensor and the vessel wall, introducing the potential risk of traumatizing a vulnerable rupture-prone plaque. Detailed plaque characterization or the assessment of plaque burden and arterial remodeling are not possible. Additional limitations to this technique include the need for proximal balloon occlusion to create a blood-free field and the subjective nature of plaque coloration grading, although continuous flush techniques that do not require proximal vessel occlusion and quantitative colorimetric methods have been proposed. However, its usefulness for characterizing coronary plaques is significantly limited by cardiac and respiratory motion, as well as the deep location of arteries. Intravascular detector coils have been developed to improve the signal-to-noise ratio at the level of the coronary wall, thereby increasing spatial resolution. Data acquisition takes 51 seconds for each sector, and the probe is manually rotated to interrogate additional sectors for more circumferential assessment. The functional assessment of inflammation, angiogenesis, and apoptosis holds significant promise in the identification and study of plaque vulnerability. Increased cysteine protease activity has been demonstrated in atherosclerosis and in the setting of vascular injury following stent implantation. Although stented coronary segments have not traditionally been included as potential vulnerable plaques, the mechanisms and risk factors underlying in-stent restenosis and stent thrombosis may be similar to those that drive rapid plaque progression and thrombosis in de novo coronary arteries.
During an acute exacerbation jacksonville impotence treatment center buy viagra professional uk, these agents can be ontinued unless the patient has acute renal insufficiency or severe hypotension best erectile dysfunction pills over the counter order viagra professional 50mg otc. Due to the risk of hyperkalemia, patients should have close monitoring of creatinine and potassium levels. The combination of hydralazine and isosorbide dinitrate increases the nitric oxide availability and maximizes the vasodilation effects. Digoxin inhibits the Na-K pump, causes weak posi ive inotropic effects, increases parasympathetic activity, blocks the atrioventricular node, reduces vasoconstriction, and improves renal blood flow. Toxicity seems to be a problem with digoxin use, especially in patients with renal insufficiency; therefore, digoxin should be dosed at a low dose. A beta blocker is started once the patient has little e idence of fluid retention. Due to this patient having risk factors of diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, coronary angiography is performed to rule out ischemic hear d sease What are reasons for patients to have an acute exacerbation Acute heart failure can be caused by scenarios such as acute coronary syndromes, coronary ischemia, severe hypertension, atrial and ventricular arrhythmias, infections, pulmonary emboli, renal failure, and medical or dietary nonadherence. What preventive measures should be taken for patients with heart fa l re upon discharge In addition o diagnostic testing, physical exam findings are key to diagnosing patients in acute heart fai ure. All systolic heart failure patients with risk factors for coronary heart disease should undergo a stress test or coronary angiography for evaluation of ischemic heart disease. Inotropic drugs are used for heart failure when the patient is unresponsive to oral medications. Anticoagulation in heart failure patients is controvers al unless the patient has atrial fibrillation, severe valvular disease, or a documented thrombus. Heart Failure Society of America 2010 Comprehensive Heart Failure Practice Guideline. Findings: His physical exam reveals jugular venous disten ion and bilateral crackles in the lower lobes of the lungs. His cardiac exam reveals a regular rhythm with an S3 heart sound and bilateral lower extremity edema with bilateral pitting to the knees. Transthoracic echocardiography reveals left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% with mild to moderate mitral regurgitation and left ventricular enlargement. Because the patient has risk factors of diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, coronary angiography is done to rule out ischemic heart disease. Upon discharge, the patient is counseled on diet comp iance, medication adherence, and exercise. He is given a follow-up appointment w th his primary care doctor within 1 week of discharge. Michelle Koolaee eb A 34-Year-Old Male With Chronic e /eb Bilateral Gluteal Pains //t m / s s A 34-year-old male presents for outpatient evaluation of 3 to 5 years of bilateral hip pains that have become progressively worse over the past few months. The pain is located in the gluteal areas bilaterally and is worse first thing in the morning, with several hours of associated morning stiffness. The hallmark of inflammatory arthritis is the presence of joint pain that is better with activity and worse with prolonged rest. Because the joints are at rest while one is asleep, it makes sense that the joints are more painful and stiff in the morning. Morning stiffness lasting less than 30 minutes is more indicative of osteoarthritis (a noninflammatory arthritis), whereas stiffness greater than 1 hour indicates more likely an inflammatory arthrit s. These symptoms were chosen because they relate directly to the differential diagnosis (see below section on differential diagnosis). Autoimmune diseases as a whole, particularly lupus and multiple sclerosis, frequently run in families. It is thought that a combination of genetic and environmental factors contribute to activating disease. However, people definitely can still develop autoimmune diseases without a family history of autoimmunity.